Abstract
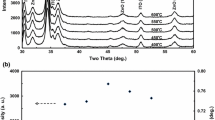
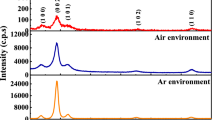
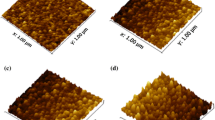
In this study, we investigated the effects of different heating processes on the structural, electrical and chemical properties of ZnO:Ga (GZO) films from the viewpoint of nucleation and growth behaviors. An infrared heating furnace and a traditional tube furnace were employed for the homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation of GZO films. XRD patterns demonstrated that the preferential growth orientation of both kinds of GZO films is still the (002) direction. XPS data implied that the infrared heating process enables more uniform distribution of the dopant material and retards the oxidization of gallium in grain boundary areas. At the same time, the textured crystallite might provide a free tunnel for oxygen diffusion. Thus, the activation of free charge carriers could be more efficient when the GZO films were annealed under vacuum. As a result, the samples annealed by the infrared heating furnace had a noticeably high carrier concentration. Although the mobility was slightly smaller than that of the samples annealed by the tube furnace, film resistivity dropped obviously in general.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Minami T (2008) Thin Solid Films 515:5822
Banerjee AN, Ghosh CK, Chattopadhyay KK, Minoura H, Sarkar AK, Akiba A, Kamiya A, Endo T (2006) Thin Solid Films 496:112
Ohyama M, Kozuka H, Yoko T (1997) Thin Solid Films 306:78
Natsume Y, Sakata H (2000) Thin Solid Films 372:30
Lin K, Chen Y-Y, Chou K-Y (2009) J Sol-gel Sci Techn 49:238
Lin K, Chen Y-Y (2009) J Sol-gel Sci Techn 51:215
Bandyopadhyay S, Paul GK, Roy R, Sen SK, Sen S (2002) Mater Chem Phys 74:83
Tiburcio-Silver A, Sanchez-Juarez A, Avila-Garcia A (1998) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 55:3
Ellmer K, Mientus R (2008) Thin Solid Films 516:5829
Islam MN, Ghosh TB, Chopra KL, Acharya HN (1996) Thin Solid Films 280:20
Majumder SB, Jain M, Dobal PS, Katiyar RS (2003) Mater Sci Eng B 103:16
Fan JCC, Goodenough JB (1977) J Appl Phys 48:3524
Major S, Kumar S, Bhatnagar M, Chopra KL (1986) Appl Phys Lett 40:394
Lin J-P, Wu J-M (2008) Appl Phys Lett 92:134103
Acknowledgments
Financial support was granted by the National Science Council of Taiwan R·O·C under contact numbers NSC 97-2221-E-218-049.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Km., Chen, YY. & Chiu, Cy. Effects of growth behaviors on chemical and physical properties of sol–gel derived ZnO:Ga films. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 55, 299–305 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2249-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2249-y