Abstract
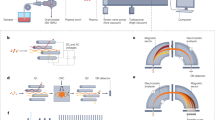
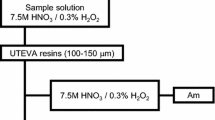
This paper describes the isotopic and quantitative analysis of single micrometer-sized uranium particles by multiple mass spectrometric techniques combined with a micromanipulating technique. Secondary ion mass spectrometry performed the best for the isotopic analysis of single uranium particles in terms of accuracy and precision compared to scanning electron microscope (SEM)/thermal ionization mass spectrometry and SEM/multicollector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (MC-ICP-MS). A single uranium particle was dissolved in high-purity acid and quantitated by MC-ICP-MS and isotope dilution MS. The resulting uranium mass per particle was close to the reference value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donohue DL (1998) Strengthening IAEA safeguards through environmental sampling and analysis. J Alloy Compd 271:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-8388(98)00015-2
Donohue DL (2002) Peer reviewed: strengthened nuclear safeguards. Anal Chem 74(1):28 A-35 A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac021909y
Amano Y (2016) IAEA safeguards: a vital contribution to international peace and security. IAEA Bull 57:1
Safeguards IAEA (2016) serving nuclear non-proliferation. IAEA Bull 57:4–7
Development and implementation support programme for nuclear verification 2020—2021 (2020) Vienna, Austria
Donohue DL (2002) Key tools for nuclear inspections. IAEA Bull 44:17–23
Esaka F, Esaka KT, Lee CG, Magara M, Sakurai S, Usuda S, Watanabe K (2007) Particle isolation for analysis of uranium minor isotopes in individual particles by secondary ion mass spectrometry. Talanta 71(3):1011–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2006.05.091
Kraiem M, Richter S, Kühn H, Aregbe Y (2011) Development of an improved method to perform single particle analysis by TIMS for nuclear safeguards. Anal Chim Acta 688(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.12.003
Park J-H, Park S, Song K (2013) Isotopic analysis of NUSIMEP-6 uranium particles using SEM-TIMS. Mass Spectrom Lett 4(3):51–54. https://doi.org/10.5478/MSL.2013.4.3.51
Gao J, Xu C, Zhao Y (2021) An improved method for determination of isotope ratios in individual uranium particles by thermal ionization mass spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta Part B 182:106252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2021.106252
Krachler M, Wallenius M, Nicholl A, Mayer K (2020) Spatially-resolved uranium isotopic analysis of contaminated scrap metal using laser ablation multi-collector ICP-MS. RSC Adv 10(28):16629–16636. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA02899A
Kappel S, Boulyga SF, Prohaska T (2012) Direct uranium isotope ratio analysis of single micrometer-sized glass particles. J Environ Radioact 113:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2012.03.017
Szakal C, Simons DS, Fassett JD, Fahey AJ (2019) Advances in age-dating of individual uranium particles by large geometry secondary ion mass spectrometry. Analyst 144(14):4219–4232. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AN00774A
Suzuki D, Tomita R, Tomita J, Esaka F, Yasuda K, Miyamoto Y (2021) Age determination analysis of a single uranium particle for safeguards. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 328(1):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07626-x
Fauré A-L, Dalger T (2017) Age dating of individual micrometer-sized uranium particles by secondary ion mass spectrometry: an additional fingerprint for nuclear safeguards purposes. Anal Chem 89(12):6663–6669. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00887
Middendorp R, Dürr M, Knott A, Pointurier F, Ferreira Sanchez D, Samson V, Grolimund D (2017) Characterization of the aerosol-based synthesis of uranium particles as a potential reference material for microanalytical methods. Anal Chem 89(8):4721–4728. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00631
Kraiem M, Richter S, Erdmann N, Kühn H, Hedberg M, Aregbe Y (2012) Characterizing uranium oxide reference particles for isotopic abundances and uranium mass by single particle isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 748:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.08.030
Richter S, Truyens J, Venchiarutti C, Aregbe Y, Middendorp R, Neumeier S, Kegler P, Klinkenberg M, Zoriy M, Stadelmann G, Macsik Z, Koepf A, Sturm M, Konegger-Kappel S, Venzin A, Sangely L, Tanpraphan T (2022) Certification of the first uranium oxide micro-particle reference materials for nuclear safety and security, irmm-2329p and irmm-2331p. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08255-8
Venchiarutti C, Richter S, Middendorp R, Aregbe Y, Centre ECJR (2019) NUSIMEP-9: uranium isotope amount ratios and uranium mass in uranium micro-particles: nuclear signatures inter-laboratory measurement evaluation programme. Publications Office of the European Union
Vogl J, Pritzkow W (2010) Isotope reference materials for present and future isotope research. J Anal At Spectrom 25(7):923–932. https://doi.org/10.1039/C000509F
Garner EL, Machlan LA, Shields WR (1971) Standard reference materials: uranium isotopic standard reference materials (Certification of uranium isotopic standard reference materials). vol 260–27. National Bureau of Standards, Washington, D.C.
Kim TH, Park J, Lee NR, Lee CG (2020) Improvement in the particle collection method to mitigate the mixing effect during uranium isotope analysis of environmental samples using secondary ion mass spectrometry. J Radionala Nucl Chem 326(3):1887–1894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07431-y
Park JH, Choi I, Song K (2010) A technique to minimize impurity signal from blank rhenium filaments for highly accurate tims measurements of uranium in ultra-trace levels. Mass Spectrom Lett 1(1):17–20. https://doi.org/10.5478/MSL.2010.1.1.017
Suzuki D, Saito-Kokubu Y, Sakurai S, Lee C-G, Magara M, Iguchi K, Kimura T (2010) A new method for isotope ratio measurement of uranium in trace amount by thermal ionization mass spectrometry: the continuous heating method. Int J Mass Spectrom 294(1):23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2010.04.007
Lee C-G, Park R, Park J, Lim SH (2020) A comparative study of ultra-trace-level uranium by thermal ionization mass spectrometry with continuous heating: Static and peak-jumping modes. Nucl Eng Technol 52(7):1532–1536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2019.12.023
Park J-H, Choi E-J (2016) Simultaneous determination of the quantity and isotopic ratios of uranium in individual micro-particles by isotope dilution thermal ionization mass spectrometry (ID-TIMS). Talanta 160:600–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.08.006
Williams JH (2016) Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement (The GUM). In: Quantifying Measurement. Morgan & Claypool Publishers. doi:https://doi.org/10.1088/978-1-6817-4433-9ch6
Usuda S, Magara M, Esaka F, Yasuda K, Saito-Kokubu Y, Lee C-G, Miyamoto Y, Suzuki D, Inagawa J, Sakurai S, Murata F (2010) QA/QC activities and estimation of uncertainty for ultra-trace analysis of uranium and plutonium in safeguards environmental samples. J Nucl Radiochem Sci 11(2):A5–A9. https://doi.org/10.14494/jnrs.11.A5
Park R, Lim SH, Han S-H, Lee MY, Park J, Lee C-G, Song K (2016) Improvement of measurement precisions for uranium isotopes at ultra trace levels by modification of the sample introduction system in MC-ICP-MS. Mass Spectrom Lett 7(2):50–54. https://doi.org/10.5478/MSL.2016.7.2.50
Lim SH, Han S-H, Park J-H, Park R, Lee MY, Park J, Lee C-G, Song K (2015) Validation of bulk analysis with simulated swipe samples containing ultra-trace amounts of uranium and plutonium using MC-ICP-MS. Mass Spectrom Lett 6(3):75–79. https://doi.org/10.5478/MSL.2015.6.3.75
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Nuclear Safety Research Program through the Korea Foundation of Nuclear Safety (KoFONS) using the financial resource granted by the Nuclear Safety and Security Commission (NSSC) of the Republic of Korea. (No. 2103086) and the Research and Operation Program of the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (No. 521330-22) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF-2021R1A2C2095822). The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.com) for the English language review. The authors would also like to thank fellow researchers in the field of the particle analysis of environmental samples for their help and advice.
Funding
The funding was provided by Nuclear Safety and Security Commission (Grant No. 2103086), Ministry of Science and ICT, South Korea (Grant No. NRF-2021R1A2C2095822) and Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (Grant No. 521330-22).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RP contributed to the study design, sample preparation, data collection, and writing the manuscript. C-G Lee and KHC contributed to the study design. JP contributed to the study design, sample preparation, data collection, and writing and editing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, R., Lee, CG., Chung, K.H. et al. Quantitative and isotopic analysis of single micrometer-sized uranium particles using multiple mass spectrometric techniques. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 2833–2840 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08683-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08683-6