Abstract
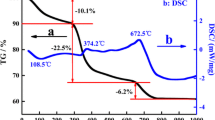
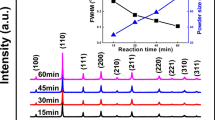
Lead-free Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 (BCZT) powders were successfully synthesized by sol–gel-hydrothermal method. The effect of NaOH concentration on microstructure and phase composition of BCZT powders was studied. The results of XRD, SEM, TEM, FTIR, and EDS showed that the synthesis temperature of BCZT powders could be decreased to a low temperature of 180 °C, which was about 1150 °C lower when compared with solid-state reaction and 800 °C lower when compared with sol–gel methods respectively. The NaOH concentration exerted a great effect on the structure of BCZT powders, as well as the average particle size. When the NaOH concentration was 8 M, BCZT powders had a cubic phase perovskite structure with a homogeneous composition, and the average particle size was about 60 nm. The BCZT ceramics followed by sintering had dense structure and excellent electrical properties (2Pr = 24.62 μC/cm2, 2Ec = 3.24 kV/cm, d33 = 488 pC/N). The significant properties could be attributed to the high activity of powders synthesized by sol–gel-hydrothermal method. The present study may provide a new method for low-temperature synthesis of lead-free piezoelectric powders with fine phase, microscopic morphology, and high activity.

Highlights
-
Well-crystallized BCZT powders were successfully synthesized by sol–gel-hydrothermal method.
-
The synthesis temperature was decreased to a low temperature of 180 °C.
-
Effects of alkaline solution concentration on structure of sol–gel-hydrothermal derived BCZT powders were analyzed and the formation mechanism was discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacob KS, Panicker NR, Selvam IP, Kumar V (2003) Sol-gel synthesis of nanocrystalline PZT using a novel system. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 28(3):289–295
Montanari G, Costa AL, Albonetti S, Galassi C (2005) Nb-doped PZT material by sol-gel combustion. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 36(2):203–211
Xu Z, Qiang H (2016) Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of (1-x)Ba0.67Sr0.33TiO3–xBa0.9Ca0.1Ti0.9Zr0.1O3 ceramics. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 77(3):650–653
Kheyrdan A, Abdizadeh H, Shakeri A, Golobostanfard MR (2018) Structural, electrical, and optical properties of sol-gel-derived zirconium-doped barium titanate thin films on transparent conductive substrates. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 86(1):141–150
Liu W, Ren X (2009) Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phys Rev Lett 103(25):257602
Li W, Xu Z, Chu R, Fu P, Zang G (2010) Piezoelectric and dielectric properties of (Ba1-xCax)(Ti0.95Zr0.05)O3 lead‐free ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 93(10):2942–2944
Li W, Xu Z, Chu R, Fu P, An P (2012) Effect of Ho doping on piezoelectric properties of BCZT ceramics. Ceram Int 38(5):4353–4355
Castkova K, Maca K, Cihlar J, Hughes H, Matousek A, Tofel P, Bai Y, Button TW (2015) Chemical synthesis, sintering and piezoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 lead‐free ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 98(8):2373–2380
Praveen JP, Kumar K, James A, Karthik T, Asthana S, Das D (2014) Large piezoelectric strain observed in sol–gel derived BZT–BCT ceramics. Curr Appl Phys 14(3):396–402
Zhang Y, Wang L, Xue D (2012) Molten salt route of well dispersive barium titanate nanoparticles. Powder technol 217:629–633
Liu Y, Pu Y, Sun Z (2014) Enhanced relaxor ferroelectric behavior of BCZT lead-free ceramics prepared by hydrothermal method. Mater Lett 137:128–131
Puli VS, Kumar A, Chrisey DB, Tomozawa M, Scott J, Katiyar RS (2011) Barium zirconate-titanate/barium calcium-titanate ceramics via sol–gel process: novel high-energy-density capacitors. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(39):395403
Praveen JP, Karthik T, James A, Chandrakala E, Asthana S, Das D (2015) Effect of poling process on piezoelectric properties of sol–gel derived BZT–BCT ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 35(6):1785–1798
Bockmeyer M, Löbmann P (2008) Formation, densification and properties of sol–gel TiO2 films prepared from triethanolamine-chelated soluble precursor powders. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 45(3):251–259
Xie L, Ma J, Wu P, Tian H, Zhao Z, Zhou J, Hu Y, Wang Y, Tao J, Zhu X (2007) Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of bismuth titanate regular tetrahedron crystallites. Mater Res Bull 42(2):389–393
Zheng H, Zhu K, Wu Q, Liu J, Qiu J (2013) Preparation and characterization of monodispersed BaTiO3 nanocrystals by sol–hydrothemal method. J Cryst Growth 363:300–307
Song Z-Q, Wang S-B, Yang W, Li M, Wang H, Yan H (2004) Synthesis of manganese titanate MnTiO3 powders by a sol–gel–hydrothermal method. Mater Sci Eng B-Adv 113(2):121–124
Yu H, Ouyang S, Yan S, Li Z, Yu T, Zou Z (2011) Sol–gel hydrothermal synthesis of visible-light-driven Cr-doped SrTiO3 for efficient hydrogen production. J Mater Chem 21(30):11347–11351
Yu D, Jin A-m, Zhang Q-l, Yang H, Hu L, Cheng D (2015) Scandium and gadolinium co-doped BaTiO3 nanoparticles and ceramics prepared by sol–gel–hydrothermal method: Facile synthesis, structural characterization and enhancement of electrical properties. Powder Technol 283:433–439
Zuo Q, Luo L, Yao Y (2015) The electrical, upconversion emission, and temperature sensing properties of Er3+/Yb3+-codoped Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3–(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 ferroelectric ceramics. J Alloy Compd 632:711–716
Jiang Y, Tang X, Ju S, Liu Q, Zhang T, Xiong H (2016) Influence of sintering temperature on the ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 ceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27(3):3048–3052
Ji X, Wang C, Li S, Zhang S, Tu R, Shen Q, Shi J, Zhang L (2018) Structural and electrical properties of BCZT ceramics synthesized by sol–gel process. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29(9):7592–7599
Li S, Wang C, Ji X, Shen Q, Zhang L (2017) Effect of composition fluctuation on structural and electrical properties of BZT-xBCT ceramics prepared by plasma activated sintering. J Eur Ceram Soc 37(5):2067–2072
Outzourhit A, Raghni MEI, Hafid M, Bensamka F, Outzourhit A (2002) Characterization of hydrothermally prepared BaTi1-xZrxO3. J Alloy Compd 340(1-2):214–219
Luo B, Wang X, Zhao Q, Li L (2015) Synthesis, characterization and dielectric properties of surface functionalized ferroelectric ceramic/epoxy resin composites with high dielectric permittivity. Compos Sci Technol 112:1–7
Wang W, Cao L, Liu W, Su G, Zhang W (2013) Low-temperature synthesis of BaTiO3 powders by the sol–gel-hydrothermal method. Ceram Int 39(6):7127–7134
Hwang UY, Park HS, Koo KK (2004) Low‐temperature synthesis of fully crystallized spherical BaTiO3 particles by the gel–sol method. J Am Ceram Soc 87(12):2168–2174
Thongtha A, Wattanawikkam C, Bongkarn T (2011) Phase formation and dielectric properties of (Pb0.925Ba0.075)(Zr1-xTix)O3 ceramics prepared by the solid-state reaction method. Phase Transit 84(11-12):952–959
Chen CF, Reagor DW, Russell SJ, Marksteiner QR, Earley LM, Dalmas DA, Volz HM, Guidry DR, Papin PA, Yang P (2011) Sol–gel processing and characterizations of a Ba0.75Sr0.25Ti0.95Zr0.05O3 ceramic. J Am Ceram Soc 94(11):3727–3732
Ghosh S, Dasgupta S, Sen A, Maiti HS (2007) Synthesis of barium titanate nanopowder by a soft chemical process. Mater Lett 61(2):538–541
Simões AZ, Moura F, Onofre T, Ramirez M, Varela JA, Longo E (2010) Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of barium strontium titanate nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 508(2):620–624
Kolenko YV, Kovnir KA, Neira IS, Taniguchi T, Ishigaki T, Watanabe T, Sakamoto N, Yoshimura M (2007) A novel, controlled, and high-yield solvothermal drying route to nanosized barium titanate powders. J Phys Chem C 111(20):7306–7318
Wang L, Kang H, Li K, Xue D, Liu C (2008) Phase evolution of BaTiO3 nanoparticles: An identification of BaTi2O5 intermediate phase in calcined stearic acid gel. J Phys Chem C 112(7):2382–2388
Reiss H (1951) The growth of uniform colloidal dispersions. J Chem Phys 19(4):482–487
Nie X, Yan S, Guo S, Cao F, Yao C, Mao C, Dong X, Wang G (2018) Influence of Ca2+ concentration on structure and electrical properties of (Ba1-xCax)(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 ceramics. Mater Res Express 5(3):036301
Lu X, Fang B, Zhang S, Yuan N, Ding J, Zhao X, Wang F, Tang Y, Shi W, Xu H (2017) Decreasing sintering temperature for BCZT lead-free ceramics prepared via hydrothermal route. Funct Mater Lett 10(4):1750046
Wu J, Xiao D, Wu W, Zhu J, Wang J (2011) Effect of dwell time during sintering on piezoelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.90Zr0.10)O3 lead-free ceramics. J Alloy Compd 509(41):359
Wu J, Xiao D, Wu W, Chen Q, Zhu J, Yang Z, Wang J (2012) Composition and poling condition-induced electrical behavior of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti1-xZrx)O3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 32(4):891–898
Hunpratub S, Maensiri S, Chindaprasirt P (2014) Synthesis and characterization of Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.9Zr0.1O3 ceramics by hydrothermal method. Ceram Int 40(8):13025–13031
Ji X, Wang C, Zhang S, Rong T, Shen Q, Shi J, Zhang L (2019) Structural and electrical properties of BCZT ceramics synthesized by sol–gel-hydrothermal process at low temperature. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30(13):12197–12203
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51972252, 51272195, and 51521001) International Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Hubei Province (2016AHB008), Nature Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2016CFA006) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WUT: 2019III029). XJ is supported to study at the Tokyo Institute of Technology for 1 year through China Scholarship Council (CSC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, X., Wang, C., Luo, W. et al. Effect of solution concentration on low-temperature synthesis of BCZT powders by sol–gel-hydrothermal method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 94, 205–212 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05177-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05177-y