Abstract
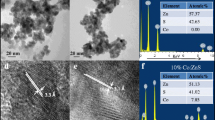
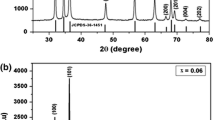
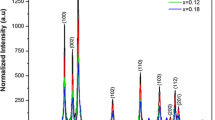
We have investigated the consequences of cobalt (Co) incorporation with different doping concentrations (0, 2, 4 and 6 %) on structural, optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. The results of X-ray diffraction spectra (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of single particle, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) authenticate the substitution of cobalt and hexagonal crystal structure without any secondary phase formation of all the samples under investigation. The ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) absorption study indicates that increase in Co concentration improves the visible region absorption (550–700 nm). The absorption edge of Co-doped ZnO shifts towards visible region with increase in Co concentration. The band gap of samples shows a red shift with increase in Co percentage. The photoluminescence (PL) study of the samples indicates that Co doping shifts the intense peak position of ZnO from violet to blue colour. The weak emission peak at 572 nm is also observed in all the samples. The emission is represented by chromaticity diagram. The room temperature magnetic properties have been studied using vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The room temperature magnetisation curve shows that an increase in Co concentration increases the linear behaviour of M–H loop. The magnetic susceptibility results indicate that all the samples have Curie–Weiss behaviour. The coercive field (Hc) and the remanence magnetisation (Mr) increase with Co doping concentration.
Graphical Abstract
Fig. M–H curve of pure and cobalt-doped ZnO nanoparticles at 300 K. Inset (a) shows absorption spectra, and inset (b) shows the emission spectra of Zn1−x Co x O nanoparticles.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dolea BN, Mote VD, Huse VR, Purushotham Y, Lande MK, Jadhav KM, Shah SS (2011) Structural studies of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles. Curr Appl Phys 11:762–766
Bououdina M, Omri K, Hilo ME, Amiri AE, Lemine OM, Alyamani A, Hlil EK, Lassri H, Mir LE (2014) Structural and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystals. Physica E 56:107–112
Rao GT, Stella RJ, Babu B, Ravindranadh K, Reddy CV, Shim J, Ravikumar RVSSN (2015) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Mn2+doped ZnO–CdS composite nanopowder. Mater Sci Eng B 201:72–78
Rekha K, Nirmala M, Nair MG, Anukaliani A (2010) Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of zinc oxide and manganese doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Phys B 405:3180–3185
Mandal SK, Das AK, Nath TK (2006) Temperature dependence of solubility limits of transition metals (Co, Mn, Fe, and Ni) in ZnO nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 89:144105
Kumar S, Basu S, Rana B, Barman A, Chatterjee S, Jha SN, Bhattacharyya D, Sahoo NK, Ghosh AK (2014) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of sol–gel derived ZnO: Co diluted magnetic semiconductor nanocrystals: an EXAFS study. J Mater Chem C 2:481
Lia M, Xu J, Chen X, Zhang X, Wu Y, Ping L, Niu X, Luo C, Lan Li (2012) Structural and optical properties of cobalt doped ZnO nanocrystals. Superlattices Microstruct 52:824–833
Abdullahi SS, Lu YK, Guner S, Kazan S, Kocaman B, Ndikilar CE (2015) Synthesis and characterization of Mn and Co codoped ZnO nanoparticles. Superlattices Microstruct 83:342–352
Tsogbadrakh N, Choi EA, Lee WJ, Chang KJ (2011) Hole doping effect on ferromagnetism in Mn-doped ZnO nanowires. Curr Appl Phys 11:236–240
Sato-Berru RY, Vazquez-Olmos A, Fernandez-Osorio AL, Sotres-Martınez S (2007) Micro-Raman investigation of transition-metal-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Raman Spectrosc 38:1073–1076
Gu F, Wang SF, Lu MK, Zhou GJ, Xu D, Yuan DR (2004) Structure evaluation and highly enhanced luminescence of Dy3+doped ZnO nanocrystals by Li+ doping via combustion method. Langmuir 20:3528–3531
Jadwisienczak WM, Lozykowski HJ, Xu A, Patel B (2002) Visible emission from ZnO doped with rare-earth ions. J Electron Mater 31:776–784
Li H, Zhang Z, Huang J, Liu R, Wang Q (2013) Optical and structural analysis of rare earth and Li co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 550:526–530
Basu S, Inamdar DY, Mahamuni S, Chakrabarti A, Kamal C, Kumar GRS, Jha N, Bhattacharyya D (2014) Local structure investigation of cobalt and manganese doped ZnO nanocrystals and its correlation with magnetic properties. J Phys Chem C118:9154–9164
Martínez B, Sandiumenge F, Ll Balcells (2005) Structure and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 72:165202
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH, Lee CG (2012) Doping effects of Co2+ ions on structural and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Microelectron Eng 89:129–132
Rao CNR, Deepak FL (2005) Absence of ferromagnetism in Mn- and Co-doped ZnO. J Mater Chem 15:573–578
Sato K, Katayama-Yoshida H (2000) Materials design for transparent ferromagnets with ZnO-based magnetic semiconductors. Jpn J Appl Phys 2(39):L555
Jalbout AF, Chen H, Whittenburg SL (2002) Monte Carlo simulation on the indirect exchange interactions of Co-doped ZnO film. Appl Phys Lett 81:2217
Zia A, Shah NA, Ahmed S, Khan EU (2014) The influence of cobalt on the physical properties of ZnO nanostructures. Phys Scr 89:105802
Arshad M, Azam A, Ahmed AS, Mollah S, Naqvi AH (2011) Effect of Co substitution on the structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel route. J Alloys Compd 509:8378–8381
Gandhi V, Ganesan R, Syedahamed HHA, Thaiyan M (2014) Effect of cobalt doping on structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation. Method J Phys Chem C118:9715–9725
Moussa H, Merlin C, Dezanet C, Balan L, Medjahdi G, Ben-Attia M, Schneider R (2016) Trace amounts of Cu2+ ions influence ROS production and cytotoxicity of ZnO quantum dots. J Hazard Mater 304:532–542
Ponnusamy R, Sivasubramanian D, Sreekanth P, Gandhiraj V, Philip R, Bhalerao GM (2015) Nonlinear optical interactions of Co: ZnO nanoparticles in continuous and pulsed mode of operations. RSC Adv 5:80756–80765
Ansari SA, Nisar A, Fatma B, Khan W, Naqvi AH (2012) Investigation on structural, optical and dielectric properties of Co doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by gel-combustion route. Mater Sci Eng B 177:428–435
Yan Q, Chen JZ, Tu MJ (2003) Study on voltage gradient and microstructure of ZnO varistor doped with La2O3. J Rare Earths 21:142
Zhou H, Yi D, Yu Z, Xiao L, Li J (2007) Preparation of aluminum doped zinc oxide films and the study of their microstructure, electrical and optical properties. Thin Solid Films 515:6909
Djaja NF, Montja DA, Saleh R (2013) The effect of Co incorporation into ZnO nanoparticles. Adv Mater Phys Chem 3:33–41
Kumar S, Asokan K, Singh RK, Chatterjee S, Kanjila D, Ghosh AK (2014) Investigations on structural and optical properties of ZnO and ZnO: Co nanoparticles under dense electronic excitations. RSC Adv 4:62123–62131
Hernández A, Maya L, Sánchez-Mora E, Sánchez EM (2007) Sol–gel synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of mixed Oxide ZnO–Fe2O3. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 42(1):71–78
Shafique MA, Shah SA, Nafees M, Rasheed K, Ahmad R (2012) Effect of doping concentration on absorbance, structural, and magnetic properties of cobalt-doped ZnO nano-crystallites. Int Nano Lett 2:31
Srinatha N, Nair KGM, Angadi B (2015) Microstructure, electronic structure and optical properties of combustion synthesized Co doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys B 474:97–104
Ramachandran S, Tiwari A, Narayan J (2004) Zn0.9Co0.1O-based diluted magnetic semiconducting thin films. Appl Phys Lett 84(25):5255–5257
Liu XC, Shi EW, Chen ZZ, Zhang HW, Song LX, Wang H, Yao SD (2006) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO films. J Cryst Growth 296:135–140
Shatnawi M, Alsmadi AM, Bsoul I, Salameh B, Alna’washi GA, Al-Dweri F, EI Akkad F (2016) Magnetic and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanocrystalline particles. J Alloys Compd 655:244–252
He R, Tan B, Ton-Hhat C, Phillips M, Tsuzuki T (2013) Physical structure and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation. J Nanoparticle Res 15:2030
Yang H, Nie S (2009) Preparation and characterization of Co-doped ZnO nanomaterials. Mater Chem Phys 114:279–282
Wang XL, Luan CY, Shao Q, Pruna A, Leung CW, Lortz R, Zapien JA, Ruotolo A (2013) Effect of the magnetic order on the room-temperature band-gap of Mn-doped ZnO thin films. Appl Phys Lett 102:102112
Hammad TM, Salem JK, Harrison RG (2013) Structure, optical properties and synthesis of Co-doped ZnO superstructures. Appl Nanosci 3:133–139
Kumar MA, Muthukumaran S (2015) Electrical, dielectric, photoluminescence and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles co-doped with Co and Cu. J Magn Magn Mater 374:61–66
Antony J, Pendyala S, Sharma A, Chen XB, Morrison J, Bergman L, Qiang Y (2005) Room temperature ferromagnetic and ultraviolet optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanocluster films. J Appl Phys 97:10D307-1
Kataoka T, Yamazaki Y, Sakamoto Y, Fujimori A, Chang F-H, Lin H-J, Huang DJ, Chen CT, Tanaka A, Mandal SK, Nath TK, Karmakar D, Dasgupta I (2010) Surface- and bulk-sensitive X-ray absorption study of the valence states of Mn and Co ions in Zn1−2x Mn x Co x O nanoparticles Appl. Phys Lett 96:252502
Kong YC, Yu DP, Zhang B, Fang SQ, Feng W (2001) Ultraviolet-emitting ZnO nanowires synthesized by a physical vapor deposition approach. Appl Phys Lett 78:407
Pal B, Giri PK (2010) High temperature ferromagnetism and optical properties of Co doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 108:084322
Pearton SJ, Heo WH, Ivill M, Norton DP, Steiner T (2004) Dilute magnetic semiconducting oxides. Semicond Sci Technol 19:R59
Ghosh CK, Chattopadhyay KK, Mitra MK (2007) Effect of Co doping on the static dielectric constant of ZnO nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 101:124911
Wang JB, Huang GJ, Zhong XL, Sun LZ, Zhou YC, Liu EH (2006) Raman scattering and high temperature ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 88:252502
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (PK) acknowledges the financial support from the Ministry of Human Resources and Development (MHRD) in the form of teaching assistantship. The authors are thankful to Prof. O. N. Srivastav and Prof. S. B. Rai, Department of Physics, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India, for providing the TEM and UV characterisation facilities, respectively. We are also thankful to Department of Pharmaceutics, IIT (BHU), for FT-IR characterisation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Pandey, P.C. Investigations on absorption, photoluminescence and magnetic properties of ZnO: Co nanoparticles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 80, 342–352 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4119-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4119-8