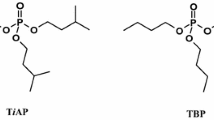
Abstract
Tri-iso-amyl phosphate (TiAP) is a promising alternative extract agent to tri-n-butyl phosphate for spent fuel reprocessing. In this work, the effect of concentration and dominant radiolysis products of TiAP in γ-irradiated TiAP/n-dodecane (nDD) solution on the extraction of UO2(NO3)2 was investigated. The extraction efficiency of U(VI) increased significantly with absorbed dose in the absence of nitric acid due to the formation of di-iso-amyl phosphoric acid (HDiAP). Density functional theory calculation further proved that coordination energy between HDiAP and U(VI) is higher than that of TiAP. Extraction performance confirmed the synergistic effect of TiAP and HDiAP on U(VI).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sood DD, Patil SK (1996) Chemistry of nuclear fuel reprocessing: current status. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Artic 203(2):547–573
Wright A, Paviet-Hartmann P (2010) Review of physical and chemical properties of tributyl phosphate/diluent/nitric acid systems. J Sep Sci Technol 45(12–13):1753–1762
Das B, Kumar S, Mondal P, Kamachi Mudali U, Natarajan R (2012) Synthesis and characterization of red-oil from tri-iso-amyl phosphate/n-dodecane/nitric acid mixtures at elevated temperature. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 292(3):1161–1171
Vasudeva Rao PR, Kolarik Z (1996) A review of third phase formation in extraction of actinides by neutral organophosphorus extractants. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch 14(6):955–993
Tripathi SC, Ramanujam A, Gupta KK, Bindu P (2001) Studies on the identification of harmful radiolytic products of 30% TBP-n-dodecane-HNO3 by gas-liquid chromatography II. Formation and characterization of high molecular weight organophosphates. J Sep Sci Technol. 36(13):2863–2883
Mishra S, Mallika C, Pandey NK, Kamachi Mudali U, Natarajan R (2015) Effect of radiolysis in altering the physiochemical and metal retention properties of solvent-diluent-acid systems. J Sep Sci Technol 50(11):1671–1676
Serenko YuV, Yudin NV, Gritcenko RT, Rodin AV, Belova EV, Ponomarev AV (2021) Competitive processes of tributyl phosphate degradation in HNO3-saturated solution in Isopar-M during radiolysis and aging. J Radiat Phys Chem 185:109495
Hasan SH, Shukla JP (2003) Tri-iso-amyl phosphate (TAP): An alternative extractant to tri-butyl phosphate (TBP) for reactor fuel reprocessing. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 258(3):563–573
Sreenivasulu B, Suresh A, Sivaraman N, Vasudeva Rao PR (2014) Solvent extraction studies with some fission product elements from nitric acid media employing tri-iso-amyl phosphate and tri-n-butyl phosphate as extractants. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303:2165–2172
Benadict Rakesh K, Suresh A, Vasudeva Rao PR (2014) Extraction and stripping behaviour of tri-iso-amyl phosphate and tri-n-butyl phosphate in n-dodecane with U(VI) in nitric acid media. J Radiochim Acta 102(7):619–628
Suresh A, Srinivasan TG, Rao PRV (1994) Extraction of U(VI), Pu(IV) and Th(IV) by some trialkyl phosphates. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch 12(4):727–744
Suresh A, Srinivasan TG, Rao PRV (2009) Parameters influencing third-phase formation in the extraction of Th(NO3)4 by some trialkyl phosphates. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch 27(2):132–158
Singh ML (2021) Excess properties of binary mixtures of tri–iso-amyl phosphate + n–hexane (or n-dodecane): physical significance of coefficients of Redlich-Kister type equation. J Mol Liq 341:117203
Mishra S, Pandey NK (2019) Physiochemical properties of γ-irradiated tri-iso-amyl phosphate–dodecane system: effect of aqueous phase acidity. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch 37(6):446–460
Mishra S, Kumar M, Pandey NK (2020) Aqueous solubility of tri-iso-amyl phosphate (TiAP): effect of acidity, temperature and metal ions. J Prog Nucl Energy 119:103166
Muthukumar M, Kumar S, Sinha PK, Mudali UK, Natarajan R (2011) Estimation of PVT properties and vapour pressure of alternate PUREX/UREX extractant tri-iso-amyl phosphate. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288(3):819–821
Mishra S, Desigan N, Venkatesan KA, Ananthasivan K (2021) Hydrolytic degradation of tri-iso-amyl phosphate-dodecane system. J Mol Liq 334:116512
Sreenivasulu B, Suresh A, Rajeswari S, Ramanathan N, Antony MP, Sivaraman N, Joseph M (2017) Physicochemical properties and radiolytic degradation studies on tri-iso-amyl phosphate (TiAP). J Radiochim Acta 105(3):249–261
Sahoo TK, Srinivasan TG, Vasudeva Rao PR (2011) Note: effect of temperature in the extraction of uranium and plutonium by tri-iso-amyl phosphate. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch 29(2):260–269
Suresh A, Srinivasan TG, Vasudeva Rao PR (2009) The effect of the structure of trialkyl phosphates on their physicochemical properties and extraction behavior. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch 27(2):258–294
Li F, Qin Y, Liao W, Li F, Lan T, Ding S, Liao J, Yang J, Yang Y, Feng W, Liu N (2022) Gamma and beta radiolysis of tri-iso-amyl phosphate: degradation of tri-iso-amyl phosphate and formation of di-iso-amyl phosphoric acid. J Radiat Phys Chem 199:110354
Mincher Bruce J, Mezyk SP (2009) Radiation chemical effects on radiochemistry: a review of examples important to nuclear power. J Radiochim Acta 97:519–534
Mincher Bruce J, Modolo G, Mezyk SP (2009) Review article: The effects of radiation chemistry on solvent extraction: 1. Conditions in acidic solution and a review of TBP radiolysis. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch. 27(1):1–25
Pearson J, Nilsson M (2014) Radiolysis of tributyl phosphate by particles of high linear energy transfer. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch 32(6):584–600
Xu W, Zhou Y, Huang D, Su M, Wang K, Xiang M, Hong M (2015) Luminescent sensing profiles based on anion-responsive lanthanide(iii) quinolinecarboxylate materials: solid-state structures, photophysical properties, and anionic species recognition. J Mater Chem 3(9):2003–2015
Becke AD (1993) Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J Chem Phys. 98(7):5648–5652
Lee C, Yang W, Parr RG (1988) Development of the Colle-salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. J Phys Rev 37(2):785–789
Cao X, Dolg M (2004) Segmented contraction scheme for small-core actinide pseudopotential basis sets. J Mol Struct 673(1–3):203–209
Küchle W, Dolg M, Stoll H, Preuss H (1994) Energy-adjusted pseudopotentials for the actinides. Parameter sets and test calculations for thorium and thorium monoxide. J Chem Phys. 100(10):7535–7542
Dolg M, Stoll H, Preuss H (1989) Energy-adjusted ab initio pseudopotentials for the rare earth elements. J Chem Phys 90(3):1730–1734
Dolg M, Stoll H, Preuss H (1993) A combination of quasirelativistic pseudopotential and ligand field calculations for lanthanoid compounds. J Theor Chim Acta 85(6):441–450
Dolg M, Stoll H, Savin A, Preuss H (1989) Energy-adjusted pseudopotentials for the rare earth elements. J Theor Chim Acta 75(3):173–194
Cao X, Dolg M, Stoll H (2003) Valence basis sets for relativistic energy-consistent small-core actinide pseudopotentials. J Chem Phys 118(2):487–496
Marenich AV, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2009) Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J Phys Chem 113(18):6378–6396
Struebing H, Ganase Z, Karamertzanis PG, Siougkrou E, Haycock P, Piccione PM, Armstrong A, Galindo A, Adjiman CS (2013) Computer-aided molecular design of solvents for accelerated reaction kinetics. J Nat Chem 5(11):952–957
Bellido AV, Rubenich MN (1984) Influence of the diluent on the radiolytic degradation of TBP in TBP, 30%(v/v)-diluent-HNO3 systems. J Radiochim Acta 36(1–2):61–64
Li R, Cao X, Zhao H, Liu C, Li Z, Wang J, Zhang L, Li Q (2018) Radiolysis products and degradation mechanism studies on tri-iso-amyl phosphate (TiAP). J Radiochim Acta 106(3):239–247
Razvi J, Merklin JF (1980) The radiolysis of dodecane-tributyl phosphate solutions II. Liquid products. J Nucl Instrum Methods 169(1):223–226
Tripathi S, Sumathi S, Ramanujam A (1999) Effects of solvent recycling on radiolytic degradation of 30% tributyl phosphate–n-dodecane–HNO3 system. J Sep Sci Technol 34(14):2887–2903
Kong F, Liao J, Ding S, Yang Y, Huang H, Yang J, Tang J, Liu N (2013) Extraction and thermodynamic behavior of U(VI) and Th(IV) from nitric acid solution with tri-iso-amyl phosphate. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298(1):651–656
Anderson TL, Braatz A, Ellis RJ, Antonio MR, Nilsson M (2013) Synergistic extraction of dysprosium and aggregate formation in solvent extraction systems combining TBP and HDBP. J Solvent Extr Ion Exch 31(6):617–633
May I, Taylor RJ, Wallwork AL, Hastings JJ, Fedorov YuS, Ya ZB, Mishin EN, Arkhipov SA, Blazheva IV, Ya PL, Livens FR, Charnock JM (2000) The influence of dibutyl phosphate on actinide extraction by 30% tributyl phosphate. J Radiochim Acta 88(5):283–290
Sarkar S, Suresh A, Sivaraman N (2020) Alpha and gamma degradation behavior of tri-n-alkyl phosphates and tris(2-methylbutyl) phosphate: a comparative study. J Radiat Phys Chem 176:108923
Sk J, Pathak S, Sengupta A (2021) Analytical application of ionic liquid in determination of trace metallic constituents in U matrix by ICP-OES: a “green” approach for drastic reduction in organic waste burden and time of analysis. J Mol Liq 343:117584
Hahn HT, Vander Wall EM (1964) Complex formation in the dilute uranyl nitrate-nitric acid-dibutyl phosphoric acid-tributyl phosphate-Amsco system. J Inorg Nucl Chem 26(1):191–202
Shukla JP, Gautam MM, Kedari CS, Hasan SH, Rupainwar DC (1997) Extraction of uranium(VI), plutonium(IV) and some fission products by tri-iso-amyl phosphate. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 219(1):61–67
Das A, Sahu P, SkM A (2017) Molecular dynamics simulation for the calibration of the OPLS force field using DFT derived partial charges for the screening of alkyl phosphate ligands by studying structure, dynamics, and thermodynamics. J Chem Eng Data 62(8):2280–2295
Huei Meznarich, Deborah A Penchoff (2021) Rare earth elements and actinides: progress in computational science applications ACS symposium series. Washington, DC
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the Department of Applied Chemistry of Peking University for providing 60Co source. The measurements of FTMS, ICP-OES and ICP-MS were performed at the Analytical Instrumentation Center of Peking University. The help from PKUAIC (Dr. Xiaoran He, Dr. Li Zhang and Dr. Jiahui Liu) was acknowledged. The authors also wish to acknowledge Prof. Song-Dong Ding (Sichuan University) for his help in providing TiAP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The first two authors contributed equally to the work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Ao, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Effect of radiolysis and radiolytic products of tri-iso-amyl phosphate on the extraction behavior of uranium. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 4089–4099 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09113-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09113-x