Abstract
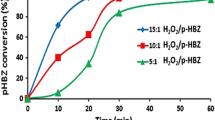
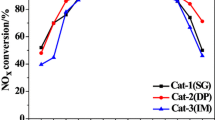
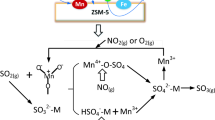
This study deals with the degradation of phenol over Pd–Fe/TiO2 catalysts at mild conditions in the presence of in situ generated H2O2 from oxygen and formic acid. This catalytic system demonstrated interesting ability to oxidize phenol by Fenton process in a one-pot reaction without the addition of ferrous ion. Lower Pd content catalysts, despite producing a higher hydrogen peroxide amount for bulk purposes, did not reach the same efficiency as the 5Pd–5Fe catalyst in phenol degradation. A close interaction between Pd and iron oxide species is necessary to obtain high active catalysts. These results highlight the advantage of in situ generation of H2O2, for oxidation reactions with respect to conventional Fenton process.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pignatello JJ, Oliveros E, Mackay A (2006) Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 36:1–84
Pera-Titus M, Garcia-Molina V, Banos MA, Gimenez J, Esplugas S (2004) Appl Catal B 47:219–256
Duesterberg CK, Cooper WJ, Waite TD (2005) Environ Sci Technol 39:5052–5058
Zazo JA, Casas JA, Mohedano AF, Gilarranz MA, Rodriaguez JJ (2005) Environ Sci Technol 39:9295–9302
Brillas E, Sires I, Oturan M (2009) Chem Rev 109:6570–6631
Alnaizy R, Akgerman A (2000) Adv Environ Res 4:233–244
Gonzalez-Olmos R, Roland U, Taufer H, Kopinke F-D, Georgi A (2009) Appl Catal B 89:356–364
Hartmann M, Kullmann S, Keller H (2010) J Mater Chem 20:9002–9017
Villa A, Janjic N, Spontoni P, Wang D, Sheng SD, Prati L (2009) Appl Catal A 364:221–228
Campos-Martin JM, Blanco-Brieva G, Fierro JLG (2006) Angew Chem Int Ed 45:6962–6984
Burch R, Ellis PR (2003) Appl Catal B 42:203–211
Yalfani MS, Contreras S, Medina F, Sueiras JE (2008) Chem Commun 33:3885–3887
Yalfani MS, Contreras S, Llorca J, Dominguez M, Sueiras JE, Medina F (2010) Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:14673–14676
Yalfani MS, Contreras S, Medina F, Sueiras JE (2009) Appl Catal B 89:519–526
Meng F, Li J, Cushing SK, Zhi M, Wu N (2013) J Am Chem Soc 135:10286–10289
Meng F, Li J, Cushing SK, Bright J, Zhi M, Rowley JD, Hong Z, Manivannan A, Bristow AD, Wu N (2013) ACS Catal 3:746–751
Bravo-Suarez JJ, Bando KK, Akita T, Fujitani T, Oyama TJ (2008) Chem Commun 28:3272–3274
Contreras S, Yalfani MS, Medina F, Sueiras JE (2011) Water Sci Technol 63:2017–2024
Schaub R, Wahlström E, Ronnau A, Lægsgaard E, Stensgaard I, Besenbacher F (2003) Science 299(5605):377–379
Pinna F, Menegazzo F, Signoretto M, Canton P, Fagherazzi G, Pernicone N (2001) Appl Catal A 219:195–200
Lieske H, Volter J (1985) J Phys Chem 89:1841–1842
Berry FJ, Smart LE, Sai Prasad PS, Lingaiah N, Kanta Rao P (2000) Appl Catal A 204:191–201
Xu GP, Zhu YX, Ma J, Yan HG, Xie YC (1997) Stud Surf Sci Catal 112:333–338
Pinna F, Selva M, Signoretto M, Strukul G, Boccuzzi F, Benedetti A, Canton P, Fagherazzi G (1994) J Catal 150:356–367
Leitz G, Nimz M, Volter J, Lazar K, Guczi L (1988) Appl Catal 45:71–83
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge Mohammad S. Yalfani from the Catalytic Center of Aachen University (Germany). We express our appreciation for his valuable discussion and contribution. Mercè Moncusi Mercadé and Mariana Stefanova Stankova from Universitat Rovira i Virgili (Spain) are acknowledged for TEM measurements. F. Medina also acknowledges ICREA Academia award from Generalitat de Catalunya.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Triki, M., Contreras, S. & Medina, F. Pd–Fe/TiO2 catalysts for phenol degradation with in situ generated H2O2 . J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 71, 96–101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3333-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3333-5