Abstract
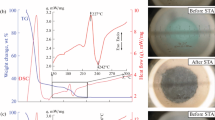
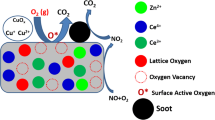
The binary phase, porous, nanocomposite xα-Fe/(1 − x)Ce0.9–K0.1–O (x = 0.05–0.2) catalysts and the catalyst-coated honeycomb ceramic device have been prepared by the citrate-gel thermal decomposition-reduction process and the sol–gel assisted dip-coating method, respectively. The nanocomposite of fluorite-type structure CeO2 nanoparticles about 18–51 nm and α-Fe nanoparticles about 32 nm is obtained at 600 °C for 2 h in a deoxidization atmosphere and the α-Fe in nanocomposite has the suppression effect on grain growth of CeO2. With Fe content increasing from 0.05 to 0.1, the specific surface area for the nanocomposites increases dramatically from about 4.4 to 43.0 m2/g, reaching a maximum value 57.7 m2/g at x = 0.15, and the pores vary from macropores to micro- or mesopores. Due to the presence of nano α-Fe, all the catalysts exhibit a very high soot catalytic activity, with the lowest T20 (255 °C) and T50 (291 °C) for the nanocomposite with x = 0.15, and it is confirmed by the bench test under practical diesel exhaust gases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russo N, Furfori S, Fino D, Saracco G, Specchia V (2008) Lanthanum cobaltite catalysts for diesel soot combustion. Appl Catal B-Environ 83:85–95
Reichert D, Bockhorn H, Kureti S (2010) Recent advances in the understanding of the direct conversion of soot and NO on Fe2O3 catalyst in diesel exhaust. Chimica oggi/Chem Today 28:51–53
Lim CB, Kusaba H, Einaga H, Teraoka Y (2011) Catalytic performance of supported precious metal catalysts for the combustion of diesel particulate matter. Catal Today 175:106–111
Kaneeda M, Iizuka H, Hiratsuka T, Shinotsuka N, Arai M (2009) Improvement of thermal stability of NO oxidation Pt/Al2O3 catalyst by addition of Pd. Appl Catal B-Environ 90:564–569
Van den Tillaart JAA, Leyrer J, Eckhoff S, Lox ES (1996) Effect of support oxide and noble metal precursor on the activity of automotive diesel catalysts. Appl Catal B-Environ 10:53–68
Bockhorn H, Kureti S, Reichert D (2007) Study on the mechanism of the catalytic conversion of NOx and soot into N2 and CO2 on Fe2O3 in diesel exhaust. Top Catal 42–43:283–286
Milt VG, Banús ED, Ulla MA, Miró EE (2008) Soot combustion and NOx adsorption on Co, Ba, K/ZrO2. Catal Today 133–135:435–440
Wu XD, Liang Q, Weng D, Lu ZX (2007) The catalytic activity of CuO–CeO2 mixed oxides for diesel soot oxidation with a NO/O2 mixture. Catal Commun 8:2110–2114
Gross MS, Ulla MA, Querini CA (2012) Diesel particulate matter combustion with CeO2 as catalyst. Part I: system characterization and reaction mechanism. J Mol Catal A-Chem 352:86–94
Meher SK, Ranga Rao G (2011) Tuning the morphology of CeO2 by counter anions under mild synthesis conditions and its catalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.09.050
Kockrick E, Schrage C, Grigas A, Geiger D, Kaskel S (2008) Synthesis and catalytic properties of microemulsion-derived cerium oxide nanoparticles. J Solid State Chem 181:1614–1620
Bassou B, Guilhaume N, Iojoiu EE, Farrusseng D, Lombaert K, Bianchi D, Mirodatos C (2010) High-throughput approach to the catalytic combustion of diesel soot II: screening of oxide-based catalysts. Catal Today 159:138–143
Muroyama H, Hano S, Matsui T, Eguchi K (2010) Catalytic soot combustion over CeO2-based oxides. Catal Today 153:133–135
Zhang YH, Zou XT, Sui L (2006) The effects of potassium halides on catalytic activities of CeO2–K based catalysts for diesel soot oxidation. Catal Commun 7:855–859
Reichenbach HM, An H, McGinn PJ (2003) Combinatorial synthesis and characterization of mixed metal oxides for soot combustion. Appl Catal B-Environ 44:347–354
Miró EE, Ravelli F, Ulla MA, Cornaglia LM, Querini CA (1999) Catalytic combustion of diesel soot on Co, K supported catalysts. Catal Today 53:631
Pisarello ML, Milt V, Peralta MA, Querini CA, Miró EE (2002) Simultaneous removal of soot and nitrogen oxides from diesel engine exhausts. Catal Today 75:465
Wang JQ, Zhang BY, Shen MQ, Wang J (2011) Effects of Fe-doping of ceria-based materials on their microstructural and dynamic oxygen storage and release properties. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 58:259–268
Pérez-Alonso FJ, Herranz T, Rojas S, Ojeda M, Granados ML, Terreros P, Fierro JLG (2007) Evolution of the bulk structure and surface species on Fe–Ce catalysts during the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Green Chem 9:663–670
Reichert D, Bockhorn H, Kureti S (2008) Study of the reaction of NO x and soot on Fe2O3 catalyst in excess of O2. Appl Catal B-Environ 80:248–259
Li L, Shen XQ, Wang P, Meng XF, Song FZ (2011) Soot capture and combustion for perovskite La–Mn–O based catalysts coated on honeycomb ceramic in practical diesel exhaust. Appl Surf Sci 257:9519–9524
Meng XX, He FL, Shen XQ, Xiang J, Wang P (2011) Nanocrystalline La1-xKxFeO3 (x = 0 − 0.4) oxides for catalytic removal of soot from practical diesel exhaust emission. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:11037–11042
An HM, Kilroy C, McGinn PJ (2004) Combinatorial synthesis and characterization of alkali metal doped oxides for diesel soot combustion. Catal Today 98:423–429
Hirano T, Tosho T, Watanabe T, Akiyama T (2009) Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis with post-heat treatment of La1-xSrxFeO3 (x = 0 − 1) perovskite as catalyst for soot combustion. J Alloy Compd 470:245–249
Fino D, Russo N, Badini C, Saracco G, Specchia V (2003) Effect of active species mobility on soot-combustion over Cs–V catalysts. AIChE J 49:2173–2180
Gong CR, Song CL, Pei YQ, Lv G, Fan GL (2008) Synthesis of La0.9K0.1CoO3 fibers and the catalytic properties for diesel soot removal. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:4374–4378
Zhu TL, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (2001) Catalytic partial oxidation of methane to synthesis gas over Ni–CeO2. Appl Catal A-Gen 208:403–417
Gross MS, Ulla MA, Querini CA (2009) Catalytic oxidation of diesel soot: new characterization and kinetic evidence related to the reaction mechanism on K/CeO2 catalyst. Appl Catal A-Gen 360:81–88
Shimokawa H, Kusaba H, Einaga H, Teraoka Y (2008) Effect of surface area of La–K–Mn–O perovskite catalysts on diesel particulate oxidation. Catal Today 139:8–14
Li XQ, Elliott DW, Zhang WX (2006) Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: materials and engineering aspects. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 31:111–122
Zhang ZL, Han D, Wei SJ, Zhang YX (2010) Determination of active site densities and mechanisms for soot combustion with O2 on Fe-doped CeO2 mixed oxides. J Catal 276:16–23
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50134020) and the Jiangsu Province’s Postgraduate Cultivation and Innovation Project (Grant No. CX10B-257Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, F., Meng, X., Shen, X. et al. Catalytic soot combustion of α-Fe/Ce–K–O nanocomposites via citrate-gel route. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 61, 551–557 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-011-2658-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-011-2658-6