Abstract
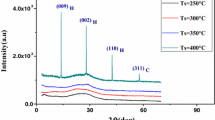
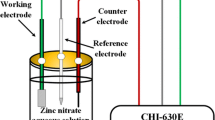
Zinc oxide nano-structured thin films have been synthesized by low-temperature and cost-effective sol–gel spin coating method. Zinc oxide films with good adherence have been deposited on soda lime glass substrates with two thicknesses 250.15 and 311.32 nm. High transmission (>95%) zinc oxide films with proper interference fringes in the visible and near infrared region have been obtained. Film thickness, optical constants and dispersion parameters have been calculated accurately by using Swanepoel method, which basely depends on the interference fringes of the transmission spectra. Zinc oxide films have direct optical band gap, its values slightly change with the annealing temperatures and film thickness. The X-ray diffraction studies indicated the hexagonal wurtzite structure for zinc oxide films with preferred orientation along (002) plane. Raman spectroscopy confirmed the hexagonal structure for the films. The average particle size is in the nano-scale and the crystallinity level increases with the annealing temperatures and film thickness.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin YH, Yang PC, Huang JS et al. (2011) High-efficiency inverted polymer solar cells with solution-processed metal oxides. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 95(8):2511–2515
Foo KL, Kashif M, Hashim U, Liu W-W (2014) Effect of different solvents on the structural and optical properties of zinc oxide thin films for optoelectronic applications. Ceram Int 40:753–761
Mandalapu LJ, Yang Z, Chu S, Liu JL (2008) Ultraviolet emission from Sb-doped p-type ZnO based heterojunction light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett 92(12):3. Article ID 122101
Yuen C, Yu SF, Lau SP, Chen GCK (2006) Design and fabrication of ZnO light-emitting devices using filtered cathodic vacuum arc technique. J Cryst Growth 287(1):204–212
Ali MG, Singh S, Chakrabarti P (2010) Ultraviolet ZnO photodetectors with high gain. J Electron Sci Technol 8:55–59
Badadhe SS, Mulla IS (2011) Effect of aluminium doping on structural and gas sensing properties of zinc oxide thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Sens Actuators B 156(2):943–948
Shishiyanu ST, Shishiyanu TS, Lupan OI (2005) Sensing characteristics of tin-doped ZnO thin films as NO2 gas sensor. Sens Actuators B 107:379–386
Suvaci E, Özer İÖ (2005) Processing of textured zinc oxide varistors via templated grain growth. J Eur Ceram Soc 25(9):1663–1673
Meron T, Markovich G (2005) Ferromagnetism in colloidal Mn2+-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 109(43):20232–20236
Yu H, Ming H, Gong J, Li H, Huang H, Pan K, Liu Y, Kang Z, Wei J, Wang D (2013) Facile synthesis of Au/ZnO nanoparticles and their enhanced photocatalytic activity for hydroxylation of benzene. Bull Mater Sci 36:367–372
Ahn JS, Lee KB (2010) High-performance semitransparent a-InGaZnO4 thin-film transistors using thin Al electrodes. J Korean Phys Soc 57:1244–1247
Samarasekara P, Wijesinghe U, Jayaweera EN (2015) Impedance and electrical properties of Cu doped ZnO thin films. GESJ 1(13):3–9. ISSN 1512-1461
Chebil W, Fouzri A, Azeza B, Sakly N, Mghaieth R, Lusson A, Sallet V (2015) Comparison of ZnO thin films on different substrates obtained by sol–gel process and deposited by spin-coating technique. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 53(8):521–529
Foo KL, Hashim U, Voon CH, Kashif M (2015) Fabrication and characterization of ZnO thin films by sol–gel spin coating method for pH measurement. Adv Mater Res 1109:99–103
Pokharel J, Shrestha M, Zhou LQ, Neto V, Fan QH (2015) Oriented zinc oxide nanocrystalline thin films grown from sol–gel solution. J Coat Sci Technol 2:46–50
Shafura AK, Mamat MH, Uzer M, Shuhaimi A, Salman AA, Haseeb AK, Rusop M (2015) Sensing properties of nanostructured zinc oxide-based gas sensor fabricated using immersion method. In: Proceedings of Malaysian International Tribology Conference, pp 306–307
Tang ZK, Wong GKL, Yu P, Kawasaki M, Ohtomo A, Koinuma H, Segawa Y (1998) Room- temperature ultraviolet laser emission from self-assembled ZnO microcrystallite thin films. Appl Phys Lett 72:3270
Abdel-Galil A, Balboul MR, Sharaf A (2015) Synthesis and characterization of Mn-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors. Phys B 477:20–28
Khanlary MR, Vahedi V, Reyhani A (2012) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanowires by thermal oxidation of Zn thin films at various temperatures. Molecules 17(5):5021–5029
Lu H, Zhai X, Liu W, Zhang M, Guo M (2015) Electrodeposition of hierarchical ZnO nanorod arrays on flexible stainless steel mesh for dye-sensitized solar cell. Thin Solid Films 586:46–53
Kim DH, Park J-H, Lee TL, Myoung J-M (2016) Superhydrophobic Al-doped ZnO nanorods-based electrically conductive and self-cleanable antireflecting window layer for thin film solar cell. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 150:65–70
Heo YW, Norton DP, Pearton SJ (2005) Origin of green luminescence in ZnO thin film grown by molecular-beam epitaxy. J Appl Phys 98(7):6. Article ID 073502
Tan ST, Chen BJ, Sun XW et al. (2005) Blueshift of optical band gap in ZnO thin films grown by metal-organic chemical-vapor deposition. J Appl Phys 98(1):5. Article ID 013505
Gadallah A-S, Nomenyo K, Couteau C, Rogers DJ, L´erondel G (2013) Stimulated emission from ZnO thin films with high optical gain and low loss. Appl Phys Lett 102(17):4. Article ID 171105
Wang QP, Zhang XJ, Wang GQ, Chen SH, Wu XH, Ma HL (2008) Influence of excitation light wavelength on the photoluminescence properties for ZnO films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Appl Surf Sci 254(16):5100–5104
Kim KC, Kim EK, Kim YS (2007) Growth and physical properties of sol–gel derived Co doped ZnO thin film. Superlattice Microstruct 42:246–250
Liu Z, Jin Z, Li W, Qiu J (2005) Preparation of ZnO porous thin films by sol–gel method using PEG template. Mater Lett 59(28):3620–3625
Swanepoel R (1983) Determination of the thickness and optical constants of amorphous silicon. J Phys E 16(12):1214
Manifacier JC, Gasiote J, Fillard JP (1976) A simple method for the determination of the optical constants n, k and the thickness of a weakly absorbing thin film. J Phys E 9:1002
Abdel-Galil A, Balboul MR, Atta A, Yahia IS, Sharaf A (2014) Preparation, structural and optical characterization of nanocrystalline CdS thin film. Phys B 447:35–41
Connell GAN, Lewis AJ (1973) Comments on the evidence for sharp and gradual optical absorption edges in amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi B 60:291
Tauc J, Menth A (1972) States in the gap. J Non Cryst Solids 8:569
Mott NF, Davis EA (1979) Electronic process in non-crystalline materials. Calendron Press, Oxford
DrDidomenico Jr M, Wemple SH (1969) Oxygen‐octahedra ferroelectrics. I. Theory of electro‐optical and nonlinear optical effects. J Appl Phys 40:720
Wemple SH, DiDomenico Jr M (1971) Behavior of the electronic dielectric constant in covalent and ionic materials. Phys Rev B 3:1338
Ravangave LS, Biradar UV (2013) Study of optical parameters of chemical bath deposited Cd1-xZnxS thin films. Glob Res Anal 2(1):185–188
Bell RJ, Ordal MA, Alexender RW (1985) Equations linking different sets of optical properties for nonmagnetic materials. Appl Opt 24(22):3680–3682
Han MY, Huang H, Chew CH, Gan LM, Zhang XJ, Ji W (1998) Large nonlinear absorption in coated Ag2S/CdS nanoparticles by inverse microemulsion. J Phys Chem B 102(11):1884–1887
Pankove JI (1975) Optical processes in semiconductors. Dover Publications Inc, New York, p 91
Yakuphanoglu F, Cukurovali A, Yilmaz I (2005) Refractive index and optical absorption properties of the complexes of a cyclobutane containing thiazolyl hydrazone ligand. Opt Mater 27(8):1363–1368
Nabeel Bakr A, Funde AM, Waman VS, Kamble MM, Hawaldar RR, Amalnerkar DP, Gosavi SR, Jadkar SR (2011) Determination of the optical parameters of a-Si:H thin films deposited by hot wire–chemical vapour deposition technique using transmission spectrum only. Pramana 76(3):519–531
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farrag, AG., Balboul, M.R. Nano ZnO thin films synthesis by sol–gel spin coating method as a transparent layer for solar cell applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 82, 269–279 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4277-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4277-8