Abstract
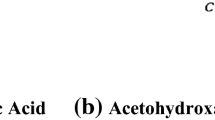
Reprocessing of high plutonium content spent nuclear fuel from fast reactors results in the generation of lean organic solution containing considerably high amount of di-butyl phosphoric acid. Use of sodium carbonate as wash reagent has constraints in the view point of process operation. In this context, an alternative method for the wash of radiolytically degraded 1.1 M TBP/n-dodecane was proposed. Studies indicated that that the use of 1.5 M of hydrazine carbonate was effective for the treatment of solvent degraded up to 300 kGy and the product obtained were comparable to the fresh solvent.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKay HAC, Miles JH, Swanson JL (1984) The Purex process. In: Schulz WW, Burger LL, Navratil JD (eds) Science and technology of tri butyl phosphate, vol 3. CRS Press, Boca Raton
Herbst RS, Baron P, Nilsson M (2011) Standard and advanced separation: PUREX processes for nuclear fuel reprocessing. Adv Sep Tech Nucl Fuel Reprocess Radioact Waste Treat 6:141–175
Pavia AP, Malik P (2004) Recent advances on the chemistry of solvent extraction applied to the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels and radioactive wastes. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 261(2):485–496
Tahraoui A, Morris JH (1995) Decomposition of solvent extraction media during nuclear reprocessing: literature review. Sep Sci Technol 30(13):2603
Dzhivanova ZV, Belova EV, Tkhorzhnitskii GP (2015) Radiation resistance of hydrocarbon diluents of tri-butyl phosphate in a two-phase system and carbonate regeneration of the solvent. Radiochemistry 57:143–151
Natarajan R (2015) Reprocessing of spent fast reactor nuclear fuels. In: Taylor R (ed) Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy, reprocessing and recycling of spent nuclear fuel, pp 213–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-78242-212-9.00009-
Satyabrata M, Mallika C, Pandey NK, Mudali UK, Natarajan R (2015) Effect of radiolysis in altering the physiochemical and metal retention properties of solvent-diluent-acid systems. Sep Sci Technol 50(11):1671–1676
Satyabrata M, Joshi S, Mallika C, Pandey NK (2017) Physicochemical properties of PUREX solvent on hydrolytic and chemical treatment. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314:2301–2308
Amber W, Patricia PH (2010) Review of physical and chemical properties of tri butyl phosphate/diluent/nitric acid systems. Sep Sci Technol 45:1753–1762
Laurence B, Marie-Christine C (2010) Radiolysis of solvents used in nuclear fuel reprocessing. In: Sengupta AK, Moyer BA (eds) Ion exchange & solvent extraction, a series of advances, vol 19, chapter 8. CRS Press, Boca Raton
Satyabrata M, Pandey NK (2019) Physiochemical properties of gamma-irradiated tri-iso-amyl phosphate-dodecane system: effect of aqueous phase acidity. Solvent Extr Ion Exch 37(6):446–460
Ginisty C, Guillaume B (1990) Solvent distillation studies for a PUREX reprocessing. Sep Sci Technol 25:1941–1952
Reif DJ (1988) Canyon solvent cleaning with activated alumina. Nucl Technol 83:190–196
Mike C, Billy K, Whittaker D, Taylor R, Wilden A, Modolo G, Iván SG, Ana NGA, Montano HG (2021) Status on solvent clean- up & recycling. GENIORS—D3.4—Issued on 2021-05-28 by NNL
Araujo BF, Matsuda HT, Kuada TA, Araujo JA (1992) Continuous removal of radiolytic products from TBP extraction systems. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Lett 166:75–84
Drain F, Moulin JP, Hugelmann D, Lucas P (1996) Advanced solvent management in reprocessing, 5 years of industrial experience. ISEC, pp 789–794
Sugai H (1992) Crud in solvent washing process for nuclear fuel reprocessing. J Nucl Sci Technol 29:445–453
Burger LL (1955) The chemistry of tri-butyl phosphate. United States Atomic Energy Commission Report HW-40910, Hanford Works, Richland, Washington
Tripathi SC, Sumathi S, Ramanujam A (1999) Effects of solvent recycling on radiolytic degradation of 30% tributyl phosphate-n dodecane-HNO3 system. Sep Sci Technol 34(14):2887–2903
Germain M, Pluot P (1980) Diluent washing of aqueous phase using centrifugal contactors. In: Proceedings of the international solvent extraction conference ISEC’80, Liege, Belgium, pp 80–218
Sicilio F, Goodgame TH, Wilkins B Jr (1961) Purification of irradiated tributyl phosphate by distillation in kerosene-type diluent. Nucl Sci Eng 9(4):455–461. https://doi.org/10.13182/NSE61-A25909P
Mailen JC, Tallent OK (1984) Improved PUREX solvent scrubbing methods, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, CONF-840802-10, Tennessee
Vishnu AP, Rajeev R, Velavendan P, Pandey NK, Mudali UK (2016) Modeling and simulation of diluent recovery unit in PUREX solvent regeneration system. Prog Nucl Energy 2016(104):359–367
Schulz WW (1970) Macro reticular ion exchange resin clean-up of PUREX process TBP solvent (No. ARH-SA-58-RD; CONF-710417-2). Atlantic Richfield Hanford Co., Richland
Schulz WW (1972) Macro reticular anion exchange resin clean-up of PUREX process TBP solvent (No. ARH-SA-129; CONF-720607-21). Atlantic Richfield Hanford Co., Richland
Mailen JC (1988) Secondary Purex solvent cleanup: laboratory development. Nucl Technol 83:182–189
Tallent OK, Mailen JC (1982) An alternative solvent cleanup method using a hydrazine oxalate wash reagent. Nucl Technol 59:51–62
Goldacker H, Schieder H, Steingrunn F, Stieglitz L (1976) A newly developed solvent wash process in nuclear fuel reprocessing decreasing the waste volume. Kerntechnik 18(10):426–430
Imaizumi H, Ban Y, Sato M, Asakura T, Morita Y (2005) Washing properties of n-butyl amine oxalate in degraded solvent. JAERI, Tokai
Klopfenstein RK, Krekeler RH, Leist NR, Hicks CT (1960) Studies of the behavior of the TBP-kerosene Solvent in uranium refining: quality evaluation and treatment techniques for used solvent. Office of Technical Services, Washington
Tallent OK, Crouse DJ, Mailen JC (1982) Method for cleaning solution used in nuclear fuel reprocessing. United States Patent US 4358426
Natarajan R, Baldev R (2015) Technology development of fast reactor fuel reprocessing in India. Curr Sci 108:30–38
Govindan P, Sukumar S, Vijayan KS, Santhosh KG, Ganesh S, Sharma PK, Dhamodharan K, Subba RR, V, Venkataraman R, Natarajan R, (2010) Recovery of plutonium from carbonate wash solutions. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 284:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0456-1
Venkatesan KA, Kumaresan R, Antony MP, Kumar T, Srinivasan TG, Vasudeva Rao PR (2012) Characterization of high active waste (155 GWd/Te) arising from fast reactor fuel reprocessing. Radiochim Acta 100(11):843–850
Satyabrata M, Anil KS, Sridhar M, Mallika C, Pandey NK, Mudali UK (2018) Identification of diluent degradation products in radiolyzed PUREX solvent. Solvent Extr Ion Exch 36(2018):54–65
Satyabrata M, Vishnu AP, Sridhar M, Pandey NK, Sankaran K, Joseph M (2019) Characterization of gamma irradiated PUREX solvent—a systematic study. Sep Sci Technol 55:1485–1494
Swanson JL (1971) The destruction of nitrous acid and hydrazoic acid in purex systems, BNWL-B-121. Battelle Pacific Northwest Laboratories
Hardy CJ, Scargill D (1959) Studies on mono- and di-n-butyl phosphoric acids—II—the solubility and distribution of mono- and di-n butyl phosphoric acids in aqueous-organic solvent systems. J Inorg Nucl Chem 11:128–143
Pierce RA, Thompson MC, Ray RJ (2001) Solubility limits of HDBP in U-nitric acid solutions. Sep Sci Technol 36(5–6):767–783
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S., Anand, P.V., Patra, C. et al. Solvent wash studies for the removal of di-butyl phosphate from spent solvent under simulated PUREX condition. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 343–353 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08729-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08729-9