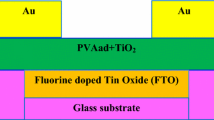
Abstract
Titania–silica hybrid films with a thickness of 300 nm are fabricated by combining a sol–gel method with a spin-coating process from the acid-catalyzed organically modified silane solution of γ-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane, methyltriethoxysilane and tetrapropylorthotitanate. The dielectric constants of the titania–silica hybrid films can be easily controlled by adjusting titanium content. Effects of titanium content and heat treatment temperature on the leakage current and surface roughness of the as-fabricated films are also optimized, thus, the hybrid film with smooth surface (R q < 0.3 nm), high dielectric constant (k = 59.44) and low leakage current density (<1 nA cm−2 at 5 V) is obtained and then used as the dielectric layer for the organic field effect transistors. Results indicate that the electrical properties of the organic field effect transistor fabricated by the titania–silica hybrid film as dielectric layer show an obvious improvement as compared with those of the organic field effect transistor fabricated by the thermally grown SiO2 as dielectric layer, especially, in the improvement of the operating voltage (−2 V), field effect mobility (0.53 cm2 V−1 s−1) and sub-threshold swing (~130 mV/dec). It can be concluded that the titania–silica hybrid film shows a potential for the dielectric layer of the organic field effect transistors.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sekitani T, Zschieschang U, Klauk U, Someya T (2010) Flexible organic transistors and circuits with extreme bending stability. Nat Mater 9:1015–1022. doi:10.1038/NMAT2896
Abe Y, Dai T, Manaka T, Iwamoto M (2014) Study of carrier transport in flexible organic field-effect transistors: analysis of bending effect and microscopic observation using electric-field-induced optical second-harmonic generation. Thin Solid Films 554:166–169. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2013.05.160
Baeg KJ, Khim D, Kim J, Han H (2012) Controlled charge transport by polymer blend dielectrics in topgate organic field-effect transistors for low-voltage-operating complementary circuts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:6176–6184. doi:10.1021/AM301793m
Gelinck G, Heremans P, Nomoto K, Anthopoulos TD (2010) Organic transistors in optical displays and microelectronic applications. Adv Mater 22:3778–3798. doi:10.1002/adma.200903559
Kim YJ, Lee HS, Noh JS (2016) Transient behaviors of ZnO thin films on a transparent, flexible polyethylene terephthalate substrate. Thin Solid Films 603:160–164. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2016.02.012
Han S, Zhuang X, Shi W, Yang X, Li L (2016) Poly(3-hexylthiophene)/polystyrene (P3HT/PS) blends based organic field-effect transistor ammonia gas sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 225:10–15. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.11.005
Wang Y-F, Tsai M-R, Lin Y-S, Wu F-C, Lin C-Y (2015) High-response organic thin-film memory transistors based on dipole-functional polymer electret layers. Org Electron 26:359–364. doi:10.1016/j.orgel.2015.08.006
Facchetti A (2007) Semiconductors for organic transistors. Mater Today 10:28–37. doi:10.1016/s1369-7021(07)70017-2
Yamashita Y (2009) Organic semiconductors for organic field-effect transistors. Sci Technol Adv Mater 10:024313. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/10/2/024313
Oniwa K, Kikuchi H, Shimotani H, Ikeda S, Asao N, Yamamoto Y (2016) 2-Positional pyrene end-capped oligothiophenes for high performance organic field effect transistors. Chem Commun 52:4800–4803. doi:10.1039/c6cc00948d
Wang Y, Zou S, Gao J, Zhang H, Lai G, Yang C (2015) High-performance organic field-effect transistors based on single-crystalline microribbons of a two-dimensional fused heteroarene semiconductor. Chem Commun 51:11961–11963. doi:10.1039/c5cc03305e
Hutchins DO, Acton O, Weidner T, Cernetic N, Baio JE, Castner DG (2012) Solid-state densification of spun-cast self-assembled monolayers for use in ultra-thin hybrid dielectrics. Appl Surf Sci 261:908–915. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.09.013
Ono S, Häusermann R, Chiba D, Shimamura K, Ono T (2014) High performance organic field-effect transistors with ultra-thin HfO2 gate insulator deposited directly onto the organic semiconductor. Appl Phys Lett 104:013307. doi:10.1063/1.4860998
Majewski LA, Schroeder R, Grell M (2005) One volt organic transistor. Adv Mater 17:192–196. doi:10.1002/adma.200400809
Deman AL, Tardy J (2005) PMMA–Ta2O5 bilayer gate dielectric for low operating voltage organic FETs. Org Electron 6:78–84. doi:10.1016/j.orgel.2005.03.002
Hwang DK, Fuentes-Hernandez C, Kim JB, Potscavage WJ, Kippelen B (2011) Flexible and stable solution-processed organic field-effect transistors. Org Electron 12:1108–1113. doi:10.1016/j.orgel.2011.04.002
Liao M, Ishiwara H, Ohmi SI (2014) Excellent current drivability and environmental stability in room-temperature-fabricated pentacene-based organic field-effect transistors with HfO2 gate insulators. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 61:569–575. doi:10.1109/ted.2013.2292904
Hasan M, Nguyen MC, Kim H, You SW, Jeon YS, Tong DT (2015) High performance solution processed zirconium oxide gate dielectric appropriate for low temperature device application. Thin Solid Films 589:90–94. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2015.04.035
Su YR, Xie WG, Li Y, Shi Y, Zhao N, Xu JB (2013) A low-temperature, solution-processed high-kdielectric for low-voltage, high-performance organic field-effect transistors (OFETs). J Phys D Appl Phys 46:095105. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/46/9/095105
Su Y, Wang C, Xie W, Xie F, Chen J, Zhao N, Xu J (2011) Low-voltage organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) with solution-processed metal-oxide as gate dielectric. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:4662–4667. doi:10.1021/am201078v
Gedda M, Subbarao NVV, Obaidulla SM, Goswami DK (2013) High carrier mobility of CoPc wires based field-effect transistors using bi-layer gate dielectric. AIP Adv 3:112123. doi:10.1063/1.4834355
Han S, Zhuang X, Shi W, Yang X, Li L, Yu J (2016) Poly(3-hexylthiophene)/polystyrene (P3HT/PS) blends based organic field-effect transistor ammonia gas sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 225:10–15. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.11.005
Bahari A, Shahbazi M (2016) Electrical properties of PVP-SiO2-TMSPM hybrid thin films as ofet gate dielectric. J Electron Mater 45:1201–1209. doi:10.1007/s11664-015-4262-y
Busani T, Devine RAB, Yu X, Seo HW (2006) Electrical and physical properties of room temperature deposited, mixed TiO2∕SiO2 oxides. J Vac Sci Technol 24:369–374. doi:10.1116/1.2172951
Benito N, Palacio C (2014) Mixed Ti–O–Si oxide films formation by oxidation of titanium–silicon interfaces. Appl Surf Sci 301:436–441. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.02.094
Peng J, Sheng C, Shi J, Li X, Zhang J (2014) High-k titanium–aluminum oxide dielectric films prepared by inorganic–organic hybrid solution. J Solgel Sci Technol 71:458–463. doi:10.1007/s10971-014-3400-y
Hacker CA, Anderson KA, Richter LJ, Richter CA (2005) Comparison of Si-O-C interfacial bonding of alcohols and aldehydes on Si(111) formed from dilute solution with ultraviolet irradiation. Langmuir 21:882–889. doi:10.1021/la048841x
Yu S, Wong TKS, Hu X, Pita K, Ligatchev V (2004) Synthesis and characterization of templating low dielectric constant organosilicate films. J Electrochem Soc 151:F123–F127. doi:10.1149/1.1688800
Que W, Hu X (2003) Influence of titanium content and temperature on optical and mechanical properties of sol-gel derived TiO2/γ-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane and methyltrimethoxysilane hybrid organic-inorganic films. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:908–914
Tan HS, Mathews N, Cahyadi T, Zhu FR, Mhaisalkar SG (2009) The effect of dielectric constant on device mobilities of high-performance, flexible organic field effect transistors. Appl Phys Lett 94:263303. doi:10.1063/1.3168523
Ortiz RP, Facchetti A, Marks TJ (2009) High-k organic, inorganic and hybrid dielectrics for low-voltage organic field-effect transistors. Chem Rev 110:205–239. doi:10.1021/ cr9001275
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China under Grant 20120201130004, the Science and Technology Developing Project of Shaanxi Province under Grant No. 2015KW-001, partially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Major Research Plan on Nanomanufacturing under Grant No. 91323303, and the 111 Project of China (B14040). The SEM work was done at the International Center for Dielectric Research, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, P. R. China, and the AFM work was done at the Micro-optoelectronic Systems Laboratories, Xi’an Technology University, P. R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Que, W., Chen, Z. et al. Titania–silica hybrid films derived by a sol–gel process for organic field effect transistors. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83, 666–674 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4459-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4459-z