Abstract
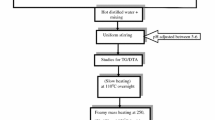
LiMn2O4 and LiZnxPryMn2−x−yO4 (x = 0.10–0.24; y = 0.01–0.10) powders have been synthesized by sol–gel method using palmitic acid as chelating agent. The synthesized samples have been subjected to thermo gravimetric and differential thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX). The sol–gel route bestows low calcination temperature, shorter heating time, high purity, good control over stoichiometry, small particle size, high surface area, good surface morphology and better homogeneity, The XRD patterns reveal high degree of crystallinity and better phase purity. SEM and TEM images exhibit nano-sized nature particles with good agglomeration. EDAX peaks of Zn, Pr, Mn and O have been confirmed in actual compositions of LiMn2O4 and LiZnxPryMn2−x−yO4. Charge–discharge studies of pristine spinel LiMn2O4 heated at 850 °C delivers discharge capacity of 132 mA h g−1 corresponding to columbic efficiency of 73 % during the first cycle. At the end of 10th cycles, it delivers maximum discharge capacity of 112 mA h g−1 with columbic efficiency of 70 % and capacity fade of 0.15 mA h g−1 cycle−1 over the investigated 10 cycles. Inter alia, all dopants concentrations, LiZn0.10Pr0.10Mn1.80O4 exhibits the better cycling performance (1st cycle discharge capacity: 130 mA h g−1 comparing to undoped spinel 132 mA h g−1) corresponding to columbic efficiency of 73 % with capacity fade of 0.12 mA h g−1 cycle−1.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon JM, McKinnon WR, Coowar F, Bowner TN, Amatucci G, Guyomard D (1994) J Electrochem Soc 141:1431
Gummow RJ, de Kock A, Thackeray MM (1994) Solid State Ion 69:67
Thackeray MM, de Kock A, Rossouw MH, Liles D, Bittihn R, Hoge DJ (1992) Electrochem Soc 139:366
Xia Y, Yoshio M (1977) J Electrochem Soc 144:2600
Pistoia G, Antonini A, Rosati R, Zane D (1996) Electrochim Acta 41:2689
Jang DH, Shin JY, Oh SM (1996) J Electrochem Soc 143:2211
Yamada A (1996) J Solid State Chem 122:165
Ohuzuku T, Takeda S, Iwanaga M (1999) J Power Sour 90:92
Song D, Ikuta H, Uchida T, Wakihara M (1999) Solid State Ion 117:156
Javed Iqbal M, Zahoor S (2007) J Power Sour 165:397
Lee JH, Hong JK, Jang DH, Sun YK, Oh SM (2000) J Power Sour 89:14
Park SH, Park KS, Sun YK, Nahm KS (2000) J Electrochem Soc 147:2121
Bach S, Henry M, Baffier N, Livage J (1990) J Solid State Chem 88:333
Perreira-Ramos JP (1995) J Power Sour 54:126
Barboux P, Tarascon JM, Shokoohi FK (1991) J Solid State Chem 94:196
Pechini MP (1967) US patent no. 3 330:697
Thirunakaran R, Kalaiselvi N, Periasamy P, Rameshbabu B, Renganathan NG, Muniyandi N (2001) Ionics 7:191
Guo SH, Zhang SC, He XM, Pu WH, Jiang CY, Wan CR (2008) J Electrochem Soc 155:A760
Thirunakaran R, Sivashanmugam A, Gopukumar S, Dunnill Charles W, Gregory Duncan H (2008) J Phys Chem Solids 69:2092
Veluchamy A, Ikuta H, Wakihara M (2001) Solid State Ion 143:171
Fey GTK, Lu CZ, Prem Kumar T (2003) Mater Chem Phys 80:318
Thirunakaran R, Sivashanmugam A, Gopukumar S, Rajalakshimi R (2009) J Power Sour 187:574
Thirunakaran R, Kim K-T, Kang YM, Seo CY, Young-Lee J (2004) J Power Sour 137:104
Thirunakaran R, Kim K-T, Kang YM, Seo CY, Young-Lee J (2005) Mater Res Bull 40:186
Thirunakaran R, Sivashanmugam A, Gopukumar S, Dunnill Charles W, Gregory Duncan H (2008) J Mater Proc Tech 208:531
Thirunakaran R, Sivashanmugam A, Gopukumar S, Dunnill Charles W, Gregory Duncan H (2008) Mater Res Bull 43:2129
Wen W, Kumarasamy B, Mukerjee S, Auinet M, Ein-Eli Y (2005) J Electrochem Soc 152:A1902
Arumugam D, Kalaigan GP, Vediappan K, Lee CW (2010) Electrochim Acta 55:8444
Lee YJ, Park S-H, Eng C, Parise JB, Clare P (2002) Grey Chem Mater 14(1):205
Zhong P, Huguo-Rong, Xiang-Yang Z, Ye-Xiang L (2002) Battery Bimon Chin J. doi:CNKI-ISSN.1001-1579.0:04-000
Xie Y, Yang R, Lan Yan L, Qi KD, He P (2007) J Power Sour 168:272
Iqbal MJ, Ahmad Z (2008) J Power Sour 179:769
Murugan AV, Kale BB, Kunde LB, Kulkarni AV (2006) J Solid State Electrochem 10:109
Kalyani P, Kalaiselvi N, Renganathan NG (2005) Mater Chem Phys 90:202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thirunakaran, R. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of duo doped spinels (zinc and praseodymium) for use in lithium rechargeable batteries. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 69, 397–406 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-3233-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-3233-0