Abstract
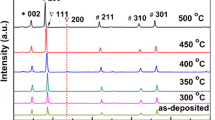
Double layer glass/fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO)/aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) multifunctional thin films were achieved via ultrasonic spray pyrolysis (USP) method without employing a post-deposition annealing. Transparent heater and near-infrared heat reflection behaviors were investigated. The samples were characterized in terms of their structural, morphological, optical, and electrical properties. The top AZO layer exhibited a polycrystalline structure without any preferred orientation. The double layer structure showed very high average transmittance (87%, 400–700 nm) in the visible and reflectance (55%, 2500 nm) in the near-infrared, regions. In addition, the sheet resistance and resistivity of the film were measured as 14.85 (Ω sq−1) and 1.78 × 10−3 (Ω cm), respectively. The saturation temperature, response time, surface temperature uniformity, areal power density, and thermal resistance values were found to be 111 °C, 174 s, 11.42%, 0.299 W/cm2, and 282.8 °C cm2 W−1 for a sample with an active area of 31.5 cm2 and input voltage of 9 V. In addition, dry-ice cooled samples (−25 °C) showed impressive deicing performance depending on the input power. In case of 12 V, all ice was defrosted, and water droplets were evaporated within 2 min and 10 s. During this process, a heating rate of ⁓43 °C/min was achieved.

Highlights
-
Glass/FTO/AZO double layer thin films were achieved using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis.
-
No post-deposition annealing was applied.
-
Relatively large area transparent heater and near-infrared heat reflecting mirror was produced.
-
55% reflectance at 2500 nm and deicing in 130 s with low voltage was demonstrated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mcmaster HA (1947) Conductive coating for glass and method of application 2,429,420
Piegari A, Flory F (2013) Optical Thin Films and Coatings: From Materials to Applications. Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, Cambridge
Kim H-J, Kim D-I, Kim S-S et al. (2017) Observation of convection phenomenon by high-performance transparent heater based on Pt-decorated Ni micromesh. AIP Adv 7:025112
Sannicolo T, Lagrange M, Cabos A, Celle C, Simonato JP, Bellet D (2016) Metallic nanowire-based transparent electrodes for next generation flexible devices: a review. Small 12:6052–6075
Celle C, Mayousse C, Moreau E, Basti H, Carella A, Simonato J-P (2012) Highly flexible transparent film heaters based on random networks of silver nanowires. Nano Res 5:427–433
Jayathilake DSY, Sagu JS, Wijayantha KGU (2019) Transparent heater based on Al,Ga co-doped ZnO thin films. Mater Lett 237:249–252
Kang TJ, Kim T, Seo SM, Park YJ, Kim YH (2011) Thickness-dependent thermal resistance of a transparent glass heater with a single-walled carbon nanotube coating. Carbon 49:1087–1093
Kang J, Kim H, Kim KS et al. (2011) High-performance graphene-based transparent flexible heaters. Nano Lett 11:5154–5158
Ergun O, Coskun S, Yusufoglu Y, Unalan HE (2016) High-performance, bare silver nanowire network transparent heaters. Nanotechnology 27:445708
Gupta R, Rao KD, Kiruthika S, Kulkarni GU (2016) Visibly transparent heaters. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:12559–12575
Papanastasiou DT, Schultheiss A, Muñoz‐Rojas D et al. (2020) Transparent heaters: a review. Adv Funct Mater 30:1910225
Minami T (2008) Substitution of transparent conducting oxide thin films for indium tin oxide transparent electrode applications. Thin Solid Films 516:1314–1321
Seo S-W, Won SH, Chae H, Cho SM (2012) Low-temperature growth of highly conductive and transparent aluminum-doped ZnO film by ultrasonic-mist deposition. Korean J Chem Eng 29:525–528
Mallick A, Ghosh S, Basak D (2020) Highly conducting and transparent low-E window films with high figure of merit values based on RF sputtered Al and In co-doped ZnO. Mater Sci Semiconductor Process 119:105240
Can HA, Tönbül B, Pişkin F, Öztürk T, Akyıldız H (2021) Processing optimization of SiO2-capped aluminum-doped ZnO thin films for transparent heater and near-infrared reflecting applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32:5116–5137
Hagendorfer H, Lienau K, Nishiwaki S et al. (2014) Highly transparent and conductive ZnO: Al thin films from a low temperature aqueous solution approach. Adv Mater 26:632–636
Wang Z, Li J, Xu J et al. (2020) Robust ultrathin and transparent AZO/Ag-SnO/AZO on polyimide substrate for flexible thin film heater with temperature over 400°C. J Mater Sci Technol 48:156–162
Barman D, Sarma BK (2020) Thin and flexible transparent conductors with superior bendability having Al-doped ZnO layers with embedded Ag nanoparticles prepared by magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 177:109367
Ghosh S, Mallick A, Dou B, van Hest MFAM, Garner SM, Basak D (2018) A novel blanket annealing process to achieve highly transparent and conducting Al doped ZnO thin films: Its mechanism and application in perovskite solar cells. Sol Energy 174:815–825
Miao DG, Jiang SX, Shang SM, Chen ZM, Liu J (2014) Infrared reflective property of AZO films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Mater Technol 29:321–325
Gong L, Ye Z, Lu J et al. (2010) Highly transparent conductive and near-infrared reflective ZnO:Al thin films. Vacuum 84:947–952
Das R, Ray S (2003) Zinc oxide—a transparent, conducting IR-reflector prepared by rf-magnetron sputtering. J Phys D: Appl Phys 36:152–155
Ni J, Zhao Q, Zhao X (2009) Transparent and high infrared reflection film having sandwich structure of SiO2/Al:ZnO/SiO2. Prog Org Coat 64:317–321
Miao D, Jiang S, Shang S, Chen Z (2014) Effect of heat treatment on infrared reflection property of Al-doped ZnO films. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 127:163–168
Babu BJ, Velumani S, Asomoza R (2011) An (ITO or AZO)/ZnO/Cu(In1-xGax)Se2 superstrate thin film solar cell structure prepared by spray pyrolysis. In: Proceedings of the 37th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 001238-001243
Xu J, Wang H, Yang L, Jiang M, Wei S, Zhang T (2010) Low temperature growth of highly crystallized ZnO:Al films by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis from acetylacetone salt. Mater Sci Eng: B 167:182–186
Marouf S, Beniaiche A, Kardarian K et al. (2017) Low-temperature spray-coating of high-performing ZnO:Al films for transparent electronics. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 127:299–308
Chen F-K, Tsai D-C, Chang Z-C, Chen E-C, Shieu F-S (2020) Influence of Al content and annealing atmosphere on optoelectronic characteristics of Al:ZnO thin films. Appl Phys A 126:743
Ikhmayies SJ, Abu El-Haija NM, Ahmad-Bitar RN (2010) Electrical and optical properties of ZnO:Al thin films prepared by the spray pyrolysis technique. Phys Scr 81:015703
Babu BJ, Maldonado A, Velumani S, Asomoza R (2010) Electrical and optical properties of ultrasonically sprayed Al-doped zinc oxide thin films. Mater Sci Eng: B 174:31–37
Crossay A, Buecheler S, Kranz L et al. (2012) Spray-deposited Al-doped ZnO transparent contacts for CdTe solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 101:283–288
Babu BJ, Velumani S, Arenas-Alatorre J et al. (2014) Structural properties of ultrasonically sprayed Al-doped ZnO (AZO) thin films: effect of ZnO buffer layer on AZO. J Electron Mater 44:699–705
Rivera MJ, Ramírez EB, Juárez B et al. (2016) Low temperature-pyrosol-deposition of aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films for transparent conducting contacts. Thin Solid Films 605:108–115
Gençyılmaz O, Atay F, Akyüz I (2015) Deposition and ellipsometric characterization of transparent conductive Al-doped ZnO for solar cell application. J Clean Energy Technol 4:90–94
Karzazi O, Soussi L, Louardi A et al. (2019) Transparent conducting properties of Mg and Al co-doped ZnO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique. Superlattices Microstruct 127:61–65
Ozório MS, Nascimento MR, Vieira DH et al. (2019) AZO transparent electrodes grown in situ during the deposition of zinc acetate dihydrate onto aluminum thin film by spray pyrolysis. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:13454–13461
Kenanakis G, Katsarakis N (2014) Ultrasonic spray pyrolysis growth of ZnO and ZnO:Al nanostructured films: application to photocatalysis. Mater Res Bull 60:752–759
Deva Arun Kumar K, Mele P, Ponraj JS et al. (2020) Methanol solvent effect on photosensing performance of AZO thin films grown by nebulizer spray pyrolysis. Semicond Sci Technol 35:085013
Tönbül B, Can HA, Öztürk T, Akyıldız H (2021) Solution processed aluminum-doped ZnO thin films for transparent heater applications. Mater Sci Semicond Process 127:105735
Yu J, Gao Y, Wang L et al. (2018) Anti-reductive properties of AZO/FTO bilayered transparent conducting films. Surf Eng 36:1–5
Chantarat N, Hsu S-H, Lin C-C, Chiang M-C, Chen S-Y (2012) Mechanism of an AZO-coated FTO film in improving the hydrogen plasma durability of transparent conducting oxide thin films for amorphous-silicon based tandem solar cells. J Mater Chem 22:8005–8012
Ravichandran K, Jabena Begum N, Swaminathan K, Sakthivel B (2013) Fabrication of a double layered FTO/AZO film structure having enhanced thermal, electrical and optical properties, as a substitute for ITO films. Superlattices Microstruct 64:185–195
Ahn K, Jeong YS, Lee HU et al. (2010) Physical properties of hydrogenated Al-doped ZnO thin layer treated by atmospheric plasma with oxygen gas. Thin Solid Films 518:4066–4070
Ravikumar P, Ravichandran K, Sakthivel B (2012) Effect of thickness of SnO2:F over layer on certain physical properties of ZnO:Al thin films for opto-electronic applications. J Mater Sci Technol 28:999–1003
Kim DH, Cho KS, Kim HK (2017) Thermally evaporated indium-free, transparent, flexible SnO2/AgPdCu/SnO2 electrodes for flexible and transparent thin film heaters. Sci Rep 7:2550
Kim YR, Jung JH, Yong SM, Hong JW, Lee SJ, Park JW (2021) Design of patterned fluorine-doped tin oxide for radome de-icing heater. J Phys D: Appl Phys 54:105301
Ke S, Xie J, Chen C et al. (2018) van der Waals epitaxy of Al-doped ZnO film on mica as a flexible transparent heater with ultrafast thermal response. Appl Phys Lett 112:031905
Kim AY, Lee K, Park JH, Byun D, Lee JK (2014) Double-layer effect on electrothermal properties of transparent heaters. Phys Status Solidi (a) 211:1923–1927
Cebulla R, Wendt R, Ellmer K (1998) Al-doped zinc oxide films deposited by simultaneous rf and dc excitation of a magnetron plasma: relationships between plasma parameters and structural and electrical film properties. J Appl Phys 83:1087–1095
Stenzel O (2005) The Physics of Thin Film Optical Spectra. Springer, Berlin, Germany
Haacke G (1976) New figure of merit for transparent conductors. J Appl Phys 47:4086–4089
Arii T, Kishi A (2003) The effect of humidity on thermal process of zinc acetate. Thermochim Acta 400:175–185
Djelloul A, Bouzid K, Guerrab F (2008) Role of substrate temperature on the structural and morphological properties of ZnO thin films deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Turk J Phys 32:49–58
Liu J, Yang Z, Lin S et al. (2020) Compact and ultrathin multi-element oxide films grown by temperature-controlled deposition and their surface-potential based transistor theoretical simulation model. J Mater Chem C 8:7358–7368
Lide DR (2006/2007) Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 87th edition. CRC Press, Boca Raton
NIST database (2021) http://www.webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/
Fan P, Zheng Z-h, Li Y-z et al. (2015) Low-cost flexible thin film thermoelectric generator on zinc based thermoelectric materials Appl Phys Lett 106:073901
Garcés FA, Budini N, Schmidt JA, Arce RD (2016) Highly doped ZnO films deposited by spray-pyrolysis. Design parameters for optoelectronic applications. Thin Solid Films 605:149–156
Shokri A, Dejam L (2018) Experimental and theoretical investigations on temperature and voltage dependence of an Au/AZO thin-film Schottky diode. Int Nano Lett 9:161–168
Garcés FA, Budini N, Arce RD, Schmidt JA (2015) Thickness dependence of crystalline structure of Al-doped ZnO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Procedia. Procedia Mater Sci 9:221–229
Salam S, Islam M, Akram A (2013) Sol–gel synthesis of intrinsic and aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films as transparent conducting oxides for thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 529:242–247
Lennon C, Tapia RB, Kodama R, Chang Y, Sivananthan S, Deshpande M (2009) Effects of annealing in a partially reducing atmosphere on sputtered Al-doped ZnO thin films. J Electron Mater 38:1568–1573
Potter DB, Parkin IP, Carmalt CJ (2018) The effect of solvent on Al-doped ZnO thin films depositedviaaerosol assisted CVD. RSC Adv 8:33164–33173
Tang K, Gu S, Liu J, Ye J, Zhu S, Zheng Y (2015) Effects of indium doping on the crystallographic, morphological, electrical, and optical properties of highly crystalline ZnO films. J Alloy Compd 653:643–648
Hamada K, Ogawa T, Okumura H, Ishihara KN (2019) The effect of substrate roughness on the properties of RF sputtered AZO thin film. MRS Commun 9:697–701
Cojocaru L, Uchida S, Jayaweera PVV et al. (2017) Effect of TiO2 surface treatment on the current-voltage hysteresis of planar-structure perovskite solar cells prepared on rough and flat fluorine-doped tin oxide substrates. Energy Technol 5:1762–1766
Ge CY, Rahman MM, Zhang W et al. (2020) An electrochemical immunosensor based on a self-assembled monolayer modified electrode for label-free detection of alpha-Synuclein. Sensors 20:617
Kim Y-R, Park J-W, Park S-H, Lee S-J (2020) Radio-frequency and optically transparent radome de-icing materials: fluorine-doped tin oxide. RSC Adv 10:35979–35987
Lim JH, Leem JW, Yu JS (2015) Solar power generation enhancement of dye-sensitized solar cells using hydrophobic and antireflective polymers with nanoholes. RSC Adv 5:61284–61289
Polyanskiy M (2008–2021) RefractiveIndex.INFO. https://refractiveindex.info/
Pan Q, Song X (2017) Al-doped ZnO films deposited by magnetron sputtering: effect of sputtering parameters on the electrical and optical properties. Mater Sci-Pol 35:374–381
Tang W, Cameron DC (1994) Aluminum-doped zinc oxide transparent conductors deposited by the sol–gel process. Thin Solid Films 238:83–87
Sun L, Grant JT, Jones JG, Murphy NR (2018) Tailoring electrical and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films grown at room temperature by reactive magnetron co-sputtering: from band gap to near infrared. Optical Mater 84:146–157
Miao D, Jiang S, Shang S, Chen Z (2014) Infrared reflective properties of AZO/Ag/AZO trilayers prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Ceram Int 40:12847–12853
Miao D, Zhao H, Peng Q, Shang S, Jiang S (2015) Fabrication of high infrared reflective ceramic films on polyester fabrics by RF magnetron sputtering. Ceram Int 41:1595–1601
Miao D, Jiang S, Shang S, Chen Z (2014) Highly transparent and infrared reflective AZO/Ag/AZO multilayer film prepared on PET substrate by RF magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 106:1–4
Lee C, Dwivedi RP, Lee W, Hong C, Lee WI, Kim HW (2007) IZO/Al/GZO multilayer films to replace ITO films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 19:981–985
Jose FP, Achary SR, Sukumaran AA, Jayaraj MK (2020) Effects of temperature and doping on aluminium doped ZnO thin film grown by spray pyrolysis. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Physics of Materials and Nanotechnology (ICPN), vol 2244, p 110005
Ravichandran K, Jabena Begum N, Snega S, Sakthivel B (2014) Properties of sprayed aluminum-doped zinc oxide films—a review. Mater Manuf Process 31:1411–1423
Luangchaisri C, Dumrongrattana S, Rakkwamsuk P (2012) Effect of heat treatment on electrical properties of fluorine doped tin dioxide films prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique. Procedia Eng 32:663–669
Muiva CM, Sathiaraj TS, Maabong K (2011) Effect of doping concentration on the properties of aluminium doped zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis for transparent electrode applications. Ceram Int 37:555–560
Hudaya C, Jeon BJ, Lee JK (2015) High thermal performance of SnO2:F thin transparent heaters with scattered metal nanodots. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:57–61
Hwang H, Ma KY, Kim JW et al. (2020) Radio-frequency-transmitting hexagonal boron nitride-based anti- and de-icing heating system. Nanoscale 12:21895–21900
Hudaya C, Park JH, Lee JK (2012) Effects of process parameters on sheet resistance uniformity of fluorine-doped tin oxide thin films. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:1–4
Baldasseroni C, Queen DR, Cooke DW, Maize K, Shakouri A, Hellman F (2011) Heat transfer simulation and thermal measurements of microfabricated x-ray transparent heater stages. Rev Sci Instrum 82:093904
DONTECH (2019) Transparent heaters. https://dontech.com/transparent-heaters/
Volman V, Tour JM, Zhu Y, Raji A-RO (2013) Conductive graphene nanoribbon thin film as heat circuit for antennas and radomes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, 14094648
NISSHA (2021) Transparent film heater. https://connect.nissha.com/filmdevice/en/transparent_film_heater/
Acknowledgements
This study was produced from the MSc thesis of Beyza TÖNBÜL and supported financially by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK; Project Number: 118M013), for which the authors are thankful. We would also like to thank to İ. Cihan KAYA and Volkan KALEM for their help in solving some technical issues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tönbül, B., Can, H.A., Öztürk, T. et al. Solution processed glass/fluorine-doped tin oxide/aluminum-doped zinc oxide double layer thin films for transparent heater and near-infrared reflecting applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 99, 482–496 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05591-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05591-1