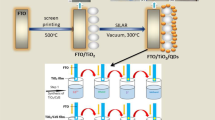
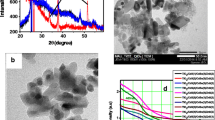
Abstract
Overall, the quantum dots sensitized solar cells were successfully prepared with the enhanced short current density from 7.7 mA/cm2 to 19 mA/cm2 based on Mn2+ ions doped on CdSe nanocrystal by successive ionic layer absorption and reaction. There were rapid effects of Mn2+ ions on optical, physical, chemical, and photovoltaic properties of the quantum dots sensitized solar cells. Consequently, the highest efficiency of the quantum dots sensitized solar cells increased dramatically from 1.7% for pure CdSe nanocrystal to 3.8% for Mn2+ ions doped on pure CdSe nanocrystal. Actually, the Mn2+ dopant rise in the conduction band of pure CdSe nanocrystal, reduces recombination, enhances the efficiency of high harvesting, and improves the charge transfer and collection. In addition, the optical properties, the direct optical energy gap, and both conduction band and valence band levels of the compositional CdS, Cd1−xMnxSe were estimated by Tauc model and discussed in details. This Tauc model is useful for us to understand the alignment energy structure of the compositions in electrodes, in particular, the conduction band and valence band levels of CdS, Cd1−xMnxSe nanoparticles. As a result, a rise or a drop of the conduction band and valence band levels when Mn2+ content was changed. Correspondingly, the Electrochemical Impedance Spectra were carried to determine dynamic resistances in QDSSCs.

The enhanced performance of the quantum dots sensitized solar cells based on Mn2+ ions doped on CdSe nanocrystal
Highlights
-
The enhanced performance of QDSSCs based on Cd1−xMnxSe
-
Determination of the CB and VB levels of materials by Tauc equation
-
Study of the obtained results through band alignment energy and EIS




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamat PV (2008) Quantum dot solar cells. Semiconductor nanocrystals as light harvesters. J Phys Chem C 112(no. 48):18737–18753
González-Pedro V, Xu X, Mora-Sero I, Bisquert J (2010) Modeling high-efficiency quantum dot sensitized solar cells. ACS nano 4(no. 10):5783–5790
Tian J, Cao G (2015) Control of nanostructures and interfaces of metal oxide semiconductors for quantum-dots-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem Lett 6(no. 10):1859–1869
Beard MC, Aaron GM, Hanna MC, Luther JM, Hughes BK, Arthur JN (2010) Comparing multiple exciton generation in quantum dots to impact ionization in bulk semiconductors: implications for enhancement of solar energy conversion. Nano Lett 10(no. 8):3019–3027
Lopez-Luke T, Wolcott A, Xu L-P, Chen S, Wen Z, Li J, Rosa EDL, Jin Z. Z (2008) Nitrogen-doped and CdSe quantum-dot-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 films for solar energy conversion applications. J Phys Chem C 112(no. 4):1282–1292
Mora-Seró I, Giménez S, Moehl T, Fabregat-Santiago F, Lana-Villareal T, Gómez R, Bisquert J (2008) Factors determining the photovoltaic performance of a CdSe quantum dot sensitized solar cell: the role of the linker molecule and of the counter electrode. Nanotechnology 19(no. 42):424007
Shen Q, Kobayashi J, Diguna LJ, Toyoda T (2008) Effect of ZnS coating on the photovoltaic properties of CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J Appl Phys 103(no. 8):084304
Lee J-W, Son D-Y, Ahn TK, Shin H-W, In Young K, Seong-Ju H, Min Jae K, Soohwan S, Hyouksoo H, Nam-Gyu P (2013) Quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell with unprecedentedly high photocurrent. Sci Rep 3:1050
Santra PK, Prashant VK (2012) Mn-doped quantum dot sensitized solar cells: a strategy to boost efficiency over 5%. J Am Chem Soc 134(no. 5):2508–2511
Zhu G, Pan L, Xu T, Sun Z (2011) CdS/CdSe-cosensitized TiO2 photoanode for quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells by a microwave-assisted chemical bath deposition method. ACS Appl Mater & Interfaces 3(no. 8):3146–3151
Lee YH, Sang Hyuk I, Jeong Ah C, Jong-Heun L, Sang Il S (2012) CdSe-sensitized inorganic–organic heterojunction solar cells: the effect of molecular dipole interface modification and surface passivation. Org Electron 13(no. 6):975–979
Hossain Md A, James Robert J, Chao S, Jia Hong P, Zhen Yu K, Nripan M, Wang. Q (2012) CdSe-sensitized mesoscopic TiO2 solar cells exhibiting > 5% efficiency: redundancy of CdS buffer layer. J Mater Chem 22(no. 32):16235–16242
Wang J, Mora-Seró I, Pan Z, Zhao K, Zhang H, Feng Y, Yang G, Zhong X, Bisquert J (2013) Core/shell colloidal quantum dot exciplex states for the development of highly efficient quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc 135(no. 42):15913–15922
Radich JG, Peeples NR, Santra PK, Kamat. PV (2014) Charge transfer mediation through CuxS. The hole story of CdSe in polysulfide. J Phys Chem C 118(no. 30):16463–16471
Yan K, Zhang L, Qiu J, Qiu Y, Zhu Z, Wang J, Yang S (2013) A quasi-quantum well sensitized solar cell with accelerated charge separation and collection. J Am Chem Soc 135(no. 25):9531–9539
Tian J, Lili Lv, Fei C, Wang Y, Liu X, Cao G (2014) A highly efficient (>6%) Cd1−xMnxSe quantum dot sensitized solar cell. J Mater Chem A no. 46:19653–19659
Thanh TH, Quang VL, Thanh Dat Huynh (2016) Influence of surface treatment and annealing temperature on the recombination processes of the quantum dots solar cells. J Nanomater 2016:36
Thanh HT, Chi CH, Nguyen VY, Thoa NTP, Thanh Dat Huynh, Quang VL (2015) Improving the performance of QDSSCs based on TiO2/CdS(Silar)/CdSe(Colloid)/Zns(Silar) photoanodes. Environ Progress Sustain Energy 34(no. 6):1774–1779
Thanh TH, Quang VL, Thanh DH (2015) Determination of the dynamic resistance of the quantum dots solar cells by one I–V curve and electrochemical impedance spectra. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 143:269–274
Thanh TH, Lam QV, Thanh Dat H (2014) The dynamic resistance of CdS/CdSe/ZnS Co-Sensitized TiO2 solar cells. Braz J Phys 44(no. 6):746–752
Wang Y, Zhang Q, Huang F, Li Z, Zheng Y-Z, Tao X, Cao G (2018) In situ assembly of well-defined Au nanoparticles in TiO2 films for plasmon-enhanced quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Nano Energy 44:135–143
Yu L, Li Z, Liu Y, Cheng F, Sun S (2014) Mn-doped CdS quantum dots sensitized hierarchical TiO2 flower-rod for solar cell application. Appl Surf Science 305:359–365
Lv J, Liu J, Zhang J, Dai K, Liang C, Wang Z, Zhu G (2018) Construction of organic–inorganic cadmium sulfide/diethylenetriamine hybrids for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production. J Colloid Interface Sci 512:77–85
Lee YL, Yi. SL (2009) Highly efficient quantum dot sensitized solar cell based on co-sensitization of CdS/CdSe. Adv Funct Mater 19(no. 4):604–609
Abdin Z, Alim MA, Saidur R, Islam MR, Rashmi W, Mekhilef S, Wadi A (2013) Solar energy harvesting with the application of nanotechnology. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 26:837–852
Wang L, Wang W, Shang M, Yin W, Sun S, Zhang L (2010) Enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light over Cd1−xZnxS solid solution with cubic zinc blend phase. Int J Hydrog Energy 35(no. 1):19–25
Zhao T, Liu X, Li Y, Zhang M, He J, Zhang X, Liu H, Wang X, Gu H (2017) Fluorescence and drug loading properties of ZnSe:Mn/ZnS-Paclitaxel/SiO2 nanocapsules templated by F127 micelles. J Colloid Interface Sci 490:436–443
Akl AA, Safwat AM, AL-Shomar SM, Hassanien AS (2018) Improving microstructural properties and minimizing crystal imperfections of nanocrystalline Cu2O thin films of different solution molarities for solar cell applications. Mater Sci Semicond Process 74:183–192
Srivastava BB, Jana S, Pradhan N (2010) Doping Cu in semiconductor nanocrystals: some old and some new physical insights. J Am Chem Soc 133(no. 4):1007–1015
Kamat PV, Tvrdy K, Baker DR, James GR (2010) Beyond photovoltaics: semiconductor nanoarchitectures for liquid-junction solar cells. Chem Rev 110(no. 11):6664–6688
Sánchez-Vergara María, Elena JuanCarlos, Alonso-Huitron Arturo, Rodriguez-Gómez, Jerry N (2012) Reider-Burstin. Determination of the optical GAP in thin films of amorphous dilithium phthalocyanine using the Tauc and Cody models. Molecules 17(no. 9):10000–10013
Corrado C, Jiang Y, Oba F, Kozina M, Bridges F, Zhang JZ (2009) Synthesis, structural, and optical properties of stable ZnS: Cu, Cl nanocrystals. J Phys Chem A 113(no. 16):3830–3839
Mandal P, Talwar SS, Major SS, Srinivasa RS (2008) Orange-red luminescence from Cu doped CdS nanophosphor prepared using mixed Langmuir–Blodgett multilayers. J Chem Phys 128(no. 11):114703
Pradhan N, Goorskey D, Thessing J, Peng X (2005) An alternative of CdSe nanocrystal emitters: pure and tunable impurity emissions in ZnSe nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 127(no. 50):17586–17587
Xie R, Peng X (2009) Synthesis of Cu-doped InP nanocrystals (d-dots) with ZnSe diffusion barrier as efficient and color-tunable NIR emitters. J Am Chem Soc 131(no. 30):10645–10651
Johnson CA, Kittilstved KR, Kaspar TC, Droubay TC, Chambers SA, Salley GM, Gamelin DR (2010) Mid-gap electronic states in Zn1−xMnxO. Phys Rev B 82(no. 11):115202
Muthukumaran S (2013) Structural, FTIR and photoluminescence properties of ZnS: Cu thin films by chemical bath deposition method. Mater Lett 93:223–225
Gan C, Zhang Y, Battaglia D, Peng X, Xiao M (2008) Fluorescence lifetime of Mn-doped ZnSe quantum dots with size dependence. Appl Phys Lett 92(no. 24):241111
Wu P, Yan X-P (2013) Doped quantum dots for chemo/biosensing and bioimaging. Chem Soc Rev 42(no. 12):5489–5521
Srivastava BB, Jana S, Karan NS, Paria S, Jana NR, Sarma DD, Narayan P (2010) Highly luminescent Mn-doped ZnS nanocrystals: gram-scale synthesis. J Phys Chem Lett 1(no. 9):1454–1458
Kong Y, Sun H, Fan W, Wang L, Zhao H, Zhao X, Yuan S (2017) Enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of tungsten oxide film by bifunctional Au nanoparticles. RSC Adv 7(no. 25):15201–15210
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank University of Science, VNU-HCM, Vietnam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phuc, D.H., Tung, H.T. Optical properties and dynamic process in Cd1−xMnxSe quantum dots sensitized solar cells. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 87, 254–262 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4725-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4725-8