Abstract
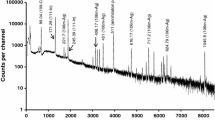
Environmentally benign aqueous biphasic separation (ABS) methods for separation of no-carrier added (NCA) 90Nb and 89Zr from alpha particle irradiated natY target have been developed using nature resourced chemical, catechins, which is the most abundant polyphenol in green tea. 90Nb was preferentially extracted in the catechins-PEG 6000 phase with a separation factor of 1.04 × 103 where the salt phase was NaHSO3. Similarly, 89Zr was also preferentially extracted in the catechins-PEG 6000 phase with a separation factor of 1.92 × 104, where the salt phase was Na2SO4.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herschman HR (2003) Molecular imaging: looking at problems, seeing solutions. Science 302:605–608
Li Z, Conti PS (2010) Radiopharmaceutical chemistry for positron emission tomography. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:1031–1051
Naskar N, Lahiri S (2022) Production of neutron deficient rare earth radionuclides by heavy ion activation. Radiochim Acta 110:725–737
Costa P, Metello LF, Alves F, Duarte Naia M (2018) Cyclotron production of unconventional radionuclides for PET imaging: the example of titanium-45 and its applications. Instruments 2(2):8
Conti M, Eriksson L (2016) Physics of pure and non-pure positron emitters for PET: a review and a discussion. EJNMMI Phys 3:1–17
Seyedi H, Nikjou A, Sharifian M, Sadeghi M (2021) Evaluation of nuclear reaction cross sections for optimization of production of the non-standard positron emitting radionuclide 90Nb using proton induced reactions on Zr target. Appl Radiat Isot 177:109917
Radchenko V, Busse S, Roesch F (2014) Desferrioxamine as an appropriate chelator for 90Nb: comparison of its complexation properties for M-Df-Octreotide (M= Nb, Fe, Ga, Zr). Nucl Med Biol 41(9):721–727
Amjed N, Naz A, Wajid AM, Hussain M, Qaim SM (2023) Evaluation of cross section data for the low and medium energy cyclotron production of the non-standard positron emitting radionuclide 90Nb. Radiat Phys Chem 209:110996
Radchenko V, Hauser H, Eisenhut M, Vugts DJ, Van Dongen GAMS, Roesch F (2012) 90Nb–a potential PET nuclide: production and labeling of monoclonal antibodies. Radiochim Acta 100(11):857–864
Wooten AL, Madrid E, Schweitzer GD, Lawrence LA, Mebrahtu E, Lewis BC, Lapi SE (2013) Routine production of 89Zr using an automated module. Appl Sci 3(3):593–613
Queern SL, Aweda TA, Massicano AVF, Clanton NA, El Sayed R, Sader JA et al (2017) Production of Zr-89 using sputtered yttrium coin targets. Nucl Med Biol 50:11–16
https://www.nndc.bnl.gov/nudat3/dec_searchi.jsp. Accessed 7 June 2023
Deri MA, Zeglis BM, Francesconi LC, Lewis JS (2013) PET imaging with 89Zr: from radiochemistry to the clinic. Nucl Med Biol 40(1):3–14
Kandil SA, Scholten B, Saleh ZA, Youssef AM, Qaim SM, Coenen HH (2007) A comparative study on the separation of radiozirconium via ion-exchange and solvent extraction techniques, with particular reference to the production of 88Zr and 89Zr in proton induced reactions on yttrium. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 274:45–52
Lahiri S, Mukhopadhyay B, Das NR (1997) Simultaneous production of 89Zr and 90,91m,92mNb in α-particle activated yttrium and their subsequent separation by HDEHP. Appl Radiat Isot 48(7):883–886
Lahiri S, Mukhopadhyay B, Das N (1997) Simultaneous production of 89Zr and 90, 91m92mNb in α-particle activated yttrium and their subsequent separation by TOA. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 218(2):229–231
Singh NL, Gadkari MS, Chintalapudi SN (2000) Measurement and analysis of alpha particle induced reactions on yttrium. Phys Scr 61(5):550–554
Radchenko V, Filosofov DV, Dadakhanov J, Karaivanov DV, Marinova A, Baimukhanova A, Roesch F (2016) Direct flow separation strategy, to isolate no-carrier-added 90Nb from irradiated Mo or Zr targets. Radiochim Acta 104(9):625–634
Maiti M, Lahiri S (2010) Separation of no-carrier-added 90Nb from proton induced natural zirconium target. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 283:637–640
Dejesus OT, Nickles RJ (1990) Production and purification of 89Zr, a potential PET antibody label. Appl Radiat Isot 41(8):789–790
Zweit J, Downey S, Sharma HL (1991) Production of no-carrier-added zirconium-89 for positron emission tomography. Appl Radiat Isot 42(2):199–201
Kandil SA, Spahn I, Scholten B, Saleh ZA, Saad SMM, Coenen HH, Qaim SM (2007) Excitation functions of (α, xn) reactions on natRb and natSr from threshold up to 26 MeV: possibility of production of 87Y, 88Y and 89Zr. Appl Radiat Isot 65(5):561–568
Lahiri S, Mukhopadhyay B, Das NR (1997) LLX separation of carrier free 94,95,97,103Ru, 93,94,95,96,99mTc and 95,96Nb produced in alpha-particle activated molybdenum by TOA. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 221:167–171
Lahiri S, Mukhopadhyay B, Das NR (1998) Studies on liquid-liquid extraction of no-carrier-added 91, 92, 96Nb and 93mMo isotopes produced in α-particle activated zirconium target with HDEHP. Radiochim Acta 83(2):93–96
Busse S, Brockmann J, Rosch F (2002) Radiochemical separation of no-carrier-added radioniobium from zirconium targets for application of 90Nb-labelled compounds. Radiochim Acta 90:411–415
Radchenko V, Filosofov DV, Bochko OK, Lebedev NA, Rakhimov AV, Hauser H et al (2014) Separation of 90Nb from zirconium target for application in immuno-PET. Radiochim Acta 102(5):433–442
Meijs WE, Herscheid JD, Haisma HJ, Wijbrandts R, van Langevelde F, Van Leuffen PJ et al (1994) Production of highly pure no-carrier added 89Zr for the labelling of antibodies with a positron emitter. Appl Radiat Isot 45(12):1143–1147
Dutta B, Maiti M, Lahiri S (2009) Production of 88, 89 Zr by proton induced activation of natY and separation by SLX and LLX. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 281(3):663–667
de Lemos LR, Santos IJB, Rodrigues GD, da Silva LHM, da Silva MCH (2012) Copper recovery from ore by liquid–liquid extraction using aqueous two-phase system. J Hazard Mat 237:209–214
Lahiri S, Choudhury D, Sen K (2018) Radio-green chemistry and nature resourced radiochemistry. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 318:1543–1558
Mitra S, Naskar N, Lahiri S, Ghosh K, Chaudhuri P (2023) Synergistic aqueous biphasic separation of 71,72As from α-particle irradiated gallium oxide target using catechins extracted from green tea leaves. 5th International Conference on Application of Radiotracers and Energetic beams in Sciences, Sidho Kanho Birsha University, Purulia
Ye JH, Li NN, Lu JL, Zheng XQ, Liang YR (2014) Bulk preparation of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate-rich extract from green tea. Food Bioprod Process 92(3):275–281
Datta A, Maiti M, Lahiri S (2014) Separation of 97Ru from niobium target using PEG based aqueous biphasic systems. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 302(2):931–937
Kim K, Shin M, Koh MY, Ryu JH, Lee MS, Hong S, Lee H (2015) TAPE: a medical adhesive inspired by a ubiquitous compound in plants. Adv Funct Mater 25(16):2402–2410
Shim W, Kim CE, Lee M, Lee SH, Park J, Do M, Yang J, Lee H (2019) Catechin solubilization by spontaneous hydrogen bonding with poly (ethylene glycol) for dry eye therapeutics. J Control Release 307:413–422
Vuong QV, Stathopoulos CE, Nguyen MH, Golding JB, Roach PD (2011) Isolation of green tea catechins and their utilization in the food industry. Food Rev Int 27(3):227–247
Pecoraro VL, Wong GB, Raymond KN (1982) Gallium and indium imaging agents. 2. Complexes of sulfonated catechoylamide sequestering agents. Inorg Chem 21(6):2209–2215
Rahim MA, Lin G, Tomanin PP, Ju Y, Barlow A, Björnmalm M, Caruso F (2020) Self-assembly of a metal–phenolic sorbent for broad-spectrum metal sequestration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(3):3746–3754
Zhu K, Gu Y, Wang R, Han R (2021) Adsorption of catechol by Zr-loaded carbon nanotubes from solution. Desalin Water Treat 236:274–284
Ghosh K, Naskar N, Choudhury D, Lahiri S (2019) Natural flavonoids as superior reagents for separation of clinically important Zr radionuclides. https://chemrxiv.org/engage/chemrxiv/article-details/60c7457e0f50dbd3a43962a0. https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv.10043237.v1
Acknowledgements
This work has been carried out under Collaborative Research Scheme no UGC-DAE-CSR-KC/CRS/ 19/RC l0/ 0984 of UGC DAE Consortium for scientific research. SM gratefully acknowledges UGC-DAE-CSR, Govt of India and University of Calcutta for providing the necessary fellowship. Authors are thankful to Variable Energy Cyclotron Staffs (VECC), Kolkata for their cooperation during the irradiation experiments. NN acknowledges Department of Science and Technology, Govt of India for offering DST-INSPIRE Faculty Fellowship. SL acknowledges Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for providing CSIR-Emeritus Scientist Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mitra, S., Naskar, N., Lahiri, S. et al. Synergistic aqueous biphasic separation of 90Nb and 89Zr from natY using green tea derived catechins. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 333, 853–863 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09321-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09321-5