Abstract
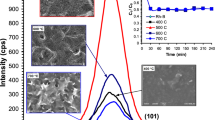
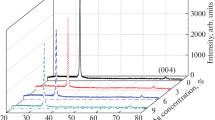
High-quality c-axis oriented Al and Er co-doped ZnO films were prepared on the quartz glasses by sol–gel method. In order to obtain the optimal processing parameters for the growth of the oriented film, an L16 (45) orthogonal experimental design was chosen. The experimental results show the rank of 5-factors as follows: Er at.% > the number of coating layer > annealing temperature > Al at.% > the concentration of the sol. The Al and Er co-doped film prepared using the optimal parameters exhibits the preferential orientation along the c-axis perpendicular to the substrate surface. In addition, the structural, morphological and optical properties of the films were studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and UV–visible spectrophotometer, respectively. The photoluminescence spectra were also used to characterize the luminescence properties of the samples. It is found that when ZnO was co-doped with 7 % Al and 1.5 % Er, the blue emission centered at 465 nm disappears and the green emission centered at 547 nm increases with a blue shift, resulted from the rapid reducing of the interstitial Zn defect, and increasing of the oxygen defects and vacancies caused by Al3+ and Er3+ dopants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang XD, Zhou J, Song JH, Liu J, Xu NS, Wang ZL (2006) Piezoelectric field effect transistor and nanoforce sensor based on a single ZnO nanowire. Nano Lett 6:2768–2772
Wang XD, Summers CJ, Wang ZL (2004) Large-scale hexagonal-patterned growth of aligned ZnO nanorods for nano-optoelectronics and nanosensor arrays. Nano Lett 4:423–426
Kong JZ, Li AD, Zhai HF, Gong YP, Wu D (2009) Preparation, characterization of the Ta-doped ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity under visible-light illumination. J Solid State Chem 182:2061–2067
Colder H, Guilmeau E, Harnois C, Marinel S, Retoux R, Savary E (2011) Preparation of Ni-doped ZnO ceramics for thermoelectric applications. J Eur Cearm Soc 31:2957–2963
Jia XH, Fan HQ, Afzaal M, Wu XY, O’Brien P (2011) Solid state synthesis of tin-doped ZnO at room temperature: characterization and its enhanced gas sensing and photocatalytic properties. J Hazard Mater 193:194–199
Lee JS, Cha SN, Kim JM, Nam HW, Lee SH, Ko WB, Wang KL, Park JG, Hong JP (2011) P-type conduction characteristics of lithium-doped ZnO nanowires. Adv Mater 23:4183–4187
Li WW, Yu WL, Wu JD, Gan J, Zhu M, Hu ZG, Chu JH (2011) Structural, electronic, and optical properties of nanocrystalline as-doped ZnO films on quartz substrates determined by Raman scattering and infrared to ultraviolet spectra. Thin Solid Films 519:8166–8172
Kinemuchi Y, Nakano H, Kaga H, Tanaka S, Uematsu K, Watari K (2011) Microstructural evidence of hall mobility anisotropy in c-axis textured Al-doped ZnO. J Am Ceram Soc 94:2339–2343
Kobayashi J, Ohashi N, Sekiwa H, Sakaguchi I, Miyamoto M, Wada Y, Adachi Y, Matsumoto K, Haneda H (2009) Properties of gallium- and aluminum-doped bulk ZnO obtained from single-crystals grown by liquid phase epitaxy. J Cryst Growth 311:4408–4413
Benhaliliba M, Benouis CE, Aida MS, Juarez AS, Yakuphanoglu F, Silver AT (2010) A comparative study on structural, optical, photoconductivity properties of In and Al doped ZnO thin films grown onto glass and FTO substrates grown by spray pyrolysis process. J Alloy Compd 506:548–553
Rao TP, Kumar MCS (2010) Physical properties of Ga-doped ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis. J Alloy Compd 506:788–793
Liu XC, Chen ZZ, Chen BY, Shi EW, Liao DQ (2010) Structural, optical and electrical properties of Ga-doped and (Ga, Co)-codoped ZnO films. J Cryst Growth 312:2871–2875
Peng LP, Fang L, Yang XF, Li YJ, Huang QL, Wu F, Kong CY (2009) Effect of annealing temperature on the structure and optical properties of In-doped ZnO thin films. J Alloy Compd 484:575–579
Aleman B, Fernandez P, Piqueras J (2010) Dense vertical nanoplates arrays and nanobelts of indium doped ZnO grown by thermal treatment of ZnS-In2O3 powders. J Cryst Growth 312:3117–3121
Zhao J, Xie S, Han S, Yang Z, Ye L, Yang T (2000) Organic light-emitting diodes with AZO films as electrodes. Synth Met 114:251–254
Shi WS, Agyeman O, Xu CN (2002) Enhancement of the light emissions from zinc oxide films by controlling the post-treatment ambient. J Appl Phys 91:5640–5644
Zhai J, Zhang L, Yao X (2000) The dielectric properties and optical propagation loss of c-axis oriented ZnO thin films deposited by sol–gel process. Ceram Int 26:883–885
Lee HW, Lau SP, Wang YG, Tse KY, Hng HH, Tay BK (2004) Structural, electrical and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared by filtered cathodic vacuum arc technique. J Cryst Growth 268:596–601
Dghoughi L, Ouachtari F, Addou M, Elidrissi B, Erguig H, Rmili A, Bouaoud A (2010) The effect of Al-doping on the structural, optical, electrical and cathodoluminescence properties of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Phys B 405:2277–2282
Kuo SY, Chen WC, Lai FI, Cheng CP, Kuo HC, Wang SC, Hsieh WF (2006) Effects of doping concentration and annealing temperature on properties of highly-oriented Al-doped ZnO films. J Cryst Growth 287:78–84
Lamrani MA, Addou M, Sofiani Z, Sahraoui B, Ebothé J, El Hichou A, Fellahi N, Bernède JC, Dounia R (2007) Cathodoluminescent and nonlinear optical properties of undoped and erbium doped nanostructured ZnO films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Opt Commun 277:196–201
Chen Y, Xu XL (2011) Effect of oxygen deficiency on optical bandgap shift in Er-doped ZnO thin films. Phys B 406:3121–3124
Zhang XH, Chen J, Wu YP, Xie ZX, Kang JY, Zheng LS (2011) A simple route to fabricate high sensibility gas sensors based on erbium doped ZnO nanocrystals. Colloid Surface A 384:580–584
Taguchi G, Konishi S (1987) Taguchi methods, orthogonal arrays and linear graphs, Tools for quality engineering. American Supplier Institute, pp 35–38
Taguchi G (1993) Taguchi onrobust technology development methods. ASME, NewYork, pp 1–4
Xu LH, Li XY, Chen YL, Xu F (2011) Structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method with different thickness. Appl Surf Sci 257:4031–4037
Koyama T, Fouda AN, Shibata N, Chichibu SF (2007) Effects of the high-temperature-annealed self-buffer layer on the improved properties of ZnO epilayers grown by helicon-wave-excited-plasma sputtering epitaxy on a-plane sapphire substrates. J Appl Phys 102:073505
Jiang X, Jia CL, Szyszka B (2002) Manufacture of specific structure of aluminum-doped zinc oxide films by patterning the substrate surface. Appl Phys Lett 80:3090–3093
Samaele N, Amornpitoksuk P, Suwanboon S (2010) Effect of pH on the morphology and optical properties of modified ZnO particles by SDS via a precipitation method. Powder Technol 203:243–247
Kong JZ, Li AD, Zhai HF, Li H, Yan QY, Ma J, Wu D (2009) Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic properties of ZnTiO3 powders. J Hazard Mater 171:918–923
Zhang CY (2010) High-quality oriented ZnO films grown by sol–gel process assisted with ZnO seed layer. J Phys Chem Solids 71:364–369
Zou JJ, Zhu B, Wang L, Zhang XW, Mi ZT (2008) Zn- and La-modified TiO2 photocatalysts for the isomerization of norbornadiene to quadricyclane. J Mol Catal A 286:63–69
Kong JZ, Li AD, Li XY, Zhai HF, Zhang WQ, Gong YP, Li H, Wu D (2010) Photo-degradation of methylene blue using Ta-doped ZnO nanoparticle. J Solid State Chem 183:1359–1364
Lyu SC, Zhang Y, Ruh H, Lee HJ, Shim HW, Suh EK, Lee CJ (2002) Low temperature growth and photoluminescence of well-aligned zinc oxide nanowires. Chem Phys Lett 363:134–138
Wu JJ, Liu SC (2002) Low-temperature growth of well-aligned ZnO nanorods by chemical vapor deposition. Adv Mater 14:215–218
Zeng H, Cai W, Liu P, Xu X, Zhou H, Klingshirn C, Kalt H (2008) ZnO-based hollow nanoparticles by selective etching: elimination and reconstruction of metal-semiconductor interface, improvement of blue emission and photocatalysis. ACS Nano 2:1661–1670
Zeng H, Duan G, Li Y, Yang S, Xu X, Cai W (2010) Blue luminescence of ZnO nanoparticles based on non-equilibrium processes: defect origins and emission controls. Adv Funct Mater 20:561–572
Gao M, Wu XN, Liu J, Liu WB (2011) The effect of heating rate on the structural and electrical properties of sol–gel derived Al-doped ZnO films. Appl Surf Sci 257:6919–6922
Miao L, Tanemura S, Tanemura M, Lau SP, Tay BK (2007) Thickness- dependent optical properties of ZnO thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 18:s343–s346
Wei XQ, Zhang ZG, Liu M, Chen CS, Sun G, Xue CS, Zhuang HZ, Man BY (2007) Annealing effect on the micro structure and photoluminescence of ZnO thin films. Mater Chem Phys 101:285–290
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the Weaponry Equipment Pre-research Foundation of China (08HK0206), and Opening Funds of The Key Laboratory of Thin Films of Jiangsu (KJS0833), Jiangsu Postdoctoral Science Research Foundation (1102056C). We would like to acknowledge them for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, JZ., Zhou, F., Wang, Z. et al. Preparation and optical properties of high-quality oriented of Al and Er co-doped ZnO thin films. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 63, 95–102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2768-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2768-9