Abstract
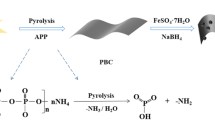
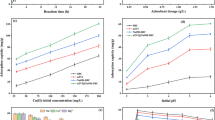
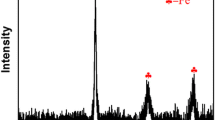
ZnCl2-modified activated carbon supported nanoscale zero-valent iron material (nZVI/BC600) was synthesized by green carbothermal reduction and liquid phase reduction to explore the removal efficiency of U(VI) under different conditions. The results showed that under the optimal conditions (C0 = 10 mg/L, C/Fe = 5:1, pH = 5.5, t = 30 min), the removal rate of U(VI) by nZVI/BC600 was 99.68%, which was 9.18% higher than that of ZnCl2-modified activated carbon and conformed to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. SEM and XPS analysis showed that nZVI was uniformly distributed on activated carbon, and U(VI) was reduced to U(IV) or U(V). The removal mechanism of U(VI) by nZVI/BC600 is chemical adsorption, redox and co-precipitation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheng L, Fein JB (2014) Uranium reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 as a function of NaHCO3 concentration: surface complexation control of reduction kinetics. Environ Sci Technol 48(7):3768–3775. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5003692
Tan WF, Li Y, Guo F, Wang YC, Ding L, Mumford K, Lv JW, Deng QW, Fang Q, Zhang XW (2020) Effect of Leifsonia sp. on ret ardation of uranium in natural soil and its potential mechanisms. J Environ Radioact 217:106202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2020.106202
Pan Z, Bártová B, LaGrange T, Butorin SM, Hyatt NC, Stennett MC, Kvashnina KO, Bernier-Latmani R (2020) Nanoscale mechanism of UO2 formation through uranium reduction by magnetite. Nat Commun 11(1):4001. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17795-0
Hu C, Liu C, Huang G, Li T, Xu H, Hu X, Xu C (2020) Analysis of total Uranium concentration in drinking water source. Chin J Radiol Health 29:628–631. https://doi.org/10.13491/j.issn.1004-714X.2020.06.013
Li XY, Zhang M, Liu YB, Li X, Yang B, Hua R, Liu Y (2015) Effect of ionic strength, anion, cation and humic acid on removal of U(VI) in aqueous solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chin J Nonferrous Metals 25:3505–3512. https://doi.org/10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2015.12.029
He S, Yang Z, Cui X, Zhang X, Niu X (2020) Fabrication of the novel Ag-doped SnS2@InVO4 composite with high adsorption-photocatalysis for the removal of uranium (VI). Chemosphere 260:127548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127548
Yan S, Chen Y, Xiang W, Bao Z, Liu C, Deng B (2014) Uranium(VI) reduction by nanoscale zero-valent iron in anoxic batch systems: the role of Fe(II) and Fe(III). Chemosphere 117:625–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.087
Li X, Zhang M, Liu Y, Li X, Liu Y, Hua R, He C (2013) Removal of U(VI) in aqueous solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron(nZVI). Expo Health 5:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-013-0084-4
Crane RA, Dickinson M, Popescu IC, Scott TB (2011) Magnetite and zero-valent iron nanoparticles for the remediation of uranium contaminated environmental water. Water Res 45(9):2931–2942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.03.012
Jing C, Landsberger S, Li YL (2017) The application of illite supported nanoscale zero valent iron for the treatment of uranium contaminated groundwater. J Environ Radioact 175:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2017.04.003
Jing C, Li YL, Landsberger S (2016) Review of soluble uranium removal by nanoscale zero valent iron. J Environ Radioact 164:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.06.027
Mueller NC, Braun J, Bruns J, Černík M, Rissing P, Rickerby D, Nowack B (2011) Application of nanoscale zero valent iron (NZVI) for groundwater remediation in Europe. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:550–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0576-3
Singh R, Misra V, Singh RP (2011) Removal of Cr(VI) by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) from soil contaminated with tannery wastes. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:210–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-011-0425-6
Zhou Z-Y, Tian N, Li J-T, Broadwell I, Sun S-G (2011) Nanomaterials of high surface energy with exceptional properties in catalysis and energy storage. Chem Soc Rev 88:210–214. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00176g
Hu Z, Wang H, Liu R, Hu B, Qiu M (2022) Removal of U(vi) from aqueous solutions by an effective bio-adsorbent from walnut shell and cellulose composite-stabilized iron sulfide nanoparticles. RSC Adv 12(5):2675–2683. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra08087c
Sun Y, Ding C, Cheng W, Wang X (2014) Simultaneous adsorption and reduction of U(VI) on reduced graphene oxide-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron. J Hazard Mater 280:399–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.023
De León MA, Sergio M, Bussi J, Ortiz de la Plata GB, Cassano AE, Alfano OM (2014) Application of a montmorillonite clay modified with iron in photo-Fenton process. Comparison with goethite and nZVI. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:864–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2681-6
Jiang Z, Lv L, Zhang W, Du Q, Pan B, Yang L, Zhang Q (2011) Nitrate reduction using nanosized zero-valent iron supported by polystyrene resins: role of surface functional groups. Water Res 45(6):2191–2198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.01.005
Kakavandi B, Kalantary RR, Farzadkia M, Mahvi AH, Esrafili A, Azari A, Yari AR, Javid AB (2014) Enhanced chromium (VI) removal using activated carbon modified by zero valent iron and silver bimetallic nanoparticles. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-014-0115-5
Li ZJ, Wang L, Yuan LY, Xiao CL, Mei L, Zheng LR, Zhang J, Yang JH, Zhao YL, Zhu ZT, Chai ZF, Shi WQ (2015) Efficient removal of uranium from aqueous solution by zero-valent iron nanoparticle and its graphene composite. J Hazard Mater 290:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.028
Saleh TA, Naeemullah N, Tuzen M, Sarı A (2016) Polyethylenimine modified activated carbon as novel magnetic adsorbent for the removal of uranium from aqueous solution. Chem Eng Res Des 117:218–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2016.10.030
Sheng G, Yang P, Tang Y, Hu Q, Li H, Ren X, Hu B, Wang X, Huang Y (2016) New insights into the primary roles of diatomite in the enhanced sequestration of UO22+ by zerovalent iron nanoparticles: An advanced approach utilizing XPS and EXAFS. Appl Catal B 193:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.035
Tseng H-H, Su J-G, Liang C (2011) Synthesis of granular activated carbon/zero valent iron composites for simultaneous adsorption/dechlorination of trichloroethylene. J Hazard Mater 192(2):500–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.047
Yu S, Wang X, Liu Y, Chen Z, Wu Y, Liu Y, Pang H, Song G, Chen J, Wang X (2019) Efficient removal of uranium(VI) by layered double hydroxides supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: a combined experimental and spectroscopic studies. Chem Eng J 365:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.024
Chen L, Feng S, Zhao D, Chen S, Li F, Chen C (2017) Efficient sorption and reduction of U(VI) on zero-valent iron-polyaniline-graphene aerogel ternary composite. J Colloid Interface Sci 490:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.050
Zhao X, Liu W, Cai Z, Fu J, Duan J, Zhao D, Bozack M, Feng Y (2020) Reductive immobilization of uranium by stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles: effects of stabilizers, water chemistry and long-term stability. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 604:125315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125315
Filip P, Popescu I-C, Humelnicu D, Humelnicu I, Scott TB, Crane RA (2013) Removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous systems by nanoscale zero-valent iron particles suspended in carboxy-methyl cellulose. J Nucl Mater 443(1–3):250–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2013.07.018
Pang H, Wu Y, Huang S, Ding C, Li S, Wang X, Yu S, Chen Z, Song G, Wang X (2018) Macroscopic and microscopic investigation of uranium elimination by Ca–Mg–Al-layered double hydroxide supported nanoscale zero valent iron. Inorg Chem Front 5(10):2657–2665. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8qi00779a
Zheng H, Ren X, Zhang X, Song G, Chen D, Chen C (2020) Mutual effect of U(VI) and phosphate on the reactivity of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) for their co-removal. J Mol Liquids 297:111853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111853
Chen Z, Xing J, Pu Z, Wang X, Yang S, Wei B, Ai Y, Li X, Chen D, Wang X (2018) Preparation of nano-Fe0 modified coal fly-ash composite and its application for U(VI) sequestration. J Mol Liq 266:824–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.118
Hu B, Mei X, Li X, Hu J, Xu D, Ma J, Huang Y (2017) Decontamination of U(VI) from nZVI/CNF composites investigated by batch, spectroscopic and modeling techniques. J Mol Liq 237:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.04.084
Hao T, Shu Z, Hongwei P, Jiaqi W, Xiangxue W, Gang S, Shujun Y (2021) Insights into enhanced removal of U(VI) by melamine sponge supported sulfurized nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Clean Prod 329:129662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129662
Pang H, Diao Z, Wang X, Ma Y, Yu S, Zhu H, Chen Z, Hu B, Chen J, Wang X (2019) Adsorptive and reductive removal of U(VI) by dictyophora indusiate-derived biochar supported sulfide NZVI from wastewater. Chem Eng J 366:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.098
Zhu H, Jia Y, Wu X, Wang H (2009) Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 172(2–3):1591–1596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.031
Pang H, Zhang E, Zhang D, Wang X, Zhao B, Liu L, Ma X, Song G, Yu S (2022) Precursor impact and mechanism analysis of uranium elimination by biochar supported sulfurized nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Environ Chem Eng 10(2):107288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107288
Hu S, Lin X, Zhao W, Luo X (2017) Efficient simultaneous removal of U(VI) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution using core–shell nZVI@SA/CMC-Ca beads. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 315:223–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5662-7
Wang JQ, Duan HW, Tang H, Yu SJ, Zhu HT, Wang XX (2020) Carbothermic synthesis of carbon-supported zero-valent iron material for removal of U(VI) from aqueous solution. J Inorgan Mater 35:373–380. https://doi.org/10.15541/jim20190378
Liu C, Lu J, Tan Y, Chen B, Yang P (2022) Removal of U(VI) from wastewater by sulfhydryl-functionalized biomass carbon supported nano-zero-valent iron through synergistic effect of adsorption and reduction. Mater Sci Eng B 284:115891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2022.115891
Liu H, Li M, Chen T, Chen C, Alharbi NS, Hayat T, Chen D, Zhang Q, Sun Y (2017) New synthesis of nZVI/C composites as an efficient adsorbent for the uptake of U(VI) from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Technol 51(16):9227–9234. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02431
Wang W, Zhou M, Mao Q, Yue J, Wang X (2010) Novel NaY zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst. Catal Commun 11(11):937–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2010.04.004
Li Q, Wang H, Chen Z, He X, Liu Y, Qiu M, Wang X (2021) Adsorption-reduction strategy of U(VI) on NZVI-supported zeolite composites via batch, visual and XPS techniques. J Mol Liq 339:116719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116719
Cruz MLD, Araño K, Pena EMD, Diaz LJL (2013) Nanoclay-supported zero-valent iron as an efficient adsorbent material for arsenic. Adv Mater Res 2322:296–304. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.686.296
Li C, Chen N, Zhao Y, Li R, Feng C (2016) Polypyrrole-grafted peanut shell biological carbon as a potential sorbent for fluoride removal: Sorption capability and mechanism. Chemosphere 163:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.016
Lu L, Lin Y, Chai Q, He S, Yang C (2018) Removal of acenaphthene by biochar and raw biomass with coexisting heavy metal and phenanthrene. Colloids Surf A 558:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.08.057
Xue DQ (2014) Magnetic properties of nano zerovalent iron particles coated with biopolymers. Trans Tech Publ Ltd 912:32–35. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.912-914.32
Crane RA, Scott T (2014) The removal of uranium onto carbon-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. J Nanopart Res 16:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2813-4
Lehmann J, Gaunt J, Rondon M (2006) Bio-char sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems—a review. Mitig Adapt Strat Glob Change 11:403–427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-005-9006-5
He R, Yuan X, Huang Z, Wang H, Jiang L, Huang J, Tan M, Li H (2019) Activated biochar with iron-loading and its application in removing Cr (VI) from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 579:123642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123642
Wang C, Wang H, Cao Y (2018) Pb(II) sorption by biochar derived from Cinnamomum camphora and its improvement with ultrasound-assisted alkali activation. Colloids Surf A 556:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.08.036
Yang F, Zhang S, Sun Y, Cheng K, Li J, Tsang DCW (2018) Fabrication and characterization of hydrophilic corn stalk biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composites for efficient metal removal. Biores Technol 265:490–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.06.029
Zhou N, Wang Y, Huang L, Yu J, Chen H, Tang J, Xu F, Lu X, Zhong M-e, Zhou Z (2019) In situ modification provided by a novel wet pyrolysis system to enhance surface properties of biochar for lead immobilization. Colloids Surf A 570:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.03.012
Su H, Fang Z, Tsang PE, Zheng L, Cheng W, Fang J, Zhao D (2016) Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by biochar-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 318:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.039
Li H, Chen YQ, Chen S, Wang XL, Guo S, Qiu YF, Liu YD, Duan XL, Yu YJ (2017) Wheat straw biochar-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron for removal of trichloroethylene from groundwater. PLoS ONE 12(3):e0172337. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172337
Fan C, Chen N, Qin J, Yang Y, Feng C, Li M, Gao Y (2020) Biochar stabilized nano zero-valent iron and its removal performance and mechanism of pentavalent vanadium(V(V)). Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 599:124882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124882
Zhang S, Lyu H, Tang J, Song B, Zhen M, Liu X (2018) A novel biochar supported CMC stabilized nano zero-valent iron composite for hexavalent chromium removal from water. Chemosphere 217:686–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.040
Yan J, Han L, Gao W, Xue S, Chen M (2014) Biochar supported nanoscale zerovalent iron composite used as persulfate activator for removing trichloroethylene. Biores Technol 175:269–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.103
Li C, Zhang L, Gao Y, Li A (2018) Facile synthesis of nano ZnO/ZnS modified biochar by directly pyrolyzing of zinc contaminated corn stover for Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cr(VI) removals. Waste Manage 79:625–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.08.035
Tang J, Lv H, Gong Y, Huang Y (2015) Preparation and characterization of a novel graphene/biochar composite for aqueous phenanthrene and mercury removal. Biores Technol 196:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.047
Xia D, Tan F, Zhang C, Jiang X, Chen Z, Li H, Zheng Y, Li Q, Wang Y (2016) ZnCl2 -activated biochar from biogas residue facilitates aqueous As(III) removal. Appl Surf Sci 377:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.109
Yu Y, An Q, Jin L, Luo N, Li Z, Jiang J (2019) Unraveling sorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by FeCl3 and ZnCl2-modified corn stalks biochar: implicit mechanism and application. Bioresour Technol 297:122466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122466
Wang J, Chen N, Li M, Feng C (2017) Efficient removal of fluoride using polypyrrole-modified biochar derived from slow pyrolysis of pomelo peel: sorption capacity and mechanism. J Polym Environ 26:1559–1572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1061-y
Quan G, Sun W, Yan J, Lan Y (2014) Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on biochar: characterization and reactivity for degradation of acid orange 7 from aqueous solution. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2195-3
Wu Y, Pang H, Yao W, Wang X, Yu S, Yu Z, Wang X (2018) Synthesis of rod-like metal-organic framework (MOF-5) nanomaterial for efficient removal of U(VI): batch experiments and spectroscopy study. Sci Bull 63(13):831–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2018.05.021
Yu J, Jiang C, Guan Q, Ning P, Gu J, Chen Q, Zhang J, Miao R (2017) Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by supported ZnO nanoparticles on biochar derived from waste water hyacinth. Chemosphere 195:632–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.128
Korichi S, Bensmaili A (2009) Sorption of uranium (VI) on homoionic sodium smectite experimental study and surface complexation modeling. J Hazard Mater 169(1–3):780–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.014
Zhang C, Zhang W, Zhou XH (2009) Immobilization of U(VI) in solution by zero-valent iron. Uranium Min Metall 28(3):155–157. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-8063.2009.03.010
Vilardi G, Palma LD, Verdone N (2019) A physical-based interpretation of mechanism and kinetics of Cr(VI) reduction in aqueous solution by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Chemosphere 220:590–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.175
Ruan Y, Zhang H, Yu Z, Diao Z, Song G, Su M, La H, Chen D, Wang S, Kong L (2021) Phosphate enhanced uranium stable immobilization on biochar supported nano zero valent iron. J Hazard Mater 424:127119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127119
Liu Q, Yiwen Xu, Guodong Z, Yilong H, Weifan L (2022) Removal of U(VI) from water by biochar supported green iron nanoparticles. Acta Materiae Compos Sinica 39(12):5934–5945. https://doi.org/10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211129.004
Wang J, Duan H, Tang H, Yu S, Zhu H, Wang X (2020) Carbothermic synthesis of carbon-supported zero-valent iron material for removal of U(VI) from aqueous solution. J Inorg Mater 35:373–380. https://doi.org/10.15541/JIM20190378
Zhang H, Ruan Y, Liang A, Shih K, Diao Z, Su M, La H, Chen D, Lu H, Kong L (2019) Carbothermal reduction for preparing nZVI/BC to extract uranium: Insight into the iron species dependent uranium adsorption behavior. J Clean Prod 239:117873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117873
Qian L, Liu S, Zhang W, Chen Y, Ouyang D, Han L, Yan J, Chen M (2018) Enhanced reduction and adsorption of hexavalent chromium by palladium and silicon rich biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Colloid Interface Sci 533:428–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.075
Zhai S, Li M, Wang D, Zhang L, Yang Y, Fu S (2019) In situ loading metal oxide particles on bio-chars: reusable materials for efficient removal of methylene blue from wastewater. J Clean Prod 220:460–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.152
Son E-B, Poo K-M, Chang J-S, Chae K-J (2017) Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions using engineered magnetic biochars derived from waste marine macro-algal biomass. Sci Total Environ 615:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.171
Xie Y, Fang Q, Li M, Wang S, Luo Y, Wu X, Lv J, Tan W, Wang H, Tan K (2019) Low concentration of Fe(II) to enhance the precipitation of U(VI) under neutral oxygen-rich conditions. Sci Total Environ 711:134827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134827
Ilton ES, Bagus PS (2011) XPS determination of uranium oxidation states. Surf Interface Anal 43(13):1549–1560. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.3836
Nico PS, Stewart BD, Fendorf S (2009) Incorporation of oxidized uranium into Fe (hydr)oxides during Fe(II) catalyzed remineralization. Environ Sci Technol 43(19):7391–7396. https://doi.org/10.1021/es900515q
Boland DD, Collins RN, Glover CJ, Payne TE, Waite TD (2014) Reduction of U(VI) by Fe(II) during the Fe(II)-accelerated transformation of ferrihydrite. Environ Sci Technol 48(16):9086–9093. https://doi.org/10.1021/es501750z
Boland DD, Collins RN, Payne TE, Waite TD (2011) Effect of amorphous Fe(III) oxide transformation on the Fe(II)-mediated reduction of U(VI). Environ Sci Technol 45(4):1327–1333. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101848a
Massey MS, Lezama-Pacheco JS, Jones ME, Ilton ES, Cerrato JM, Bargar JR, Fendorf S (2014) Competing retention pathways of uranium upon reaction with Fe(II). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 142:166–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2014.07.016
Mei H, Tan X, Tan L, Meng Y, Chen C, Fang M, Wang X (2018) Retention of U(VI) by the formation of Fe precipitates from oxidation of Fe(II). ACS Earth Space Chem 2(10):968–976. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.8b00055
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11705082 and 51874180) and Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2023JJ30513) as well as Research Project of Education Department of Hunan Province (22A0303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Q., Wang, J., Liu, Q. et al. High-efficiency removal of U(VI) from low-concentration uranium-bearing wastewater using ZnCl2-modified activated carbon loading nZVI. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 3977–3990 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09091-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09091-0