Abstract
Modified sol–gel processed silica matrices were prepared to explore the possibilities of using these matrices for electrophoresis applications. The sol–gel was prepared at room temperature using tetraethyl orthosilicate as a precursor at different molar ratios (R = 4, 16, 32 and 64) in the presence of sodium phosphate buffer. The sol–gel derived from R = 32 formed smooth and transparent gel, and showed high transmittance value (97%) compared to other molar ratios. Transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy studies of gel matrix (R-32) confirmed randomly distributed interstitial space of variable size (30–60 nm) with slit like openings on the gel surface. The R = 32-based matrix internal and surface characteristics were suitable for gel electrophoresis. Therefore, sol–gel electrophoresis was carried out using gel matrix (R = 32) on molecular markers and pre-stained proteins (08–220 kDa). The silica gel matrix allowed migration as well as separation of proteins based on their molecular weights. The results were compared with standard gels (agarose and polyacrylamde). The aim of the work to prepare a silica matrix suitable for gel electrophoresis which could be utilised to develop electrophoresis-based point-of-care technologies for clinical diagnostics.
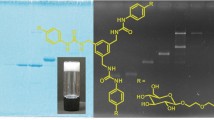
Graphical Abstract
Schematic illustration of sol–gel electrophoresis (SoGE), showing different stages of sol–gel preparation and its utilisation for separation of proteins 8–220 kDa. 






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinker CJ (1990) Sol-gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. Academic, Boston
Owens GJ, Singh RK, Foroutan F, Alqaysi M, Han C, Mahapatra C, Knowles JC (2016) Sol–gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog Mater Sci 77:1–79. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.12.001
Gupta R, Chaudhury N (2007) Entrapment of biomolecules in sol–gel matrix for applications in biosensors: Problems and future prospects. Biosens Bioelectron 22(11):2387–2399. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2006.12.025
Bhatia RB, Brinker CJ, Gupta AK, Singh AK (2000) Aqueous Sol−Gel Process for Protein Encapsulation. Chem Mater 12(8):2434–2441. doi:10.1021/cm000260f
Schmidt H, Geiter E, Mennig M, Krug H, Becker C, Winkler R (1998) The sol-gel process for nano-technologies: new nanocomposites with interesting optical and mechanical properties. J Solgel Sci Technol 13(1/3):397–404. doi:10.1023/a:1008660909108
Stacey A Yamanaka, Fumito Nishida, Lisa M Ellerby, Clinton R Nishida, Bruce Dunn, Joan S Valentine, Jeffrey I Zink (1992) Enzymatic activity of glucose oxidase encapsulated in transparent glass by the sol-gel method. Chem Mater 4(3):495–497. doi:10.1021/cm00021a001
Bhaskar M Murari, Sneh. Anand, Nivedita K Gohil, Nabo. K Chaudhury (2007) Fluorescence spectroscopic study of dip coated sol-gel thin film internal environment using fluorescent probes Hoechst33258 and Pyranine. J Solgel Sci Technol 41(2):147–155. doi:10.1007/s10971-006-0515-9
Jin W, Brennan JD (2002) Properties and applications of proteins encapsulated within sol–gel derived materials. Anal Chim Acta 461(1):1–36. doi:10.1016/s0003-2670(02)00229-5
Nakamura Hideaki, Karube Isao (2003) Current research activity in biosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 377(3):446–468. doi:10.1007/s00216-003-1947-5
MacCraith BD, McDonagh CM, O'Keeffe G, McEvoy AK, Butler T, Sheridan FR (1995) Sol-gel coatings for optical chemical sensors and biosensors. Sens Actuators B Chem 29(1–3):51–57. doi:10.1016/0925-4005(95)01662-7
Petit-Dominguez MD, Shen H, Heineman WR, Seliskar CJ (1997) Electrochemical Behavior of Graphite Electrodes Modified by Spin-Coating with Sol−Gel-Entrapped Ionomers. Anal Chem 69(4):703–710. doi:10.1021/ac960839q
Aronsson T, Grönwall A (1957) Improved Separation of Serum Proteins in Paper Electrophoresis — A New Electrophoresis Buffer. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 9(4):338–341. doi:10.1080/00365515709079983
Hench Larry L, West Jon K (1990) The sol-gel process. Chem Rev 90(1):33–72. doi:10.1021/cr00099a003
Wang J, Monton MR, Zhang X, Filipe CD, Pelton R, Brennan JD (2014) Hydrophobic sol–gel channel patterning strategies for paper-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 14(4):691–695. doi:10.1039/c3lc51313k
Avnir D, Coradin T, Lev O, Livage J (2006) Recent bio-applications of sol–gel materials. J Mater Chem 16(11):1013–1030. doi:10.1039/b512706h
Glezer Victor, Lev Ovadia (1993) Sol-gel vanadium pentaoxide glucose biosensor. J Am Chem Soc 115(6):2533–2534. doi:10.1021/ja00059a072
Lin J, Brown CW (1997) Sol-gel glass as a matrix for chemical and biochemical sensing. Trends Analyt Chem 16(4):200–211. doi:10.1016/S0165-9936(97)00021-6
Martin C, Aksay I (2004) Submicrometer-Scale Patterning of Ceramic Thin Films. J Electroceram 12(1/2):53–68. doi:10.1023/b:jecr.0000034001.15359.98
Kang J, Wistuba D, Schurig V (2002) Electrophoresis 23(7–8):1116. doi:10.1002/1522-2683(200204)23:7/8<1116::AID-ELPS1116>3.0.CO;2-O
Shin MJ, Park JY, Park K, Song SH, Yoo YJ (2007) Novel sol-gel immobilization of horseradish peroxidase employing a detergentless micro-emulsion system. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 12(6):640–645. doi:10.1007/bf02931080
Gabriela P, Otilia B, Vlad-Oros B (2011). Sol-gel technology in enzymatic electrochemical biosensors for clinical analysis. In: Pier Andrea Serra (ed) Biosensors for Health, Environment and Biosecurity, InTech, Rijeka. doi: 10.5772/19622
Guo Y, Imahori GA, Colón LA (1996) Hydrolytically stable amino-silica glass coating material for manipulation of the electroosmotic flow in capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 744(1–2):17–29. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(96)00277-4
Guo Y, Colon LA (1995) A stationary phase for open tubular liquid chromatography and electrochromatography using sol-gel technology. Anal Chem 67(15):2511–2516. doi:10.1021/ac00111a003
Kirkland J (1973) Porous silica microsphere column packings for high-speed liquid-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 83:149–167. doi:10.1016/s0021-9673(00)97035-3
Köhler J, Chase DB, Farlee RD, Vega AJ, Kirkland JJ (1986) Comprehensive characterization of some silica-based stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 352:275–305. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)83386-0
Nakanishi K (1997) J Porous Mater 4:67. doi:10.1023/A:1009627216939
Guiochon G (2007) Monolithic columns in high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1168(1–2):101–168. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.05.090
Tanaka Nobuo, Kobayashi Hiroshi, Ishizuka Norio, Minakuchi Hiroyoshi, Nakanishi Kazuki, Hosoya Ken, Ikegami Tohru (2002) Monolithic silica columns for high-efficiency chromatographic separations. J Chromatogr A 965(1–2):35–49. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01582-5
Minakuchi Hiroyoshi, Nakanishi Kazuki, Soga Naohiro, Ishizuka Norio, Tanaka Nobuo (1997) Effect of skeleton size on the performance of octadecylsilylated continuous porous silica columns in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 762(1–2):135–146. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(96)00944-2
Ishizuka N, Minakuchi H, Nakanishi K, Soga N, Hosoya K, Tanaka N (1998) J High Resolut Chromatogr 21(8):477. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4168(19980801)21:8<477::AID-JHRC477>3.0.CO;2-K
Minakuchi Hiroyoshi, Nakanishi Kazuki, Soga Naohiro, Ishizuka Norio, Tanaka Nobuo (1996) Octadecylsilylated porous silica rods as separation media for reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Anal Chem 68(19):3498–3501. doi:10.1021/ac960281m
Ishizuka Norio, Minakuchi Hiroyoshi, Nakanishi Kazuki, Soga Naohiro, Nagayama Hisashi, Hosoya Ken, Tanaka Nobuo (2000) Performance of a monolithic silica column in a capillary under pressure-driven and electrodriven conditions. Anal Chem 72(6):1275–1280. doi:10.1021/ac990942q
Ishizuka Norio, Minakuchi Hiroyoshi, Nakanishi Kazuki, Soga Naohiro, Tanaka Nobuo (1998) Designing monolithic double-pore silica for high-speed liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 797(1–2):133–137. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(97)01202-8
Cabrera K, Lubda D, Eggenweiler H-M, Minakuchi H, Nakanishi K (2000) A New Monolithic-Type HPLC Column For Fast Separations. J High Resolut Chromatogr 23:93–99. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4168(20000101)23:1<93::AID-JHRC93>3.0.CO;2-2
Michael C Breadmore, Kelley A Wolfe, Imee G Arcibal, Wayne K Leung, Dana Dickson, Braden C Giordano, Mary E Power, Jerome P Ferrance, Sanford H Feldman, Pamela M Norris, James P Landers (2003) Microchip-based purification of DNA from biological samples. Anal Chem 75(8):1880–1886. doi:10.1021/ac0204855
Narang U, Paras PN, Bright FV, Kumar A, Kumar ND, Malhotra BD, Kamalasanan MN, Chandra S (1994) A novel protocol to entrap active urease in a tetraethoxysilane-derived sol-gel thin-film architecture. Chem Mater 6(10):1596–1598. doi:10.1021/cm00046a004
Starosvetsky J, Starosvetsky E, Armon R (2008) Electrophoretic applications of sol–gel matrices. Ceram Int 34(6):1443–1448. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.04.007
Barril P, Nates S (2012). In: Sameh Magdeldin (ed) Introduction to agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis matrices with respect to their detection sensitivities, gel electrophoresis—principles and basics. InTech, Rijeka. doi:10.5772/2205
Krizek DM, Rick ME (2002) Agarose gel electrophoresis of proteins. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 15:6.7:6.7.1–6.7.13. doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb0607s15
Bonifacino J S, Harford J B, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Yamada K M (eds) (2001) Common stock solutions, buffers, and media. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. Wiley. doi:10.1002/0471143030.cba02as00
Iler RK (1979) The Chemistry Of Silica, 1st ed. Wiley, New York, NY. ISBN: 978-0-471-02404-0. http://as.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-047102404X.html
Brinker CJ (1988) Hydrolysis and condensation of silicates: Effects on structure. J Non Cryst Solids 100(1–3):31–50. doi:10.1016/0022-3093(88)90005-1
Touam Tahar, Znaidi Lamia, Vrel Dominique, Ninova-Kuznetsova Iva, Brinza Ovidiu, Fischer Alexis, Boudrioua Azzedine (2013) Low loss sol-gel TiO2 thin films for waveguiding applications. Coatings 3(1):49–58. doi:10.3390/coatings3010049
Raoufi Davood, Hosseinpanahi Faegh (2013) The effect of film thickness on surface morphology of ITO thin films. J Theor Appl Phys 7(1):21. doi:10.1186/2251-7235-7-21
Xi Yao, Liangying Zhang, Sasa Wang (1995) Pore size and pore-size distribution control of porous silica. Sens and Actuators B Chem 25(1–3):347–352. doi:10.1016/0925-4005(95)85078-3
Hoang Geun Chang (1997) J Korean Phys Soc 31(1):227. doi:10.3938/jkps.31.227
Helmut Ritter Ella, Bezdushna Carsten, Koopmans Maricica, Munteanu Monir, Tabatabai Kurt E, Geckeler F Nihal, Tüzün Ersel, Arçevik (2010) Pore modification in porous ceramic membranes with sol-gel process and determination of gas permeability and selectivity. Macromol Symp 287(1):135–142. doi:10.1002/masy.201050119
Wang Sasa, Liu Hongling, Zhang Liangying, Yao Xi (1995) Pore size control of porous silica by sol-gel process. Ferroelectrics Letters Section 19(3–4):89–94. doi:10.1080/07315179508204280
Boonamnuayvitaya V, Tayamanon C, Sae-Ung S, Tanthapanichakoon W (2006) Synthesis and characterization of porous media produced by a sol–gel method. Chem Eng Sci 61(5):1686–1691. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2005.10.002
Murakata Tadahiro, Sato Shimio, Ohgawara Takashi, Watanabe Tetushi, Suzuki Tohru (1992) Control of pore size distribution of silica gel through sol-gel process using inorganic salts and surfactants as additives. J Mater Sci 27(6):1567–1574. doi:10.1007/BF00542919
Parikh Nisha I, Vasan Ramachandran S (2007) Assessing the clinical utility of biomarkers in medicine. Biomark Med 1(3):419–436. doi:10.2217/17520363.1.3.419
Jain KK (2015) The handbook of biomarkers. Springer, New York, NY
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs. S Vidhya for assistance in sol–gel preparation and Dr. Avisek Ghose for the constructive discussions and suggestions. The authors also thank VIT University, Vellore, India and WIT, Waterford, Ireland for providing finance and research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadgir, M.M., Coffey, . & Murari, . Modified sol–gel processed silica matrix for gel electrophoresis applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83, 155–164 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4401-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4401-4