Abstract
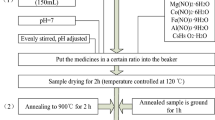
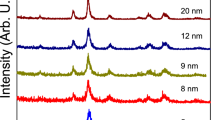
Nanocrystalline Mg–Cu–Zn ferrite powders were successfully synthesized through nitrate–citrate gel auto-combustion method. Characterization of the nitrate–citrate gel, as-burnt powder and calcined powders at different calcination conditions were investigated by using XRD, DTA/TG, IR spectra, EDX, VSM, SEM and TEM techniques. IR spectra and DTA/TGA studies revealed that the combustion process is an oxidation–reduction reaction in which the NO3 − ion is oxidant and the carboxyl group is reductant. The results of XRD show that the decomposition of the gel indicated a gradual transition from an amorphous material to a crystalline phase. In addition, increasing the calcination temperature resulted in increasing the crystallite size of Mg–Cu–Zn ferrite powders. VSM measurement also indicated that the maximum saturation magnetization (64.1 emu/g) appears for sample calcined at 800 °C while there is not much further increase in M s at higher calcination temperature. The value of coercivity field (H c) presents a maximum value of 182.7 Oe at calcination temperature 700 °C. TEM micrograph of the sample calcined at 800 °C showed spherical nanocrystalline ferrite powders with mean size of 36 nm. The toroidal sample sintered at 900 °C for 4 h presents the initial permeability (μ i) of 405 at 1 MHz and electrical resistivity (ρ) of 1.02 × 108 Ω cm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyal A, Loos K, Noto M et al (2003) J Am Chem Soc 125:1684
Choi EJ, Ahn Y, Kim S et al (2003) J Magn Magn Mater 262:L198
Sinha A, Nayar S, Murthy GVS et al (2003) J Mater Res 18:1309
Caizer C, Stefaneson M (2002) J Phys D Appl Phys 35:3035
Hrianca I, Caizer C, Schlett Z (2002) J Appl Phys 92:2125
Liu C, Zou B, Rondinone AJ et al (2000) J Am Chem Soc 122:6263
Shinkai M (2002) J Biosci Bioeng 94:606
Lubbe AS, Alexiou C, Bergemann C (2001) J Surg Res 95:200
Tiefenauer LX, Tschirky A, Kuhne G et al (1996) Magn Reson Imaging 14:391
Skmoski R (2003) J Phys Condens Matter 15:R841
Gibbs MRJ, Opin C (2003) Solid State Mater Sci 7:83
Yue Z, Zhou J, Wang X et al (2001) Mater Sci Eng B86:64
Qi X, Zhou J, Yue Z et al (2002) J Magn Magn Mater 251:316
Yue Z, Zhou J, Wang X et al (2001) J Mater Sci Lett 20:1327
Jiao X, Chen D, Hu Y (2002) Mater Res Bull 37:1583
Hwang C, Tsai J, Huang T (2005) J Mater Chem Phys 110:1
Peng CH, Hwang C, Chen S (2004) J Mater Sci Eng 107:295
Chen DH, He XR (2001) Mater Res Bull 36:1369
Mouallem-bahout M, Bertrand S, Pena O (2005) J Solid State Chem 178:1080
Verma A, Goel TC, Mendiratta RG et al (2000) J Magn Magn Mater 208:13
Chen Q, Rondinone AJ, Chakoumakos BC et al (1999) J Magn Magn Mater 194:1
Barati MR, Seyyed Ebrahimi SA, Badiei A (2008) Key Eng Mater 368–372:598
Barati MR, Seyyed Ebrahimi SA, Badiei A (2008) Mod Phys B22:3153
Azadmanjiri J, Salehani HK, Barati MR et al (2007) J Mater Lett 61:84
Deka S, Joy PA (2006) Mater Chem Phys 100:98
Rezlescu N, Rezlescu E, Popa PD et al (1998) J Magn Magn Mater 182:199
Huang Y, Tang Y, Wang J et al (2006) Mater Chem Phys 97:394
Zhang HE, Zhang BF, Wang GF et al (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 312:126
Costa ACFM, Tortella E, Morelli MR et al (2003) J Magn Magn Mater 256:174
Globus A, Duplex P, Guyot M (1971) IEEE Trans Magn 7:617
Perduijin DJ, Peloschek HP (1968) Proc Br Ceram Soc 10:263
Manjurul HM, Huq M, Hakim MA (2008) J Phys D Appl Phys 41:55007
Acknowledgments
The author would like to express their thanks to Mr. Yourdkhani and Mr. Nikkhah-Moshaie for useful helps and discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barati, M.R. Characterization and preparation of nanocrystalline MgCuZn ferrite powders synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 52, 171–178 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-2023-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-2023-1