Abstract
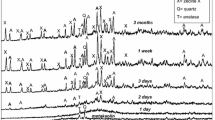
Using metakaolin and uranium tailings as raw materials and sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate as activators, an orthogonal experimental study was conducted to investigate the effects of metakaolin content, water glass modulus, and liquid–solid ratio on uranium tailings solidified body weight loss rate. SEM, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) were used to characterize the solidified product, as well as to measure the radon exhalation rate and analyze the radon exhalation law. The results show that the mass loss rate of the solidified body decreases as the liquid–solid ratio increases, first decreases and then increases as the metakaolin content increases, and first increases and then decreases as the water glass modulus increases. Metakaolin content is the most important influencing factor. Metakaolin incorporation effectively reduced sample mass loss and inhibited radon exhalation. The rate of radon exhalation was inversely related to metakaolin content. The orthogonal experiment determined that the optimal mixing ratio is 30% metakaolin, 0.4 liquid–solid ratio, and 1.2 water glass modulus. This experiment is significant in terms of long-term development for uranium tailings decommissioning and environmental protection.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galhardi JA, García-Tenorio R, Bonotto DM, Francés ID, Motta JG (2017) Natural radionuclides in plants, soils and sediments affected by U-rich coal mining activities in Brazil. J Environ Radioactiv 177:37–47
Nair RN, Sunny F, Manikandan ST (2010) Modelling of decay chain transport in groundwater from uranium tailings ponds. Appl Math Model 34(9):2300–2311
Dempsey S, Lyons S, Nolan A (2018) High Radon Areas and lung cancer prevalence: Evidence from Ireland. J Environ Radioactiv 182:12–19
Winde F, Brugge D, Nidecker A, Ruegg U (2017) Uranium from Africa—An overview on past and current mining activities: re-appraising associated risks and chances in a global context. J Afr Earth Sci 129:759–778
Zhang WY, Choi H, Sagawa T, Hama Y (2017) Compressive strength development and durability of an environmental load-reduction material manufactured using circulating fluidized bed ash and blast-furnace slag. Constr Build Mater 146:102–113
Hodhod OA, Alharthy SE, Bakr SM (2020) Physical and mechanical properties for metakaolin geopolymer bricks. Constr Build Mater 265:120217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120217
Chi M (2016) Synthesis and characterization of mortars with circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash and ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Constr Build Mater 123:565–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.07.071
van Jaarsveld JGS, van Deventer JSJ, Lukey GC (2002) The effect of composition and temperature on the properties of fly ash- and kaolinite-based geopolymers The effect of composition and temperature on the properties of fly ash- and kaolinite-based geopolymers. Chem Eng J 89(1):63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(02)00025-6
Davidovits J (1989) Geopolymers and geopolymeric materials. J Therm Anal 35(2):429–441
Matteo M, Valentina M, Elettra P, Francesco M, Elena L, Ferruccio D (2016) Geopolymers as solid adsorbent for CO2 capture. Chem Eng Sci 148:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2016.04.013
Nath SK, Maitra S, Mukherjee S, Kumar S (2016) Microstructural and morphological evolution of fly ash based geopolymers. Constr Build Mater 111:758–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.106
Tchadjié LN, Djobo JNY, Ranjbar N, Tchakouté HK, Kenne BBD, Elimbi A et al (2016) Potential of using granite waste as raw material for geopolymer synthesis. Ceram Int 42(2):3046–3055
Zeng SX, Wang JL (2016) Characterization of mechanical and electric properties of geopolymers thesized using four locally available fly ashes. Constr Build Mater 121:386–399
Zheng L, Wang W, Shi YC (2010) The effects of alkaline dosage and Si/Al ratio on the immobilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash-based geopolymer. Chemosphere 79(6):665–671
Liang GW, Zhu HJ, Zhang ZH, Wu QS, Du JZ (2019) Investigation of the waterproof property of alkali-activated metakaolin geopolymer added with rice husk ash. J Clean Prod 230:603–612
Kim B, Lee S (2020) Review on characteristics of metakaolin-based geopolymer and fast setting. J Korean Ceram Soc 57(4):368–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-020-00043-y
Rahman ROA, Rakhimov RZ, Rakhimova NR, Ojovan MI (2014) Cementitious Materials for Nuclear Waste Immobilization. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Hoboken
Güneyisi E, Gesoğlu M, Karaoğlu S, Mermerdaş K (2012) Strength, permeability and shrinkage cracking of silica fume and metakaolin concretes. Constr Build Mater 34:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.02.017
Sabir BB, Wild S, Bai J (2001) Metakaolin and calcined clays as pozzolans for concrete: a review. Cement Concr Compos 23(6):441–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(00)00092-5
Jian Tongding LZ (2018) Effects of metakaolin and silica fume on properties of concrete. Aci Mater J 99(4):393–398
Xu M, He Y, Wang C, He X, He X, Liu J et al (2015) Preparation and characterization of a self-supporting inorganic membrane based on metakaolin-based geopolymers. Appl Clay Sci 115:254–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.03.019
He Y, Cui X, Liu X, Wang Y, Zhang J, Liu K (2013) Preparation of self-supporting NaA zeolite membranes using geopolymers. J Membr Sci 447:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.07.027
Tang Q, He Y, Wang Y, Wang K, Cui X (2016) Study on synthesis and characterization of ZSM-20 zeolites from metakaolin-based geopolymers. Appl Clay Sci 129:102–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.05.011
Jinmo A, Won-Seok K, Wooyong U (2019) Development of metakaolin-based geopolymer for solidification of sulfate-rich hybrid sludge waste. J Nucl Mater 518:247–255
Wan Q, Rao F, Song SX, Patino CAL, Ma YQ, Yin WZ (2019) Consolidation of mine tailings through geopolymerization at ambient temperature. J Am Ceram Soc 102(5):2451–2461
Ge YY, Cui XM, Liao CL, Li ZL (2017) Facile fabrication of green geopolymer/alginate hybrid spheres for efficient removal of Cu (II) in water: batch and column studies. Chem Eng J 311:126–134
Vincent Cantarel TMAI (2018) Geopolymers and their potential applications in the nuclear waste management field—a bibliographical study. JAEA-review https://doi.org/10.11484/jaea-review-2017-014
Ma C, Zhao B, Guo SL, Long GC, Xie YJ (2019) Properties and characterization of green one-part geopolymer activated by composite activators. J Clean Prod 220:188–199
Sun JW, Chen ZH (2019) Effect of silicate modulus of water glass on the hydration of alkaliactivated converter steel slag. J Therm Anal Calorim 138:47–56
Xiao R, Ma YT, Jiang X, Zhang MM, Zhang YY, Wang YH et al (2020) Strength, microstructure, efflorescence behavior and environmental impacts of waste glass geopolymers cured at ambient temperature. J Clean Prod 252(C):119610
Yu GL, Jia YM (2021) Preparation of geopolymer composites based on alkali excitation. Arab J Geosci 14(7):1–8s
Tong GQ, Zhang WY, Gao YT, Tang XY (2022) Mechanicaal Properties and Micromechanism of Alkali-activated Fly Ash Geopolymer. MATERICAL REPORES 36(04):129–134
Pacheco-Torgal F, Abdollahnejad Z, Camões AF, Jamshidi M, Ding Y (2012) Durability of alkali-activated binders: a clear advantage over Portland cement or an unproven issue? Constr Build Mater 30:400–405
Huang X, Pang J, Liu G, Chen Y (2020) experimental study on physicomechanical properties of deep sandstone by coupling of dry–wet cycles and acidic environment. Adv Civ Eng 2020:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2760952
Müllerová M, Holý K, Blahušiak P, Bulko M (2018) Study of radon exhalation from the soil. J Radioanal Nucl Ch 315(2):237–241
Feng SY, Xiong DB, Chen GJ, Cui Y, Chen PX (2020) Convection-diffusion model for radon migration in a three-dimensional confined space in turbulent conditions. Fluid Dyn Mater Process 16(3):651–663
Tene T, Vacacela GC, Tubon UG, Suquillo B, Bellucci S (2021) Measurement of radon exhalation rate from building materials: the case of Highland region of Ecuador. Constr Build Mater 293:123282
Murad AM, Farida B (2019) Measurement of radon exhalation rate in various building materials used in Morocco. Int J Low Radiat 11(2):158–171
Yongmei L, Wanyu T, Kaixuan T, Zehua L, Qi F, Junwen L et al (2018) The effect of laterite density on radon diffusion behavior. Appl Radiat Isotopes 132:164–169
Xie D, Wu Y, Wang C, Yu CW, Tian L, Wang H (2021) A study on the three-dimensional unsteady state of indoor radon diffusion under different ventilation conditions. Sustain Cities Soc 66:102599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102599
Sarkar M, Dana K (2021) Partial replacement of metakaolin with red ceramic waste in geopolymer. Ceram Int 47(3):3473–3483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.191
Lyu S, Wang T, Cheng T, Ueng T (2013) Main factors affecting mechanical characteristics of geopolymer revealed by experimental design and associated statistical analysis. Constr Build Mater 43:589–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.02.033
Bagci C, Kutyla GP, Kriven MW (2017) Fully reacted high strength geopolymer made with diatomite as a fumed silica alternative. Ceram Int 43(17):14784–14790
Krizan D, Zivanovic B (2002) Effects of dosage and modulus of water glass on early hydration of alkali–slag cements. Cement Concr Res 32(8):1181–1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00717-7
Ꝋstergaard K, Pottegård A, Hallas J, Bak S, Depont Christensen R, Gaist D (2014) Discontinuation of antiplatelet treatment and risk of recurrent stroke and all-cause death: a cohort study. Neuroepidemiology 43(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1159/000365732
Koshy N, Dondrob KG, Hu LM, Wen QB, Meegoda JN (2019) Synthesis and characterization of geopolymers derived from coal gangue, fly ash and red mud. Constr Build Mater 206:287–296
Rattanasak U, Chindaprasirt P (2009) Influence of NaOH solution on the synthesis of fly ash geopolymer. Miner Eng 22(12):1073–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2009.03.022
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.11875164); Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province; About the sixth batch of projects in the "Thirthteen Five-Year Plan" for basic technical research (Grant Nos.JSZL2019403C001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Liu, Y., Chen, Y. et al. Microscopic characterization and radon exhalation of metakaolin-uranium tailings polymer solidified body under alkali activation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331, 4601–4614 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08557-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08557-x