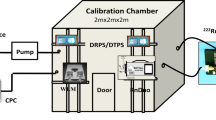
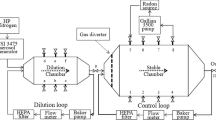
Abstract
To accurately measure and evaluate the radiation dose of 220Rn and its progeny, a 220Rn chamber with an airflow model has been developed and studied, but it is difficult to take into consideration many relevant factors such as adsorption, wall attachment, and decay. This paper proposes the concept of cyclic loss rate of 220Rn progeny based on progeny supplement technology, establishes a theoretical formula to calculate the cyclic loss rate, and analyzes the relationship between cyclic loss rate, fan frequency, and aerosol particle size through both experiments and modelling methods. The feasibility of the cyclic loss rate model is experimentally verified.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosino F, Buompane R, Pugliese M et al (2018) RaMonA system for radon and thoron measurement. Il Nuovo cimento della societa Italiana di fisica, C. Geophys Space Phys 41(6):1–7
Ambrosino F, Sabbarese C, Giudicepietro F et al (2021) Study of surface emissions of 220Rn (Thoron) at two sites in the campi flegrei caldera (Italy) during volcanic unrest in the period 2011–2017. Appl Sci 11(13):5809
Nuhu H, Hashim S, Sanusi MSM et al (2022) Thoron activity concentration in Malaysian soil gas: geogenic impact assessment. Radiat Phys Chem 200:110303
Sun QF, Shinji T, Hou CS (2005) Concentrations of indoor radon and thoron in cave-dwellings with discussions on risk estimation of lung cancer. Chin J Radiat Mediat Prot 25(1):5
Kumar M, Sharma N (2021) Estimation of 222Rn, 220Rn exhalation rate and 226Ra, 232Th, 40K radionuclides in the soil samples of different regions of Gurdaspur district, Punjab. Mater Today Proc 49:3396–3402
UNSCEAR (2008) Source and effects of ionizing radiation. United nations scientific committee on the effects of atomic radiation
Bigu J (1988) Effect of selected variables on airborne 220Rn progeny concentrations. Health Phys 54(1):93–98
Rttger A, Honig A, Dersch R et al (2010) A primary standard for activity concentration of Rn-220 (thoron) in air. Appl Radiat Isot Incl Data Instrum Methods Agric Ind Med 68(7–8):1292–1296
Rottger A, Honig A, Arnold D (2009) The German thoron progeny chamber-concept and application. Appl Radiat Isot 67(5):839–842
Sorimachi A, Ishikawa T, Tokonami S (2014) Development of an aerosol chamber for calibration of 220Rn progeny detectors. Rev Sci Instrum 85(9):095104
Kobayashi Y, Tokonami S, Takahashi H et al (2005) Practicality of the thoron calibration chamber system at NIRS, Japan. Int Congr 1276:281–282
Ambrosino F, Sabbarese C, Buompane R et al (2017) Analysis of alpha particles spectra of the Radon and Thoron progenies generated by an electrostatic collection detector using new software. Appl Radiat Isot Incl Data Instrum Methods Agric Ind Med 122:180–185
Rinaldi L, Ambrosino F, Roca V et al (2022) Study of 222–220Rn measurement systems based on electrostatic collection by using Geant4+COMSOL simulation. Appl Sci 12(1):507
Xiao D, Zhou J, Qiu S, et al (2011) Research on calibration and experimental device of 220Rn and its progeny measuring instrument. Radiation protection sub-volume, volume two. China Nucl Sci Technol Progress Rep (in Chinese)
Lin J, Xiao D, He Z et al (2021) Regulation and control methods for the unattached fraction of 220Rn progeny in a 220Rn progeny chamber. J Environ Radioact 235–236:106653
Zhao C, Zhuo W, Chen B et al (2010) Characteristic and performance of a simple thoron chamber. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 141(4):444–447
Pressyanov D, Mitev K, Georgiev S et al (2017) Laboratory facility to create reference radon plus thoron atmosphere under dynamic exposure conditions. J Environ Radioact 166:181–187
Moere H, Falk R, Nyblom L (1996) A bench-top calibration chamber for 220Rn activity in air. Environ Int 22(S1):1147–1153
Faa B, Vr B, Rba B et al (2020) Development and calibration of a method for direct measurement of 220Rn (thoron) activity concentration - ScienceDirect. Appl Radiat Isot 166:109310
Mishra R, Mayya YS (2008) Study of a deposition-based direct thoron progeny sensor (DTPS) technique for estimating equilibrium equivalent thoron concentration (EETC) in indoor environment. Radiat Meas 43(8):1408–1416
Mishra R, Mayya YS, Kushwaha HS (2009) Measurement of 220Rn/222Rn progeny deposition velocities on surfaces and their comparison with theoretical models. J Aerosol Sci 40(1):1–15
Mishra R, Prajith R, Sapra BK et al (2010) Response of direct thoron progeny sensors (DTPS) to various aerosol concentrations and ventilation rates. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 268(6):671–675
He Z (2014). Study on technology of regulating and controlling 220Rn progeny in 220Rn chamber, University of South China (in Chinese)
Li WW, Zhou QZ, He ZZ et al (2020) Optimization of the thoron progeny compensation system of a thoron calibration chamber. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 324(3):1255–1263
He Z, Xiao D, Lidan L et al (2017) Stable control of thoron progeny concentration in a thoron chamber for calibration of active sampling monitors. Radiat Meas 102:27–33
Qiu S (2006) Calibration of a 220Rn flow-through source. Radiat Environ Biophys 45(3):215–220
Model TSI (2002) Model 3475 condensation monodisperse aerosol generator. TSI Incorporated, Shoreview
Zhou Q, Zhao G, Xiao D (2009) Reconstruction measurement method of 222Rn, 220Rn progeny levels by alpha spectrum data. Nucl Technol 32(6):164–168 (in Chinese)
Porstendorfer IJ (1984) Behaviour of radon daughter products in indoor air. Radiat Prot Dosim 7(1–4):107–113
Acknowledgements
The research work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11875035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Li, G., Zhou, Q. et al. Study of the cyclic loss rate of 220Rn progeny in a 220Rn chamber by an airflow model. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 2633–2641 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-08930-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-08930-4