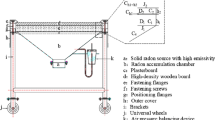
Abstract
The aim of this study is to improve and simplify the measurement of radon exhalation rate using the closed-loop accumulation method. Based on the 222Rn concentration data obtained from reference the standard module of uranium ore sands and cement, this work simplifies the 222Rn concentration growth model for calculating radon exhalation rate using the least squares method and proves its accuracy. Through fitting residual analysis, anomalies are screened at the significance level of α = 0.05 to enhance fitting precision. Herein, the influence of the starting point on the fitting effect and the calculation of radon exhalation rate is explored. The results indicate that after screening anomalous data, the fitting effects of the two sets of experimental data are further improved, and the relative errors in radon exhalation rate measurements are reduced from 1.77 to 1.41% and 13.08 to less than 10% respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sinitsky MY, Druzhinin VG (2014) The application of the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay on peripheral blood lymphocytes for the assessment of genome damage in long-term residents of areas with high radon concentration. J Radiat Res 55(1):61–66
Kim JW, Joo HY, Kim R, Moon JH (2018) Investigation of the relationship between earthquakes and indoor radon concentrations at a building in Gyeongju. Korea Nucl Eng Technol 50(3):512–518
Li C, Tang Q, Feng X, Qiu S, Yang C, Guo C, Li C (2022) Construction of a low-temperature activated carbon radon adsorption system using air cooler. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331(4):1839–1845
Papp B, Deák F, Horvath A, Kiss A, Rajnai G, Szabo C (2008) A new method for the determination of geophysical parameters by radon concentration measurements in bore-hole. J Environ Radioact 99(11):1731–1735
Clement CH, Tirmarche M, Harrison JD, Laurier D, Paquet F, Blanchardon E, Marsh JW (2010) Lung cancer risk from radon and progeny and statement on radon. Ann ICRP 40(1):1–64
World Health Organization (2009) WHO handbook on indoor radon: a public health perspective. World Health Organization
Bersimbaev R, Pulliero A, Bulgakova O, Kussainova A, Aripova A, Izzotti A (2020) Radon biomonitoring and microRNA in lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21(6):2154
Shiraishi F, Takami Y, Hashimoto T, Sieminski M (1990) A new approach to measure Rn exhalation rate out of building walls. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 37(2):878–882
Hosoda M, Sorimachi A, Yasuoka Y, Ishikawa T, Sahoo SK, Furukawa M, Uchida S (2009) Simultaneous measurements of radon and thoron exhalation rates and comparison with values calculated by UNSCEAR equation. J Radiat Res 50(4):333–343
Shweikani R, Raja G (2009) Radon exhalation from some finishing materials frequently used in Syria. Radiat Meas 44(9–10):1019–1023
Schery SD, Huang S (2004) An estimate of the global distribution of radon emissions from the ocean. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021051
Igarashi G, Saeki S, Takahata N, Sumikawa K, Tasaka S, Sasaki Y, Sano Y (1995) Ground-water radon anomaly before the Kobe earthquake in Japan. Science 269(5220):60–61
Kumar A, Singh S, Mahajan S, Bajwa BS, Kalia R, Dhar S (2009) Earthquake precursory studies in Kangra valley of North West Himalayas, India, with special emphasis on radon emission. Appl Radiat Isot 67(10):1904–1911
Alharbi SH, Akber RA (2014) Radon-222 activity flux measurement using activated charcoal canisters: revisiting the methodology. J Environ Radioact 129:94–99
Tsapalov A, Kovler K, Miklyaev P (2016) Open charcoal chamber method for mass measurements of radon exhalation rate from soil surface. J Environ Radioact 160:28–35
Aldenkamp FJ, De Meijer RJ, Put LW, Stoop P (1992) An assessment of in situ radon exhalation measurements, and the relation between free and bound exhalation rates. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 45(1–4):449–453
Quindos-Poncela LS, Fernandez PL, Sainz C, Arteche J, Arozamena JG, George AC (2003) An improved scintillation cell for radon measurements. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A 512(3):606–609
Jonassen N (1983) The determination of radon exhalation rates. Health Phys 45(2):369–376
López-Coto I, Mas JL, Bolívar JP, García-Tenorio R (2009) A short-time method to measure the radon potential of porous materials. Appl Radiat Isot 67(1):133–138
Gutiérrez-Álvarez I, Guerrero JL, Martín JE, Adame JA, Bolívar JP (2020) Influence of the accumulation chamber insertion depth to measure surface radon exhalation rates. J Hazard Mater 393:122344
Gutiérrez-Álvarez I, Martín JE, Adame JA, Grossi C, Vargas A, Bolívar JP (2020) Applicability of the closed-circuit accumulation chamber technique to measure radon surface exhalation rate under laboratory conditions. Radiat Meas 133:106284
Tan Y, Xiao D (2014) A simple model for automatically measuring radon exhalation rate from medium surface. Radiat Meas. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2014.04.006
Liu X, Qiu S (2007) A Rapid and accurate method for measuring radon exhalation rate. Radiat Prot 03:156–162
Tan Y, Xiao D (2010) Revision for measuring the radon exhalation rate from the medium surface. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 58(1):209–213
Tan Y (2011) Research on some problems of radon exhalation rate measurement. University of South China (in Chinese)
Zhong S, Study on the influence of air flow rate on the radon exhalation rate measuring (2017). University of South China (in Chinese)
Hu X, Zhu Q (2021) Screening and analysis of pointing error data under frame model. Astron Res Technol 18(01):77–86
Liu Q, Wang M (2017) On the weighting method for mixed least squares–total least squares problems. Numer Linear Algebra Appl 24(5):e2094
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 12375310, Qingzhi Zhou.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, J., Lin, Z. et al. Screening and analysis of 222Rn concentration data under the simplified correction model for calculating the radon exhalation rate. J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-024-09510-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-024-09510-w