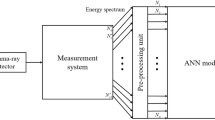
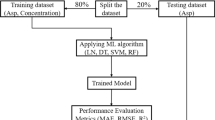
Abstract
A method to analyse radio-isotope activity in a large number of low-resolution gamma-ray bands corresponding to a mix of isotopes is conferred in the current article. Analysis of overlapped low-resolution gamma-ray bands of radio-isotope mixtures selected for this the work. Machine learning is suitable for radio-isotope mixture evaluations because it uses abstract spectrum informa-tion like overlapping peak geometries and the Compton continuum. Among the most promising options for automating gamma-ray spectroscopy, pattern recognition methods like convolution neural networks are best suitable. CNNs may automate gamma-ray spectroscopy. These models simulate professional spectroscopy. These models discovered gamma-ray bands with substantial calibration error and unknown background radiation fields.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trevisi R, Risica S, D’Alessandro M, Paradiso D, Nuccetelli C (2012) Natural radioactivity in building materials in the European Union: a database and an estimate of radiological significance. J Environ Radioact 2012(105):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2011.10.001
Markkanen M (1995) Radiation dose assessments for materials with elevated natural radioactivity. Painatuskeskus Oy, Helsinki, p 38
Turhan Ş (2008) Assessment of the natural radioactivity and radiological hazards in Turkish cement and its raw materials. J Environ Radioact 99:404–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2007.11.001
Righi S, Bruzzi L (2006) Natural radioactivity and radon exhalation in building materials used in Italian dwellings. J Environ Radioact 88:158–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2006.01.009
Khan K, Khan HM (2001) Natural gamma-emiting radionuclides in Pakistani Portland cement. Appl Radiat Isotopes 54:861–865. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8043(00)00327-4
Kim YH, Kim DG, Pak K, Jeong JY, Kim JC, Yang HC, Goh SB, Kim YK (2023) Identification of multiple radioisotopes through convolutional neural networks trained on 2-D transformed gamma spectral data from CsI(Tl) spectrometer. Radiat Phys Chem 210:111054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2023.111054
Piccolo A (2023) Thesis: identification of radioisotope using Artificial Intelligence techniques for gamma-ray spectra measurements
Usman R, Ibrahim U, Yusuf SD, Mustapha IM, Ugwu EI, Ayanninuola OS (2022) Identification of Medical and Industrial Used Radioisotopes in Mining Sites of Nasarawa, Nasarawa State, Nigeria. J Oncol Resarch 4:27–33
Kim J, Lee D, Kim J, Kim G, Hwang J, Kim W, Cho G (2022) Radioisotope identification using sparse representation with dictionary learning approach for an environmental radiation monitoring system. Nucl Eng Technol 54(3):1037–1048
Tomita H, Hara S, Mukai A, Yamagishi K, Ebi H, Shimazoe K, Kamada K (2022) Path-planning system for radioisotope identification devices using 4π gamma imaging based on random forest analysis. Sensors 22(12):4325
AMADÈ NS, Bettelli M, Zappettini A, Zambelli N (2022) U.S. Patent Application No. 17/507,177
Masri S, LeBrón AM, Logue MD, Flores P, Ruiz A, Reyes A, Rubio JM, Wu J (2022) Use of radioisotope ratios of lead for the identification of historical sources of soil lead contamination in Santa Ana California. Toxics 10(6):304
Wang Y, Li S, Huo Y, Yang J, Zhang Q (2022) Explainable neural network algorithm for rapid radionuclide identification under low count gamma-ray spectrum data. In International conference on nuclear engineering. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Vol 86397, p V005T05A051
Elmaghraby EK, Tohamy M, Comsan MNH (2019) Determination of isotopes activity ratio using gamma ray spectroscopy based on neural network model. Appl Radiat Isot 148:19–26
Gomez-Fernandez M, Wong WK, Tokuhiro A, Welter K, Alhawsawi AM, Yang H, Higley K (2021) Isotope identification using deep learning: an explanation. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A 988:164925
Cooper A, Doyle O, Bourke A (2021) Supervised Clustering for Subgroup Discovery: An Application to COVID-19 Symptomatology. Joint European conference on machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases. Springer, Cham, pp 408–422
Marton S, Lüdtke S, Bartelt C (2022) Explanations for neural networks by neural networks. Appl Sci 12(3):980
He J, Tang X, Gong P, Wang P, Wen L, Huang X, Han Z, Yan W, Gao L (2018) Rapid radionuclide identification algorithm based on the discrete cosine transform and BP neural network. Ann Nucl Energy 112:1–8
Moshkbar-Bakhshayesh K (2020) Development of an efficient technique for constructing energy spectrum of NaI (Tl) detector using spectrum of NE102 detector based on supervised model-free methods. Radiat Phys Chem 176:109063
Zhang C, Hu G, Luo F, Xiang Y, Ding G, Chu C, Zeng J, Ze R, Xiang Q (2019) Identification of SNM based on low-resolution gamma-ray characteristics and neural network. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A 927:155–160
Galib SM, Bhowmik PK, Avachat AV, Lee HK (2021) A comparative study of machine learning methods for automated identification of radioisotopes using NaI gamma-ray spectra. Nucl Eng Technol 53(12):4072–4079
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author have declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Paleti, B., Sastry, G.H. Identification of gamma emitting natural isotopes in environmental sample spectra: convolutional neural network approach. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 5273–5281 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09052-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09052-7