Abstract
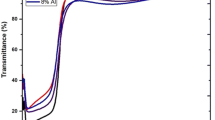
This study investigates the influences of the microstructures and doping effect on electrical and optical properties of ZnO:Al films deposited by sol–gel method. Experimental results showed that aluminum concentration affected the crystallite size obviously and enhanced the relative intensity i (002) faintly. Based on photoluminescence results, too much doping atoms generally can cause film crystallinity to deteriorate. Hall measurements indicated the carrier concentration rose only to a certain level after several coating processes. According to ellipsometric data, higher carrier mobility was mainly caused by the escalating density resulted by the increasing film thickness. However, the formation mechanism of charge carrier by doping technique in the sol–gel process is different from that of sputtering technique. The best sample having a sheet resistance of 182 Ω/sq and a transmittance of over 80% in visible region was obtained in aluminum concentration of 1.0 at.%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Look DC (2001) Mater Sci Eng B 80:382. doi:10.1016/S0921-5107(00)00604-8
Suzuki S, Miyata T, Ishii M, Minami T (2003) Thin Solid Films 434:14. doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(03)00463-2
Lamrani MA, Addou M, Sofiani Z, Sahraoui B, Ebothe J, El Hichou A, Fellahi N, Bernede JC, Dounia R (2007) Opt Commun 277:196. doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2007.04.033
Morales-Saavedra OG, Castañeda L (2007) Opt Commun 269:370
Morales-Saavedra OG, Castañeda L, Bañuelos JG, Ortega-Martínez R (2007) Laser Phys 18:283
Minami T, Miyata T (2006) Proceeding of the 1st International Symposium on Transparent Conducting Oxides, Greece
Major S, Kumar S, Bhatnagar M, Chopra KL (1986) Appl Phys Lett 49(7):394. doi:10.1063/1.97598
Dhere NG (2006) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:2181. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2006.02.018
Cooray NF et al (1997) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 49:291. doi:10.1016/S0927-0248(97)00055-X
Hagiwara Y, Nakada T, Kunioka A (2001) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 67:267. doi:10.1016/S0927-0248(00)00291-9
Springer J, Rech B, Reetz W, Mueller J, Vanecek M (2005) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 85:1
Rostan PJ, Rau U, Nguyen VX, Kirchartz T, Schubert MB, Werner JH (2006) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:1345. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2005.11.010
Minami T, Miyata T, Ihara K, Minamino Y, Tsukada S (2006) Thin Solid Films 494:47. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2005.07.167
Shan FK, Liu GX, Lee WJ, Lee GH, Kim IS, Shin BC, Kim YC (2005) J Cryst Growth 277:284. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.01.016
Groenen R, Linden JL, van Lierop HRM, Schram DC, Kuypers AD, van de Sanden MCM (2001) Appl Surf Sci 173:40. doi:10.1016/S0169-4332(00)00875-8
Fu Z, Lin B, Zu J (2002) Thin Solid Films 402:302. doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(01)01363-3
Lee J-H, Park B-O (2004) Mater Sci Eng B 106:242. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2003.09.040
Tang W, Cameron DC (1994) Thin Solid Films 238:83. doi:10.1016/0040-6090(94)90653-X
Ohyama M, Kozuka H, Yoko T (1997) Thin Solid Films 306:78. doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(97)00231-9
Natsume Y, Sakata H (2002) Thin Solid Films 372:30. doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(00)01056-7
Paul GK, Sen SK (2002) Mater Lett 57:742. doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(02)00865-0
Musat V, Teixeira B, Fortunato E, Monteiro RCC, Vilarinho P (2004) Surf Coat Tech 180–181:659
Lee S-Y, Park B-O (2005) Thin Solid Films 484:184. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2005.03.007
Lin K, Tsai P (2007) Mater Sci Eng B 139:81. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2007.01.050
Lin K, Tsai P (2007) Thin Solid Films 515:8601. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2007.04.012
Tsai P, Lin K (2005) International Symposium on Nano Science and Technology, Taiwan
West AR (1984) Solid State Chem. Wiley, New York, p 174
Guide to using WVASE32® (2003) J.A. Woollam Co., Inc., Lincoln, NE
Lin K, Chou K-Y, Chen P-M (2008) Phys Status Solid C 5:3128. doi:10.1002/pssc.200779265
Van der Pauw LJ (1958) Philips Res Rep 13:1
Kittel C (1976) Introduction to solid state Physics. Wiley, New York, p 169
Acknowledgements
Financial support was granted by the National Science Council of Taiwan under contact numbers NSC 96-2221-E-218-054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Km., Chen, YY. & Chou, KY. Solution derived Al-doped zinc oxide films: doping effect, microstructure and electrical property. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 49, 238–242 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-008-1850-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-008-1850-9