Abstract
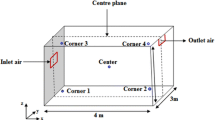
Radon exhaled from building materials infiltrates the indoor atmosphere and is transported into the indoor space by buoyancy-driven airflow. This paper investigated the dynamic coupling of radon concentration in the building wall area and indoor space. An indoor radon migration model under natural convection caused by temperature gradient was established. The radon exhalation rate, average Nusselt number, and average Sherwood number at the building wall and indoor space interface were quantified. The mechanism of radon migration from building materials into the indoor atmosphere was elucidated. Results show that natural convection influences the flow of indoor air and the radon concentration distribution, which increases with the increase of temperature gradient.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study obtained from the corresponding author (fengshengyang@usc.edu.cn) upon reasonable request.
References
Frumkin H, Samet J (2001) Radon CA-A cancer. J Clin 51:337–344.
Lubin JH, Boice JD, Edling C et al (1995) Lung cancer in radon-exposed miners and estimation of risk from indoor exposure. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:817–827. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/87.11.817
Feng SY, Wang HQ, Cui Y et al (2019) Monte Carlo method for determining radon diffusion coefficients in porous media. Radiat Meas 126: 106130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2019.106130
Borgoni R, De FD, De BD, Tzavidis N (2014) Hierarchical modeling of indoor radon concentration: how much do geology and building factors matter ? J Environ Radioact 138:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.08.022
Appleton JD (2007) Radon: sources, health risks, and hazard mapping. A J Hum Environ 36:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[85:RSHRAH]2.0.CO;2
Huang D, Liu Y, Liu YH et al (2022) Identification of sources with abnormal radon exhalation rates based on radon concentrations in underground environments. Sci Total Environ 807:150800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150800
Liang KQ, Hong CS, Luo J et al (2022) Radon attenuation characteristics of compacted soil layer for uranium mill tailings pond subjected to drying-wetting cycles. Sci Total Environ 851:158184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158184
Popovic D, Todorovic D (2006) Radon indoor concentrations and activity of radionuclides in building materials in Serbia. FACTA Univ 4:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a031533
Papachristodoulou C, Ioannides K, Spathis S (2007) The effect of moisture content on radon diffusion through soil: assessment in laboratory and field experiments. Health Phys 92:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.HP.0000248147.46038.bc
Borgoni R, Tritto V, Bigliotto C, de Bartolo D (2011) A geostatistical approach to assess the spatial association between indoor radon concentration, geological features and building characteristics: the case of Lombardy, Northern Italy. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8:1420–1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8051420
Darby S, Hill D, Auvinen A et al (2005) Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: Collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies. Br Med J 330:223–226. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38308.477650.63
Leech JA, Nelson WC, Burnett RT et al (2002) It’s about time: A comparison of Canadian and American time-activity patterns. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 12:427–432. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500244
Field RW, Steck DJ, Smith BJ et al (2001) The Iowa radon lung cancer study - phase I: residential radon gas exposure and lung cancer. Sci Total Environ 272:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00666-0
Xu DQ, Shang B, Cao ZJ (2007) Investigation of key indoor air pollutants in residence in part of the cities in China. J Hyg Res 36:473–476. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-8020.2007.04.019
Shang B, He QH, Wang ZY, Zhu CS (2003) Studies of indoor action level of radon in China. Chin J Radiol Med Prot 23:462–465.
Yao YP, Chen B, Zhuo WH (2021) Reanalysis of residential radon surveys in China from 1980 to 2019. Sci Total Environ 757:143767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143767
Yan W, Feng YL, Yu MG, Chao YH et al (2012) Comprehensive utilization of fly ash. Adv Mater Res 518–523:701–704. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.518-523.701
Jin SX, Zhao ZH, Jiang SF et al (2021) Comparison and summary of relevant standards for comprehensive utilization of fly ash at home and abroad. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 621:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/621/1/012006
Zhao CF, Lu XW, Li N, Yang G (2012) Natural radioactivity measurements of building materials in Baotou, China. Radiat Prot Dosim 152:434–437. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncs054
Lu XW, Yang G, Ren CH (2012) Natural radioactivity and radiological hazards of building materials in Xianyang, China. Radiat Phys Chem 81:780–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2012.02.043
Morin J-P, Seidel J-L, Monnin M (1993) A tri-dimensional model for radon transport in a porous medium. Nucl Tracks Radiat Meas 22:415–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/0969-8078(93)90097-N
Urosevic V, Nikezic D, Vulovic S (2008) A theoretical approach to indoor radon and thoron distribution. J Environ Radioact 99:1829–1833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.07.010
Vasilyev AV, Zhukovsky MV (2013) Determination of mechanisms and parameters which affect radon entry into a room. J Environ Radioact 124:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2013.04.014
Baltrenas P, Grubliauskas R, Danila V (2020) Seasonal variation of indoor radon concentration levels in different premises of a university building. Sustain 12:566. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156174
Rabi R, Oufni L (2017) Study of radon dispersion in typical dwelling using CFD modeling combined with passive-active measurements. Radiat Phys Chem 139:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2017.04.012
Chauhan N, Chauhan RP, Joshi M et al (2014) Study of indoor radon distribution using measurements and CFD modeling. J Environ Radioact 136:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.05.020
Cavallo A, Gadsby K, Reddy TA (1996) Comparison of natural and forced ventilation for radon mitigation in houses. Environ Int 22:1073–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(96)00221-8
Xie D, Wu YX, Wang CH et al (2021) A study on the three-dimensional unsteady state of indoor radon diffusion under different ventilation conditions. Sustain Cities Soc 66:102599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102599
Demoury C, Ielsch G, Hemon D et al (2013) A statistical evaluation of the influence of housing characteristics and geogenic radon potential on indoor radon concentrations in France. J Environ Radioact 126:216–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2013.08.006
Pampuri L, Caputo P, Valsangiacomo C (2018) Effects of buildings’ refurbishment on indoor air quality. Results of a wide survey on radon concentrations before and after energy retrofit interventions. Sustain Cities Soc 42:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.07.007
Sahoo BK, Sapra BK, Gaware JJ et al (2011) A model to predict radon exhalation from walls to indoor air based on the exhalation from building material samples. Sci Total Environ 409:2635–2641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.03.031
Zhang Z, Zhu MA, Zhang YX (2010) Radon protection technology of underground engineering and human environment. Atomic Energy Press.
Ishimori Y, Lange K, Martin P, et al (2013) Measurement and calculation of radon releases from NORM residues. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Rogers VC, Nielson KK (1991) Correlations for predicting air permeabilities and Rn-222 diffusion coefficients of soils. Health Phys 61:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-199108000-00006
Musavi M, Negarestani A (2017) Processing the spike- like radon anomaly exhalation from the soil surface by electrical model. Appl Radiat Isot 125:4–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.03.022
Feng SY, Wang HQ, Cui Y et al (2020) Fractal discrete fracture network model for the analysis of radon migration in fractured media. Comput Geotech 128:103810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103810
Rabi JA, Mohamad AA (2006) Parametric modelling and numerical simulation of natural-convective transport of radon-222 from a phosphogypsum stack into open air. Appl Math Model 30:1546–1560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2005.08.001
Feng SY, Li C, Cui Y et al (2021) Novel method for measuring temperature-dependent diffusion coefficient of radon in porous media. Appl Radiat Isot 169:56656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2020.109506
Morris MD (1991) Factorial sampling plans for preliminary computational experiments. Technometrics 33:161–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1991.10484804
Sobol IM (2001) Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates. Math Comput Simul 55:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4754(00)00270-6
Weltens H, Bressler H, Terres F et al (1993) Optimisation of catalytic converter gas flow distribution by CFD prediction. SAE Tech Pap. https://doi.org/10.4271/930780
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 11705083), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (grant number 2023JJ30494), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (grant number 22A0296), Foundation of Equipment Pre-research Area (grant number 80927015101) and Science and Technology Plan Project of Hengyang City (grant number 202150063436).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Liu, Y., Chen, P. et al. Numerical investigations on radon migration from building walls into indoor atmosphere under natural convection. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 333, 651–663 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09319-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09319-z