Abstract
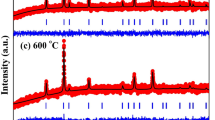
Single phase cobalt ferrite and chromium-substituted cobalt ferrite magneto-ceramic nano-powders are prepared by sol–gel self-combustion method. Chromium substitution is made within in the range of 10 mol% of iron in the cobalt ferrite powder. The XRD analysis of the prepared samples confirms the formation of single-phase nano-particles. Chromium substitution effect on the magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrite nano-powders (in pellet form with high porosity) have been discussed. The effects are attributed to the mismatch between the magnetic moments of chromium and iron ions. In this paper we show that self-combustion method, without having to change the pH of precursor, is a simple and viable technique to synthesize cobalt ferrite nano-powders. Chromium substitution helps to tune the magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite. From AC dielectric permittivity analysis we observe that chromium substitution suppresses the small electrical relaxation peak at 1 MHz frequency of cobalt ferrite. This behavior can find application in magnetic storage devices.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawatzky GA, Van der Woude F, Morrish AH (1968) J Appl Phys 39:1204
Mohapatra S (2011) Monodisperse mesoporous cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis and application in targeted delivery of antitumor drugs. J Mater Chem 21:9185–9193
Bate G (1975) In: Craik DJ (ed) Magnetic oxides, part 2. Wiley, New York, p 703
Sharrock MP (1989) IEEE Trans Magn 25:4374
Abe M, Gomi M (1990) Magneto-optical recording on garnet films. J Magn Magn Mater 84(3):222–228
Ramos AV, Santos TS, Miao GX, Guittet M-J, Moussy J-B, Moodera JS (2008) Phys Rev B 78:180402
Uday Bhasker S et al (2012) Preparation and characterization of cobalt magnesium nano ferrites using auto-combustion method. Adv Mater Res 584:280
Ranvah N, Melikhov Y, Nlebedim IC, Jiles DC, Snyder JE, Moses AJ, Williams PI (2009) J Appl Phys 105:07A518
Paulsen JA, Lo CCH, Snyder JE, Ring AP, Jones LL, Jiles DC (2003) IEEE Trans Magn 39(5):3316
Srivastava M, Ojha AK, Chaubey S, Sharma PK, Pandey AC (2010) Mater Sci Eng B 175:14
Reddy GK, Gunasekara K, Boolchand P, Smirniotis PG (2011) J Phys Chem C 115:920–930
Singhal S (2012) J Mol Struct 1012:182–188
Hankare PP, Sankpal UB, Patil RP, Mulla IS, Lokhande PD, Gajbhiye NS (2009) J Alloy Compd 485:798–801
Cedeño-Mattei Y (2007) Optimization of magnetic properties in cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. In: ENS’07 Paris, France
Rezlescu N, Rezlescu E, Pasnicu C, Craus ML (1994) Effects of rare-earth ions on some properties of a nickel-zincferrite. J Phys Condens Matter 234:114–117 (6:5716)
Zhou XD, Huebner W (2001) Appl Phys Lett 79:3512
Rajendran M et al (2001) J Magn Magn Mater 232:71–83
Templeton TL, Arrott AS, Curzon AE, Gee MA, Li X-Z, Yoshida Y, Schurer PJ, LaCombe JL (1993) J Appl Phys 73:6728–6730
Berkowitz AE, Lahut JA, VanBuren CE (1980) Properties of magnetic fluid particles. IEEE Trans Magn 16(2):184–190
Nogues J, Sort J, Langlias V, Skumryev V, Suriñach S, Muñoz JS, Baró MD (2005) Exchange bias in nanostructures. Phys Rep 422(3):65–117
Berkowitz AE, Lahut JA, Jacobs IS, Levinson LM, Forester DW (1975) Spin pinning at ferrite-organic interfaces. Phys Rev Lett 34(10):594–597
Ferreira JM (1988) Effect of Cr2+ ions on magnetic anisotropy of chromium chalcogenide spinels. QUIMICANOVA 11(1):107-111
Wu CC, Kumarkrishna S, Mason TO (1981) Thermopower composition dependence in ferrospinels. J Solid State Chem 37:144-150
Verwey EJW, Haymann PW, Romejin FC (1947) Physical properties and cation arrangement of oxides with spinel structures. II. Electronic conductivity. J Chem Phys 15:181-187
Maxwell JC (1982) A treatise on electricity and magnetism. Clarendon Press, Oxford, p 328
Wagner KW (1913) Zur Theorie der unvollkommenen Dielektrika. Ann Phys 40:817-855
Koop’s CG (1951) On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys Rev 83:121–124
Gonsalves LR Synthesis, characterization and solid state studies of Co–Zn and Co–Ni ferrites: a comparative study of the bulk with the nano. Ph.D. Thesis. http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/handle/10603/12690
Krishna Surendra M (2011) Magnetic and dielectric properties study of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 1368. doi:10.1557/opl.2011.1281
Zhou J-P (2010) Dielectric and magnetic properties of ZnO-doped cobalt ferrite. J Ceram Process Res 11(2):263-272
Jeppson P (2006) Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Achieving the superpapramagnetic limit by chemical reduction. J Appl Phys 100(11):4324
M Rajendran (2001) Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline CoFe2O4 powders prepared at room temperature: variation with crystallite size. J Magn Magn Mater 232:71-83
Acknowledgments
One of the author, S. Uday Bhasker would like to thank R.K. Kotnala from NPL New Delhi India for VSM and Dielectric measurements. M.V.R.R. thanks UGC, New Delhi for providing financial assistance in the form of project [UGC-MRP, F.No.41-907/2012 (sr)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uday Bhasker, S., Ramana Reddy, M.V. Effect of chromium substitution on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of magneto-ceramic cobalt ferrite nano-particles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 73, 396–402 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3546-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3546-7