Abstract
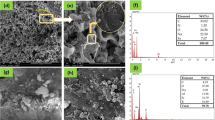
Jarosite has shown excellent adsorption capacity in heavy metal adsorption processes. In this study, jarosite was synthesized using different methods, including the bio-oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (BAF), rapid addition of H2O2 (RAH), and slow addition of H2O2 (SAH). The synthesized jarosite samples were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The influence of pH, adsorption time, and adsorbent dosage on the adsorption performance of U(VI) by jarosite was investigated through static adsorption experiments. The results revealed that jarosite with petal-like, granular, and spherical morphologies was obtained using the BAF, RAH, and SAH methods, respectively. Among jarosite synthesized by the three methods, bio-synthesized jarosite exhibited the best adsorption performance, with a maximum adsorption capacity of 96.2 mg/g for U(VI). Under the conditions of pH 7 and an adsorbent dosage of 0.8 g/L, the adsorption equilibrium was reached within 80 min. The adsorption process of U(VI) by jarosite synthesized through three methods all followed the Langmuir model. Adsorption kinetics follow a pseudo-second-order rate expression, indicating a chemical interaction between the adsorbent and the presence of U(VI). These results suggest that bio-synthesized jarosite has great potential for adsorbing U(VI) from U(VI)-contaminated wastewater.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis JA, Meece DE, Kohler M et al (2004) Approaches to surface complexation modeling of uranium (VI) adsorption on aquifer sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(18):3621–3641
Drot R, Roques J, Simoni E (2007) Molecular approach of the uranyl/mineral interfacial phenomena. C R Chim 10(10–11):1078–1091
Wang X, Liu Y, Sun Z et al (2017) Heap bioleaching of uranium from low-grade granite-type ore by mixed acidophilic microbes. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314(1):251–258
Min X, Li Y, Ke Y et al (2017) Fe-FeS2 adsorbent prepared with iron powder and pyrite by facile ball milling and its application for arsenic removal. Water Sci Technol 76(1):192–200
Ke Y, Peng N, Xue K et al (2018) Sulfidation behavior and mechanism of zinc silicate roasted with pyrite. Appl Surf Sci 435:1011–1019
Wang X, Li P, Liu Y et al (2018) Uranium bioleaching from low-grade carbonaceous-siliceous-argillaceous type uranium ore using an indigenous Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 317(2):1033–1040
Chai LY, Wang X, Wang HY et al (2018) Formation of one-dimensional composites of poly (m-phenylenediamine) s based on Streptomyces for adsorption of hexavalent chromium. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15(7):1411–1422
Wang T, Zhang L, Li C et al (2015) Synthesis of core–shell magnetic Fe3O4@ poly (m-phenylenediamine) particles for chromium reduction and adsorption. Environ Sci Technol 49(9):5654–5662
Qian L, Ma M, Cheng D (2015) Adsorption and desorption of uranium on nano goethite and nano alumina. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303(1):161–170
Xu Y, Zhang K, Wang C et al (2020) Fabrication of magnetic functionalized m-carboxyphenyl azo calix[4]arene amine oxime derivatives for highly efficient and selective adsorption of uranium (VI). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 323(3):1145–1155
Abdi S, Nasiri M, Mesbahi A et al (2017) Investigation of uranium (VI) adsorption by polypyrrole. J Hazard Mater 332:132–139
Bakather OY, Zouli N, Abutaleb A et al (2020) Uranium (VI) ions uptake from liquid wastes by Solanum incanum leaves: biosorption, desorption and recovery. Alex Eng J 59(3):1495–1504
Mahmoud MA (2015) Design of batch process for preconcentration and recovery of U(VI) from liquid waste by powdered corn cobs. J Environ Chem Eng 3(3):2136–2144
Donati CP (2000) Immobilisation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: importance of jarosite precipitation. Process Biochemistry 35(9):997–1004
Liu YL, Ding DX, Li GY et al (2010) Comparative study on the precipitates of chemical leaching and bacterial leaching of uranium ore. Chin J Process Eng 10(4):679–684
Papike JJ, Karner JM, Shearer CK (2006) Comparative planetary mineralogy: implications of martian and terrestrial jarosite. A crystal chemical perspective. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70(5):1309–1321
Zhao R, Li Y, Chan CK (2016) Synthesis of jarosite and Vanadium jarosite analogues using microwave hydrothermal reaction and evaluation of composition-dependent electrochemical properties. J Phys Chem C 120(18):9702–9712
Wei H, Dong F, Chen M et al (2020) Removal of uranium by biogenetic jarosite coupled with photoinduced reduction in the presence of oxalic acid: a low-cost remediation technology. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 324(2):715–729
Aguilar-Carrillo J, Herrera-Garcia L, Reyes-Dominguez IA et al (2020) Thallium(I) sequestration by jarosite and birnessite: structural incorporation vs surface adsorption. Environ Pollut 257:113492
Tomioka Y, Hiroyoshi N, Kubo Y et al (2005) Effect of jarosite on the removal of arsenic ions in sulfuric acid solution. Shigen-to-Sozai 121(12):597–602
Picazo-Rodríguez NG, Carrillo-Pedroza FR, Soria-Aguilar MDJ et al (2022) Use of thermally modified jarosite for the removal of hexavalent chromium by adsorption. Crystals 12(1).
Bai S, Xu Z, Wang M et al (2012) Both initial concentrations of Fe(II) and monovalent cations jointly determine the formation of biogenic iron hydroxysulfate precipitates in acidic sulfate-rich environments. Mater Sci Eng, C 32(8):2323–2329
Islas H, Flores MU, Reyes IA et al (2020) Determination of the dissolution rate of hazardous jarosites in different conditions using the shrinking core kinetic model. J Hazard Mater 386:121664
Dutrizac JE (1997) The behavior of thallium during jarosite precipitation. Metall Mater Trans B 28(5):765–776
Labib S, Abdelaal S, Abdelhady AM et al (2020) Preparation and characterization of jarosite nanorods synthesized by microwave hydrothermal method. Mater Chem Phys, 256.
Wang H, Bigham JM, Tuovinen OH (2006) Formation of schwertmannite and its transformation to jarosite in the presence of acidophilic iron-oxidizing microorganisms. Mater Sci Eng, C 26(4):588–592
Chen H-J, Tian W, Ding W (2018) Effect of preparation methods on morphology of active manganese dioxide and 2,4-dinitrophenol adsorption performance. Adsorpt Sci Technol 36(3–4):1100–1111
Zhao R, Chen J, Liu J et al (2015) Morphologies-controlling synthesis of silicalite-1 and its adsorption property. Mater Lett 139:494–497
Dan H, Ding Y, Lu X et al (2016) Adsorption of uranium from aqueous solution by mesoporous SBA-15 with various morphologies. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 310(3):1107–1114
Du J, Liu L, Yu Y et al (2019) Mesoporous carbon materials with different morphology for pesticide adsorption. Appl Nanosci 10(1):151–157
Natarajan KA (2008) Microbial aspects of acid mine drainage and its bioremediation. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 18(6):1352–1360
Sasaki K, Konno H (2000) Morphology of jarosite-group compounds precipitated from biologically and chemically oxidized Fe ions. Canad Mineral 38(1):45–56
Torab-Mostaedi M, Ghaemi A, Ghassabzadeh H et al (2011) Removal of strontium and barium from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto expanded perlite. Can J Chem Eng 89(5):1247–1254
Xu Z, Bai S, Liang J et al (2013) Photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) by citric and oxalic acids over biogenetic jarosite. Mater Sci Eng C Mater biol Appl 33(4):2192–2196
Eneroth E, Koch CB (2004) Fe-Hydroxysulphates from bBacterial Fe2+oxidation. Hyperfine Interact 156–157(1–4):423–429. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:hype.0000043263.25269.2f.
Sasaki K, Konno H (2000) Morphology of jarosite-group compounds precipitated from biologically and chemically oxidized Fe ions. Can Mineral 38(1):45–56
Queenuddin SM, Tripathy S, Sahoo PK et al (2010) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of acid mine drainage and water pollution at Makum Coalfield, India. J Geochem Exploration 105(3):0–82.
Bisson W, Wills AS (2006) Intermediate phase in the oxidative hydrothermal synthesis of potassium jarosite, a model kagome antiferromagnet. arXiv preprint arXiv:cond-mat/0610119.
Akcil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. J Clean Prod 14(12–13):1139–1145
Knorr K-H, Blodau C (2007) Controls on schwertmannite transformation rates and products. Appl Geochem 22(9):2006–2015
Kirby CS, Brady JAE (1998) Field determination of Fe2+ oxidation rates in acid mine drainage using a continuously-stirred tank reactor. Appl Geochem 13(4):509–520
Daoud J, Karamanev D (2006) Formation of jarosite during Fe2+ oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Miner Eng 19(9):960–967
Osorio H, Mangold S, Denis Y et al (2013) Anaerobic sulfur metabolism coupled to dissimilatory iron reduction in the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(7):2172–2181
Liu Y, Fang HHP (2003) Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on flocculation, settling, and dewatering of activated sludge. Critic Rev Environ Sci Technol 33(3):237–273
Hott RC, Maia LFO, Santos MS et al (2018) Purification of arsenic-contaminated water with K-jarosite filters. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(14):13857–13867
Meng X, Zhang C, Zhuang J et al (2020) Assessment of schwertmannite, jarosite and goethite as adsorbents for efficient adsorption of phenanthrene in water and the regeneration of spent adsorbents by heterogeneous fenton-like reaction. Chemosphere 244:125523
Flores M, Iván R, Palacios E, et al (2019) Kinetic analysis of the thermal decomposition of a synthetic mercury jarosite. Minerals 9(4):200.
Bibi I, Singh B, Silvester E (2011) Akaganéite (β-FeOOH) precipitation in inland acid sulfate soils of south-western New South Wales (NSW), Australia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75(21):6429–6438
Zhu J, Min G, Dan Z et al (2013) The nature of Schwertmannite and Jarosite mediated by two strains of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans with different ferrous oxidation ability. Mater Sci Eng, C 33(5):2679–2685
Jonsson J, Persson P, Sjoberg S et al (2005) Schwertmannite precipitated from acid mine drainage: phase transformation, sulphate release and surface properties. Appl Geochem 20(1):179–191
Spratt HJ, Rintoul L, Avdeev M et al (2013) The crystal structure and vibrational spectroscopy of jarosite and alunite minerals. Am Miner 98(10):1633–1643
Frost R, Wills R, Kloprogge J et al (2006) Thermal decomposition of hydronium jarosite (H 3 O) Fe3(SO4)2(OH)6. J Therm Anal Calorim 83(1):213–218
Regenspurg S, Brand A, Peiffer S (2004) Formation and stability of schwertmannite in acidic mining lakes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(6):1185–1197
Li W, Troyer LD, Lee SS et al (2017) Engineering nanoscale iron oxides for uranyl sorption and separation: optimization of particle core size and bilayer surface coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(15):13163–13172
Guo Z, Li Y, Wu W (2009) Sorption of U(VI) on goethite: effects of pH, ionic strength, phosphate, carbonate and fulvic acid. Appl Radiat Isot 67(6):996–1000
Humelnicu D, Blegescu C, Ganju D (2014) Removal of uranium (VI) and thorium (IV) ions from aqueous solutions by functionalized silica: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299(3):1183–1190
Yang P, Liu Q, Liu J et al (2017) Interfacial growth of a metal–organic framework (UiO-66) on functionalized graphene oxide (GO) as a suitable seawater adsorbent for extraction of uranium (VI). J Mater Chem A 5(34):17933–17942
Huang S, Zhou L (2012) Fe2+ oxidation rate drastically affect the formation and phase of secondary iron hydroxysulfate mineral occurred in acid mine drainage. Mater Sci Eng, C 32(4):916–921
Shashkova IL, Ivanets AI, Kitikova NV et al (2017) Effect of phase composition on sorption behavior of Ca-Mg phosphates towards Sr (II) ions in aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 80:787–796
Regenspurg S, Schild D, Schäfer T et al (2009) Removal of uranium(VI) from the aqueous phase by iron(II) minerals in presence of bicarbonate. Appl Geochem 24(9):1617–1625
Shuibo X, Chun Z, Xinghuo Z et al (2009) Removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption of hematite. J Environ Radioact 99(2):162–166
Shao L, Wang X, Ren Y et al (2016) Facile fabrication of magnetic cucurbit[6]uril/graphene oxide composite and application for uranium removal. Chem Eng J 286:311–319
Zong P, Wang S, Zhao Y et al (2013) Synthesis and application of magnetic graphene/iron oxides composite for the removal of U(VI) from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 220:45–52
Hui JW, Liu Y, Cao Y, Zhang X, Dai Z, Liu Y, Yunha. (2019) Effects of pH, carbonate, calcium ion and humic acid concentrations, temperature, and uranium concentration on the adsorption of uranium on the CTAB-modified montmorillonite. J Radioanal Nuclear Chem Int J Deal All Aspects Appl Nuclear Chem 319(3).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Defense Basic Research Program (JCKY2019401D003) and the Key Project of the Jiangxi Provincial Key R & D Program (20232BBG70007), Research and Innovation Partnership Fund of State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resources and Environment (2023NRE-LH-15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Zhou, Z., Yuan, J. et al. Effect of preparation methods on the morphology of jarosite and its adsorption performance for U(VI). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 333, 317–328 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09231-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09231-6