Abstract
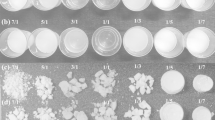
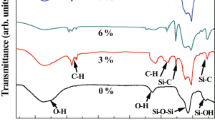
The experimental results by using various exchanging solvents in the preparation of two step (acid and base) processed ambient pressure dried hydrophobic silica aerogels, are reported. Silica alcogels were prepared by hydrolysis with oxalic acid and condensation with NH4OH of ethanol diluted tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) precursor and hexamethyldisilazane(HMDZ) methylating agent. The exchanging solvents used were: hexane, cyclohexane, heptane, benzene, toluene and xylene. The physical properties such as % of volume shrinkage, density, pore volume, % of porosity, thermal conductivity, % of optical transmission, surface area, pore size distribution and contact angle (θ) of the silica aerogels with water, were measured as a function of EtOH/TEOS molar ratios (R) for all the exchanging solvents. It was found that the physical and hydrophobic properties of the silica aerogels strongly depend on the nature of the solvent and R. Heptane solvent resulted in highly transparent (≈90% optical transmission at 700 nm for 1 cm thick sample), low density (≈0.060 g/cm3), low thermal conductive (≈0.070 W/m·K), high % of porosity (97%), high surface area (750 m2/g), uniform porosity and hydrophobic (θ ≈ 160°) aerogels compared to other solvents. On the otherhand, xylene resulted in aerogels with higher hydrophobicity (θ ≈ 172°) among other solvents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.W. Hrubesh, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 225, 335 (1998).
C.A.M. Moulder and J.G. van Lierop, in Aerogels, edited by J. Fricke (Springer, Berlin, 1986), p. 68.
A.J. Hunt and K.D. Lofftus, Adv. Sol-Energy. Technol. 4, 146 (1998).
V. Wittwer, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 145, 233 (1992).
R. Gerlach, O. Kraus, J. Fricke, P.-Ch. Eccardt, N. Kroemer, and V. Magori, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 145, 227 (1992).
G.M. Pajonk, App. Catal. 72, 217 (1991).
G.M. Pajonk and S.J. Teichner, in Aerogel, edited by J. Fricke (Springer, Berlin, 1986), p. 193.
S.S. Kistler, Nature 27, 741 (1931).
R. Deshpande, D.M. Smith, and C.J. Brinker, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 144, 32 (1992).
S.S. Prakash, C.J. Brinker, A.J. Hurd, and S.M. Rao, Nature 374, 439 (1995).
S.S. Prakash, C.J. Brinker, and A.J. Hurd, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 190, 264 (1995).
H.S. Yang, S.Y. Choi, S.H. Hyun, H.H. Park, and J.K. Hong, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 221, 151 (1997).
L. Duffours, T. Woignier, and J. Phalippou, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 186, 321 (1995).
L. Duffours, T. Woignier, and J. Phalippou, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 194, 283 (1996).
A. Parvathy Rao, G.M. Pajonk, and A. Venkateswara Rao, J. Mater. Sci. 40, 1 (2005).
N.A. Lange (Ed.), Handbook of Chemistry (Handbook Publishers INC, Sandusky Ohio, 1946).
C.J. Brinker and G.W. Scherer, Sol-Gel Science, The Physics and Chemistry of the Sol-Gel Processing (Acedemic Press, San Diego, 1990).
G.W. Scherer, S. Haereid, E. Nilsen, and M.-A. Einarsrud, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 202, 42 (1996).
D.J. Stein, A. Maskara, S. Haeireid, J. Anderson, and D.M. Smith, in Better Ceramics Through Chemistry VI Mat. Res. Soc. Synthesis. Proc. A.K. Cheetam, C.J. Brinker, M.A. Mc Cartney, and C. Sanchez (Eds.), (Pittsburg, PA 346 1994643).
D.M. Smith, G.W. Scherer, and J.M. Anderson, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 188, 191 (1995).
D.M. Smith, D. Stein, J.M. Anderson, and W. Ackerman, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 186, 104 (1995).
S. Kitahara, N. K. Zasski 90, 237 (1969).
S. Kitahara, Chem. Abstr. 70, 118461z (1969).
Mitsyuk Etal, B.M. Mitsyuk, Z.Z. Vysotski, and M.V. Polykov, Kokol Attad Nauk SSSR 155(6), 416 (1964) (English version)
D.J. Stein, A. Maskara, S. Haeireid, J. Anderson, and D.M. Smith, in Better Ceramics Through Chemistry VI Mater. Res. Soc. Proc., A.K. Cheetam, C.J. Brinker, M.A. Mc Cartney, and C. Sanchez (Eds.), Vol. 346.
R.K. Iler, The Chemistry of Silica (Wiley, New York, 1979).
B.E. Yoldas, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 63, 145 (1984).
C.J. Brinker, US Patent 5,565,142.
W.C. Ackerman, M. Vlachos, R. Rouanet, and J. Fruendt, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 285, 264 (2001).
F.A.L. Dullien, Porous Media (Academic Press, Sandiego, CA, 1991) p. 122.
C.J. Pouchert (Ed.), Aldrich Library of FTIR Spectra (Aldrich Chemical, Wisconsin, 1985) Vol. 2.
K. Lele, S.Y. Kim, and K.P. Yoo, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 186, 18 (1995).
A. Venkateswara Rao, G.M. Pajonk, N.N. Parvathy, and E.E. Elaloui, in Sol-gel Processing and Applications, edited by A. Attia (Plenum Press, New York, 1994) p. 237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, A.P., Rao, A.V. & Pajonk, G.M. Hydrophobic and Physical Properties of the Two Step Processed Ambient Pressure Dried Silica Aerogels with Various Exchanging Solvents. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 36, 285–292 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-005-4662-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-005-4662-1