Abstract
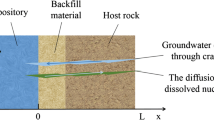
Clay surrounding nuclear waste in an underground repository for radioactive waste gets modified by fluid emanating from surrounding host rock. In this work, caesium (Cs+) diffusion was investigated in smectite-rich natural clay saturated with varying exchange ions (Na+, K+). In a transient in-diffusion process carried over 28–60 °C, Cs+ diffusion was found faster (Diffusion coefficient, Da = 6.5 × 10–12–5.2 × 10–12 m2s−1) in K+–saturated clay compared to that in Na+–clay. Small-angle X-ray diffraction revealed three and two molecular water layers present in interlayer of compacted water-saturated Na+–clay and K+–clay, respectively. These studies were rationalised considering exchange ions–dependent stacking of clay platelets and a role of clay microstructural details in Cs+ diffusion characteristics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) (2014) Geological disposal: a review of the development of bentonite barriers in the KBS-3V disposal concept. Technical note no. 21665941
Grambow B, Landesman C, Ribet S (2014) Nuclear waste disposal: I. laboratory simulation of repository properties. Appl Geochem 49:237–246
Kienzler B, Geckeis H (2018) Radioactive wastes and disposal options. EPJ Web Conf 189:14–35
Carlson L, Karnland O, Oversby VM, Rance AP, Smart NR, Snellman M, Vahanen M, Werme LO (2007) Experimental studies of the interactions between anaerobically corroding iron and bentonite. Phys Chem Earth 32:334–345
Appelo CAJ, Van Loon LR, Wersin P (2010) Multicomponent diffusion of a suite of tracers (HTO, Cl, Br, I, Na, Sr, Cs) in a single sample of Opalinus clay. Geochem Cosmochim Acta 74:1201–1219
Gimmi T, Kosakowski G (2011) How mobile are sorbed cations in clays and clay rocks. Environ Sci Technol 45:1443–1449
Sánchez FG, Van Loon LR, Gimmi T, Jakob A, Glaus MA, Diamond LW (2008) Self-diffusion of water and its dependence on temperature and ionic strength in highly compacted montmorillonite illite and kaolinite. Appl Geochem 23:3840–3851
Melkior T, Gaucher EC, Brouard C, Yahiaoui S, Thoby D, Clinar Ch, Ferrage E, Guyonnet D, Tournassat C, Coelho D (2009) Na+ and HTO diffusion in compacted bentonites: effect of surface chemistry and related texture. J Hydrol 370:9–20
Missana T, Alonso U, Fernández AM, García-Gutiérrez M (2018) Colloidal properties of different smectite clays: significance for the bentonite barrier erosion and radionuclide transport in radioactive waste repositories. Appl Geochem 97:157–166
Tertre E, Delville A, Dimitri P, Hubert F, Ferrage E (2015) Cation diffusion in the interlayer space of swelling clay minerals – A combined macroscopic and microscopic study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 149:251–267
Van Loon LR, Glaus MA, Muller W (2007) Anion exclusion effects in compacted bentonites: towards a better understanding of anion diffusion. Appl Geochem 22:2536–2552
Kozaki T, Fujishima A, Sato S, Ohashi H (1998) Self-diffusion of sodium ions in compacted sodium montmorillonite. Nucl Technol 121:63–69
Suzuki S, Haginuma M, Suzuki K (2004) Study of sorption and diffusion of 137Cs in compacted bentonites saturated with saline water at 60 0C. J Nucl Sci Techol 44:81–89
Pusch R (2002) The buffer and backfill handbook, Part 1: Definitions, basic relationships and laboratory methods. SKB Technical Report TR 02 - 20
Idiart A, Pekala M (2016) Models for diffusion in compacted Bentonite. SKB TR - 15 - 06 Report
Tachi Y, Yotsuji K (2014) Diffusion and sorption of Cs+, Na+, I-, and HTO in compacted sodium montmorillonite as a function of porewater salinity: Integrated sorption and diffusion model. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 132:75–93
Bourg IC, Sposito G, Bourg ACM (2006) Tracer diffusion in compacted water-saturated bentonite. Clays Clay Miner 54:363–374
Whittaker ML, Lammers LN, Carrero S, Gilbert B, Banfield JF (2019) Ion exchange selectivity in clay is controlled by nanoscale chemical-mechanical coupling. PNAS 44:22052–22057
Kasar S, Kumar S, Bajpai RK, Tomar BS (2016) Diffusion of Na(I), Cs(I), Sr(II) and Eu(III) in smectite rich natural clay. J Environ Radioact 151:218–223
Kasar S, Kumar S, Saha A, Bajpai RK, Tomar BS (2017) Mechanistic and thermodynamic aspects of Cs(I) and Sr(II) interactions with smectite-rich natural clay. Environ Earth Sci 76:274–279
Kumar S, Pente AS, Bajpai RK, Kaushik CP, Tomar BS (2013) Americium sorption on smectite-rich natural clay from granitic ground water Appl. Geochem 35:28–34
Meier LP, Kahr G (1999) Determination of the cation exchange capacity of Clay minerals using the complexes of copper(II) ion with triethylenetetramine and tetraethylenerpentamine. Clays Clay Miner. 47:386–388
Crank J (1975) The mathematics of diffusion 2ndedn. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 11–21
Kozaki T, Liu J, Sato S (2008) Diffusion mechanism of sodium ions in compacted montmorillonite under different NaCl concentration. Phys Chem Earth 33:957–961
Watanabe T, Sato T (1988) Expansion characteristics of montmorillonite and saponite under various relative humidity conditions. Clay Sci 7:129–138
Bourg IC (2004) Tracer diffusion of water and inorganic ions in compacted saturated sodium Bentonite. University of California Berkeley, UK
Cherif MA, Martin-Garin A, Gerad F, Bildstein O (2017) A robust and parsimonious model for caesium sorption on clay minerals and natural clay materials. Appl Geochem 87:22–37
Missana T, Benedicto A, García-Gutiérrez M, Alonso U (2014) Modeling caesium retention onto Na-, K- and Ca-smectite: effects of ionic strength, exchange and competing cations on the determination of selectivity coefficients. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 128:266–277
Pusch R, Karnland O, Muurinen A (1989) Swedish nuclear fuel and waste management. SKB Tech. Rep. 34 – 89
Sato H, Ashida T, Kohara Y, Yui M, Sasaki N (1992) Effect of dry density on diffusion of some radionuclides in compacted sodium bentonite. J Nucl Sci Technol 29(9):873–882
Bourg IC, Sposito G, Bourg ACM (2007) Modelling cation diffusion in compacted water-saturated sodium bentonite at low ionic strength. Environ Sci Technol 41:8118–8122
Tessier D (1990) Behaviour and microstructure of clay minerals. In: de Boodt, M.F. et al. (Eds.) Soil Colloids and their Associations in Aggregates. Plenum Press. pp. 387 – 415 (Chapter 14)
Sato T, Watanabe T, Otsuka R (1992) Effects of layer charge, charge location, and energy change on expansion properties of dioctahedral smectites. Clays Clay Mineral 40:103–113
Bérend I, Cases JM, François M, Uriot JP, Michot LJ, Masion A, Thomas F (1995) Mechanism of adsorption and desorption of water vapour by homoionic montmorillonites: 2. The Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+ and Cs+ exchanged forms. Clays Clay Miner 43:324–336
Acknowledgements
Authors (SK, AC) are thankful to Head, CCS, RACD and Head RACD for their constant support and encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Chandane, A., Sengupta, A. et al. Diffusion of Cs+ in compacted Na+/K+–saturated smectite-rich natural clay: role of clay microstructure. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 203–210 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08709-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08709-z