Abstract
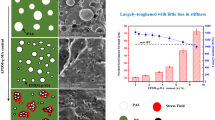
Silica packed epoxy networks are prepared in two steps via in situ, solvent free sol–gel processing of tetraethoxysilane in liquid epoxy monomer and curing the mixture with a flexible diamine afterwards. The influence of filler content and processing conditions on the mechanical properties and the fracture behavior is studied by means of the static mechanical analysis and AFM characterization of the pristine and the fractured polymer surfaces, and a mechanism to enhance polymer strength and toughness is proposed. The in–situ evolution and packing of silica nanostructures into epoxy networks influences the overall morphology and performance of polymers under high stress. It is found that smaller silica domains distributed at the molecular level cause efficient crack distribution by absorbing energy and thus improve the strength and toughness of silica packed epoxy polymers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Innocenzi P, Kidchob T, Yoko T (2005) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 35:225–235
Wang H, Han W, Tian H, Wang Y (2007) Mater Lett 59:94–99
Nazir T, Afzal A, Siddiqi HM, Ahmad Z, Dumon M (2010) Prog Org Coatings 69:101–106
Pascault JP, Williams RJJ (2010) Epoxy polymers: new materials and innovations. Wiley, Weinheim, pp 137–157
Afzal A, Siddiqi HM (2011) Polymer 52:1345–1355
Matejka L, Dukh O, Kolarik J (2000) Polymer 41:1449–1459
Benes H, Galy J, Gerard JF, Plestil J, Valette L (2011) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol. doi:10-1007/s10971-011-2534-4
Riegel B, Blittersdorf S, Kiefer W, Hofacker S, Muller M, Schottner G (1998) J Non–Cryst Solids 226:76–84
Innocenzi P, Brusatin G, Gugliemi M, Bertani R (1999) Chem Mater 11:1672–1679
ASTM D882-10 (2010) Annual book of ASTM standards. Am Soc Testing Mater 08.01 (PA)
Matejka L, Dukh O, Hlavatà D, Meissner B, Brus J (2001) Macromolecules 34:6904–6914
Lu SR, Zhang HL, Zhao CX, Wang XY (2005) J Mater Sci 40:1079–1085
Chen C, Justice RS, Schaefer DW, Baur JW (2008) Polymer 49:3805–3815
Manjunatha CM, Johnsen BB, Kinloch AJ, Mohammed RD, Taylor AC, Sprenger S (2007) Polymer 48:530–541
Ma J, Mo MS, Du XS, Rosso P, Friedrich K, Kuan HC (2008) Polymer 49:3510–3523
Acknowledgments
The financial support by the URF, Quaid–i–Azam University is gratefully acknowledged. A.A is grateful to Prof. F. L. Dickert (University of Vienna, Austria) for providing the AFM facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afzal, A., Siddiqi, H.M., Mujahid, A. et al. AFM substantiation of the fracture behavior and mechanical properties of sol–gel derived silica packed epoxy networks. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 61, 44–48 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-011-2588-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-011-2588-3