Abstract
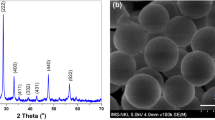
Highly colloidal Gd2O3:Eu nanoparticles (core-NPs) were synthesized by thermal decomposition via weak base at low temperature. The sol–gel chemical process was employed for silica layer surface coating to increase solubility, colloidal stability, biocompatibility, and non-toxicity at the ambient conditions. XRD results indicate the highly purified, crystalline, single phase, and cubic phase Gd2O3 nanocrystals. TEM image shows that the mesoporous thick silica layer was effectively coated on the core nanocrystals, which have irregular size with nearly spherical shape and grain size about 10–30 nm. An absorption spectra and zeta potential results in aqueous media revealed that solubility, colloidal stability, and biocompatibility character were enhanced from core to core–shell structure because of silica layer surface encapsulation. The samples, demonstrated excellent photoluminescence properties (dominant emission 5D0 → 7F2 transition in the red region at 610 nm), indicated to be used in optical bio-detection, bio-labeling, etc. The photoluminescence intensity of the silica shell modified core/shell NPs was suppressed relatively core-NPs; it indicates the multi-photon relaxation pathways arising from the surface coated high vibrational energy molecules of the silanol groups. The core/nSiO2/mSiO2 nanocrystals display strong emission (5D0 → 7F2) transition along with excellent solubility and biocompatibility, which may find promising applications in the photonic based biomedical field.

Highlights
-
• Multi-silica layers coated luminescent Gd2O3:Eu@nSiO2@mSiO2 core–shell nanoparticles.
-
• Mesoporous, highly aqueous dispersible core-shell nanoparticles.
-
• Impact of silica shell on physiochemical properties.
-
• Excellent absorbance and photoluminescence properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li IF, Su CH, Sheu HS, Chiu HC, Lo YW, Lin WT, Chen JH, Yeh CS (2008) Gd2O(CO3)(2)center dot H2O particles and the corresponding Gd2O3: synthesis and applications of magnetic resonance contrast agents and template particles for hollow spheres and hybrid composites. Adv Funct Mater 18:766–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200700702
Shao YZ, Tian XM, Hu WY, Zhang YY, Liu H, He HQ, Shen YY, Xie FK, Li L (2012) The properties of Gd2O3-assembled silica nanocomposite targeted nanoprobes and their application in MRI. Biomaterials 33:6438–6446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.05.065
Liu YC, Yang PP, Wang WX, Dong HX, Lin J (2010) Fabrication and photoluminescence properties of hollow Gd2O3:Ln (Ln = Eu3+, Sm3+) spheres via a sacrificial template method. Crystengcomm 12:3717–3723. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0ce00145g
Tian G, Gu ZJ, Liu XX, Zhou LJ, Yin WY, Yan L, Jin S, Ren WL, Xing GM, Li SJ, Zhao YL (2011) Facile fabrication of rare-earth-doped Gd2O3 hollow spheres with upconversion luminescence, magnetic resonance, and drug delivery properties. J Phys Chem C 115:23790–23796. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp209055t
Yang GX, Lv RC, Gai SL, Dai YL, He F, Yang PP (2014) Multifunctional SiO2@Gd2O3:Yb/Tm hollow capsules: controllable synthesis and drug release properties. Inorg Chem 53:10917–10927. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic501121t
Raju GSR, Pavitra E, Yu JS (2013) Facile template free synthesis of Gd2O(CO3)(2).H2O chrysanthemum-like nanoflowers and luminescence properties of corresponding Gd2O3:RE3+Spheres. Dalton Trans 42:11400–11410. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt51154e
Shi HZ, Li L, Zhang LY, Wang TT, Wang CG, Su ZM (2015) Facile fabrication of hollow mesoporous Eu3+-doped Gd2O3 nanoparticles for dual-modal imaging and drug delivery. Dyes Pigments 123:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2015.07.015
Huang CC, Liu TY, Su CH, Lo YW, Chen JH, Yeh CS (2008) Superparamagnetic hollow and paramagnetic porous Gd2O3 particles. Chem Mater 20:3840–3848. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm703195u
Ansari AA, Parchur AK, Alam M, Azzeer A (2014) Effect of surface coating on optical properties of Eu3+-doped CaMoO4 nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta A 131:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.04.036
Ansari AA, Parchur AK, Alam M, Labis J, Azzeer A (2014) Influence of surface coating on structural and photoluminescent properties of CaMoO4:Pr nanoparticles. J Fluoresc 24:1253–1262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-014-1409-9
Zhu L, Liu XM, Liu XD, Li Q, Li JY, Zhang SY, Meng J, Cao XQ (2006) Facile sonochemical synthesis of CePO4: Tb/LaPO4 core/shell nanorods with highly improved photoluminescent properties. Nanotechnology 17:4217–4222. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/16/036
Chai RT, Lian HZ, Yang PAP, Fan Y, Hou ZY, Kang XJ, Lin J (2009) In situ preparation and luminescent properties of LaPO4:Ce3+, Tb3+ nanoparticles and transparent LaPO4:Ce3+, Tb3+/PMMA nanocomposite. J Colloid Interf Sci 336:46–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.03.079
Grzyb T, Weclawiak M, Lis S (2012) Influence of nanocrystals size on the structural and luminescent properties of GdOF:Eu3+. J Alloy Compd 539:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.06.047
Ding MY, Lu CH, Ni YR, Xu ZZ (2014) Rapid microwave-assisted flux growth of pure beta-NaYF4:Yb3+, Ln(3+) (Ln = Er, Tm, Ho) microrods with multicolor upconversion luminescence. Chem Eng J 241:477–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.045
Mi CC, Tian ZH, Han BF, Mao CB, Xu SK (2012) Microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of water-soluble rare-earth doped fluoride luminescent nanoparticles with tunable colors. J Alloy Compd 525:154–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.02.095
Liu XX, Ni YR, Zhu C, Fang L, Kou JH, Lu CH, Xu ZZ (2016) Controllable self-assembly of NaREF4 upconversion nanoparticles and their distinctive fluorescence properties. Nanotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/29/295605
Naccache R, Vetrone F, Mahalingam V, Cuccia LA, Capobianco JA (2009) Controlled synthesis and water dispersibility of hexagonal phase NaGdF4:Ho3+/Yb3+ nanoparticles. Chem Mater 21:717–723. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm803151y
Chaudhary S, Kumar S, Umar A, Singh J, Rawat M, Mehta SK (2017) Europium-doped gadolinium oxide nanoparticles: a potential photoluminescencent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe3+ and Cr3+ions. Sens Actuators B 243:579–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.002
Chen GW, Qi WC, Li YB, Yang CS, Zhao XP (2016) Hydrothermal synthesis of Y2O3:Eu3+ nanorods and its growth mechanism and luminescence properties. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:5628–5634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4470-0
Dhananjaya N, Nagabhushana H, Nagabhushana BM, Rudraswamy B, Shivakumara C, Chakradhar RPS (2011) Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and Raman studies of Eu3+ activated Gd2O3 nanorods. Phys B Condens Matter 406:1639–1644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.09.050
Marques VS, Cavalcante LS, Sczancoski JC, Alcantara AFP, Orlandi MO, Moraes E, Longo E, Varela JA, Li MS, Santos MRMC (2010) Effect of different solvent ratios (water/ethylene glycol) on the growth process of CaMoO4 crystals and their optical properties. Cryst Growth Des 10:4752–4768. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg100584b
Runowski M, Ekner-Grzyb A, Mrowczynska L, Balabhadra S, Grzyb T, Paczesny J, Zep A, Lis S (2014) Synthesis and organic surface modification of luminescent, lanthanide-doped core/shell nanomaterials (LnF(3)@SiO2@NH2@organic acid) for potential bioapplications: spectroscopic, structural, and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation. Langmuir 30:9533–9543. https://doi.org/10.1021/la501107a
Shete PB, Patil RM, Thorat ND, Prasad A, Ningthoujam RS, Ghosh SJ, Pawar SH (2014) Magnetic chitosan nanocomposite for hyperthermia therapy application: preparation, characterization and in vitro experiments. Appl Surf Sci 288:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.09.169
Song YH, You HP, Huang YJ, Yang M, Zheng YH, Zhang LH, Guo N (2010) Highly uniform and monodisperse Gd2O2S:Ln(3+) (Ln = Eu, Tb) submicrospheres: solvothermal synthesis and luminescence properties. Inorg Chem 49:11499–11504. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic101608b
Yang J, Quan ZW, Kong DY, Liu XM, Lin J (2007) Y2O3: Eu3+ microspheres: solvothermal synthesis and luminescence properties. Cryst Growth Des 7:730–735. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg060717j
Zhang CM, Cheng ZY, Yang PP, Xu ZH, Peng C, Li GG, Lin J (2009) Architectures of strontium hydroxyapatite microspheres: solvothermal synthesis and luminescence properties. Langmuir 25:13591–13598. https://doi.org/10.1021/la9019684
Jia G, You HP, Liu K, Zheng YH, Guo N, Zhang HJ (2010) Highly uniform Gd2O3 hollow microspheres: template-directed synthesis and luminescence properties. Langmuir 26:5122–5128. https://doi.org/10.1021/la903584j
Jia GA, You HP, Song YH, Huang YJ, Yang M, Zhang HJ (2010) Facile synthesis and luminescence of uniform Y2O3 hollow spheres by a sacrificial template route. Inorg Chem 49:7721–7725. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic100430g
Ansari AA, Alam M, Labis JP, Alrokayan SA, Shafi G, Hasan TN, Syed NA, Alshatwi AA (2011) Luminescent mesoporous LaVO4:Eu3+ core–shell nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, biocompatibility and their cytotoxicity. J Mater Chem 21:19310–19316. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm12871j
Ansari AA, Labis JP, Manthrammel MA (2017) Designing of luminescent GdPO4:Eu@LaPO4@SiO2 core/shell nanorods: synthesis, structural and luminescence properties. Solid State Sci 71:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2017.07.012
Slowing II, Trewyn BG, Lin VSY (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of membrane-impermeable proteins. J Am Chem Soc 129:8845–8849. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0719780
Ansari AA, Hasan TN, Syed NA, Labis JP, Parchur AK, Shafi G, Alshatwi AA (2013) In-vitro cyto-toxicity, geno-toxicity, and bio-imaging evaluation of one-pot synthesized luminescent functionalized mesoporous SiO2@Eu(OH)(3) core-shell microspheres. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 9:1328–1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2013.05.006
Ansari AA, Labis JP (2012) One-pot synthesis and photoluminescence properties of luminescent functionalized mesoporous SiO2@Tb(OH)(3) core-shell nanospheres. J Mater Chem 22:16649–16656. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm33583b
Radu DR, Lai CY, Jeftinija K, Rowe EW, Jeftinija S, Lin VSY (2004) A polyamidoamine dendrimer-capped mesoporous silica nanosphere-based gene transfection reagent. J Am Chem Soc 126:13216–13217. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja046275m
Luo Z, Cai KY, Hu Y, Zhao L, Liu P, Duan L, Yang WH (2011) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles end-capped with collagen: redox-responsive nanoreservoirs for targeted drug delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:640–643. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201005061
Paek J, Lee CH, Choi J, Choi SY, Kim A, Lee JW, Lee K (2007) Gadolinium oxide nanoring and nanoplate: anisotropic shape control. Cryst Growth Des 7:1378–1380. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg070229r
Gaspar RDL, Mazali IO, Sigoli FA (2010) Particle size tailoring and luminescence of europium(III)-doped gadolinium oxide obtained by the modified homogeneous precipitation method: dielectric constant and counter anion effects. Colloids Surf A 367:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.07.003
Guo HC, Idris NM, Zhang Y (2011) LRET-based biodetection of DNA release in live cells using surface-modified upconverting fluorescent nanoparticles. Langmuir 27:2854–2860. https://doi.org/10.1021/la102872v
Wang Y, Yang T, Ke HT, Zhu AJ, Wang YY, Wang JX, Shen JK, Liu G, Chen CY, Zhao YL, Chen HB (2015) Smart albumin-biomineralized nanocomposites for multimodal imaging and photothermal tumor ablation. Adv Mater 27: 3874. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500229
Park JY, Baek MJ, Choi ES, Woo S, Kim JH, Kim TJ, Jung JC, Chae KS, Chang Y, Lee GH (2009) Paramagnetic ultrasmall gadolinium oxide nanoparticles as advanced T-1 MR1 contrast agent: account for large longitudinal relaxivity, optimal particle diameter, and in vivo T-1 MR images. Acs Nano 3:3663–3669. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900761s
Paul N, Mohanta D (2016) Evaluation of optoelectronic response and Raman active modes in Tb3+ and Eu3+-doped gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3) nanoparticle systems. Appl Phys A. http://doi.org/1007/s00339-016-0347-6
Runowski M, Goderski S, Paczesny J, Ksiezopolska-Gocalska M, Ekner-Grzyb A, Grzyb T, Rybka JD, Giersig M, Lis S (2016) Preparation of biocompatible, luminescent-plasmonic core/shell nanomaterials based on lanthanide and gold nanoparticles exhibiting SERS effects. J Phys Chem C 120:23788–23798. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b06644
Grzyb T, Runowski M, Dąbrowska K, Giersig M, Lis S (2013) Structural, spectroscopic and cytotoxicity studies of TbF3@CeF3 and TbF3@CeF3@SiO2 nanocrystals. J Nanopart Res 15:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1958-x
Runowski M, Grzyb T, Zep A, Krzyczkowska P, Gorecka E, Giersig M, Lis S (2014) Eu3+ and Tb3+ doped LaPO4 nanorods, modified with a luminescent organic compound, exhibiting tunable multicolour emission. RSA Adv 4:46305–46312. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra06168c
Huang CC, Su CH, Li WM, Liu TY, Chen JH, Yeh CS (2009) Bifunctional Gd2O3/C Nanoshells for MR Imaging and NIR Therapeutic Applications. Adv Funct Mater 19:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200801454
Li ZQ, Wang LM, Wang ZY, Liu XH, Xiong YJ (2011) Modification of NaYF4:Yb,Er@SiO2 Nanoparticles with Gold Nanocrystals for Tunable Green-to-Red Upconversion Emissions. J Phys Chem C 115:3291–3296. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp110603r
Ansari AA, Aldalbahi AK, Labis JP, Manthrammel MA (2017) Impact of surface coating on physical properties of europium-doped gadolinium fluoride microspheres. J Fluor Chem 199:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2017.03.015
Xu ZH, Li CX, Ma PA, Hou ZY, Yang DM, Kang XJ, Lin J (2011) Facile synthesis of an up-conversion luminescent and mesoporous Gd2O3:Er3 + @nSiO(2)@mSiO(2) nanocomposite as a drug carrier. Nanoscale 3:661–667. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0nr00695e
Szczeszak A, Ekner-Grzyb A, Runowski M, Szutkowski K, Mrowczynska L, Kazmierczak Z, Grzyb T, Dabrowska K, Giersig M, Lis S (2016) Spectroscopic, structural and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of luminescent, lanthanide doped core@shell nanomaterials GdVO4:Eu(3+)5%@SiO2@NH2. J Colloid Interf Sci 481:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.07.025
Grzyb T, Runowski M, Dabrowska K, Giersig M, Lis S (2013) Structural, spectroscopic and cytotoxicity studies of TbF3@CeF3 and TbF3@CeF3@SiO2 nanocrystals. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 15. UNSP 195810.1007/s11051-013-1958-x
Ansari AA, Yadav R, Rai SB (2016) Enhanced luminescence efficiency of aqueous dispersible NaYF4:Yb/Er nanoparticles and the effect of surface coating. RSC Adv 6:22074–22082. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra00265j
Ansari AA, Parchur AK, Kumar B, Rai SB (2016) Influence of shell formation on morphological structure, optical and emission intensity on aqueous dispersible NaYF4:Ce/Tb nanoparticles. J Fluoresc 26:1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-016-1824-1
Ansari AA, Manthrammel MA (2017) Surface coating effect on structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of Eu3+ doped yttrium fluoride nanoparticles. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 27:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-016-0463-y
Lechevallier S, Lecante P, Mauricot R, Dexpert H, Dexpert-Ghys J, Kong HK, Law GL, Wong KL (2010) Gadolinium-Europium carbonate particles: controlled precipitation for luminescent biolabeling. Chem Mater 22:6153–6161. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm102134k
Ren H, Zhang LY, Wang TT, Li L, Su ZM, Wang CG (2013) Universal and facile synthesis of multicolored upconversion hollow nanospheres using novel poly(acrylic acid sodium salt) microspheres as templates. Chem Commun 49:6036–6038. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc41284a
Kang JG, Min BK, Sohn Y (2015) Synthesis and characterization of Gd(OH)(3) and Gd2O3 nanorods. Ceram Int 41:1243–1248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.09.053
Li JG, Zhu Q, Li XD, Sun XD, Sakka Y (2011) Colloidal processing of Gd2O3:Eu3+ red phosphor monospheres of tunable sizes: solvent effects on precipitation kinetics and photoluminescence properties of the oxides. Acta Mater 59:3688–3696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.03.004
Macedo AG, Ferreira RAS, Ananias D, Reis MS, Amaral VS, Carlos LD, Rocha J (2010) Effects of phonon confinement on anomalous thermalization, energy transfer, and upconversion in Ln(3+)-doped Gd2O3 nanotubes. Adv Funct Mater 20:624–634. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200901772
Xu ZH, Gao Y, Huang SS, Ma PA, Lin J, Fang JY (2011) A luminescent and mesoporous core-shell structured Gd2O3:Eu3+@nSiO(2)@mSiO(2) nanocomposite as a drug carrier. Dalton Trans 40:4846–4854. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1dt10162e
Ansari AA, Labis JP (2012) Preparation and photoluminescence properties of hydrothermally synthesized YVO4:Eu3+ nanofibers. Mater Lett 88:152–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.08.033
Ansari AA, Labis JP, Alrokayan SAH (2012) Synthesis of water-soluble luminescent LaVO4:Ln(3+) porous nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11051-012-0999-X
Goglio G, Kaur G, Pinho SLC, Penin N, Blandino A, Geraldes CFGC, Garcia A, Delville MH (2015) Glycine-nitrate process for the elaboration of Eu3+-doped Gd2O3 bimodal nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Eur J Inorg Chem 7:1243–1253. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201402721
Guo KM, Li MY, Fang XL, Luoshan MD, Bai LH, Zhao XZ (2014) Performance enhancement in dye-sensitized solar cells by utilization of a bifunctional layer consisting of core shell beta-NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+@SiO2 submicron hexagonal prisms. J Power Sources 249:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.10.067
He EJ, Zheng HR, Dong J, Gao W, Han QY, Li JN, Hui L, Lu Y, Tian HN (2014) Facile fabrication and upconversion luminescence enhancement of LaF3:Yb3+/Ln(3+)@SiO2 (Ln = Er, Tm) nanostructures decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/25/4/045603
Kang XJ, Cheng ZY, Li CX, Yang DM, Shang MM, Ma PA, Li GG, Liu NA, Lin J (2011) Core–shell structured up-conversion luminescent and mesoporous NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+@nSiO(2)@mSiO(2) nanospheres as carriers for drug delivery. J Phys Chem C 115:15801–15811. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp203039t
Kostiv U, Patsula V, Noculak A, Podhorodecki A, Vetvicka D, Pouckova P, Sedlakova Z, Horak D (2017) Phthalocyanine-conjugated upconversion NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+@SiO2 nanospheres for NIR-triggered photodynamic therapy in a tumor mouse model. ChemMedChem 12:2066–2073. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201700508
Jacobsohn LG, Bennett BL, Muenchausen RE, Tornga SC, Thompson JD, Ugurlu O, Cooke DW, Sharma ALL (2008) Multifunction Gd2O3: Eu nanocrystals produced by solution combustion synthesis: structural, luminescent, and magnetic characterization. J Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2931024
Ansari AA, Parchur AK, Kumar B, Rai SB (2016) Highly aqueous soluble CaF2:Ce/Tb nanocrystals: effect of surface functionalization on structural, optical band gap, and photoluminescence properties. J Mater Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10856-016-5791-5
Shi F, Zhai XS, Zheng KZ, Zhao D, Qin WP (2011) Synthesis of monodisperse NaYF4:Yb, Tm@SiO2 nanoparticles with intense ultraviolet upconversion luminescence. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:9912–9915. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2011.5248
Sotiriou GA, Franco D, Poulikakos D, Ferrari A (2012) Optically stable biocompatible flame-made SiO2-coated Y2O3: Tb3+ nanophosphors for cell imaging. Acs Nano 6:3888–3897. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn205035p
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through Research Group No. RG-1436-005.
Authors contributions
The idea is from Dr. Ali Aldalbahi and Dr. Anees A Ansari, the manuscript was mainly written by AAA and AA. MR helped in the technical support for the characterization. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. and there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aldalbahi, A., Rahaman, M. & Ansari, A.A. Mesoporous silica modified luminescent Gd2O3:Eu nanoparticles: physicochemical and luminescence properties. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 89, 785–795 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4897-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4897-2