Abstract
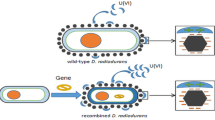
This review thoroughly presents the recent progress of Deinococcus radiodurans, recombinant D. radiodurans and immobilized D. radiodurans as superior adsorbents to efficiently remove toxic heavy metals ions and radionuclides. Finally, a summary and prospect on the opportunities and challenges of D. radiodurans are provided.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang M, Sun X, Xu J (2020) Heavy metal pollution in the East China Sea: A review. Mar Pollut Bull 159:111473
Selvakumar R, Ramadoss G, Mridula PM (2018) Challenges and complexities in remediation of uranium contaminated soils: A review. J Environ Radioact 192:592–603
Dhaliwal SS, Singh J, Taneja PK (2020) Remediation techniques for removal of heavy metals from the soil contaminated through different sources: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(2):1319–1333
Manobala T, Shukla SK, Rao TS (2021) Kinetic modelling of the uranium biosorption by Deinococcus radiodurans biofilm. Chemosphere 269:128722
Sayali K, Anand B, Shree KA (2013) Bioprecipitation of uranium from alkaline waste solutions using recombinant Deinococcus radiodurans. J Hazard Mater 262:853–861
Zhou DM, Hao XZ, Xue Y (2004) Research progress on remediation technology of contaminated soil. Ecol Environ Sci 13(2):234–242
Douay F, Roussel H, Pruvot C (2008) Assessment of a remediation technique using the replacement of contaminated soils in kitchen gardens nearby a former lead smelter in Northern France. Sci Total Environ 401:29–38
Khan FI, Husain T, Hejazi R (2004) An overview and analysis of site remediation technologies. J Environ Manage 71:95–122
Yao Z, Li J, Xie H (2012) Review on remediation technologies of soil contaminated by heavy metals. Procedia Environ Sci 16:722–729
Zhou DM, Deng CF (2003) Review: Electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. J Agro-Environ Sci 22(4):505–508
Ke X, Li PJ, Gong ZQ (2004) Advances in flushing agents used for remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil. Chin J Ecol 33(5):145–149
Gao GL, Zhang W, Zhou LB (2013) Advances in chemical leaching technology of heavy metal contaminated soil. Non- ferrous Metals Eng 3(1):49–52
Zhao SH, Chen ZL, Zhang TP (2013) Research progress on solidification /stabilization of heavy metal contaminated soil. Chin J Soil Sci 44(6):1531–1536
O’Day P, Vlassopoulos D (2010) Mineral-based amendments for remediation. Elements 6:375–381
Porter SK, Scheckel KG, Impellitteri CA (2004) Toxic metals in the environment: Thermodynamic considerations for possible immobilization strategies for Pb, Cd, As, and Hg. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 34:495–604
Gong Y, Zhao D, Wang Q (2018) An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: Technical progress over the last decade. Water Res 147:440–460
Derakhshan NZ, Jung MC, Kim KH (2018) Remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals with an emphasis on immobilization technology. Environ Geochem Health 40:927–953
Mahmood Q, Mirza N, Shaheen S (2015) Phytoremediation using algae and macrophytes. In: Ansari AA, Gill SS, Gill R (eds) Phytoremediation: Management of environmental contaminants 2: 265–289.
Chaney RL, Baklanov IA (2017) Phytoremediation and phytomining: Status and promise. In: Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J (eds) Advances in Botanical Research 83: 189–221.
Nahmani J, Hodson M, Black SA (2007) Review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworm. Environ Pollut 145:402–424
Tang H, Zhu J, Huang SF (2013) Research progress on application of earthworms in heavy metal pollution of soil and its remediation. Soil 45(01):17–25
Ye W, Zhou YJ, Yan SW (2019) Advancement of research on application of microbial mineralization technology in remediation of arsenic contaminated environment. Acta Pedol Sin 58(4):862–875
He F, Gao J, Pierce E (2015) In situ remediation technologies for mercury-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(11):8124–8147
Guemiza K, Coudert L, Metahni S (2017) Treatment technologies used for the removal of As, Cr, Cu, PCP and/or PCDD/F from contaminated soil: A review. J Hazard Mater 333:194–214
Qu L, Shi C (2019) Research progress of remediation technology for heavy metals in soil. China Metal Bull 09:178–179
Prakash D, Gabani P, Chandel AK (2013) Bioremediation: a genuine technology to remediate radionuclides from the environment. Microb Biotechnol 6(4):349–360
Guo ZZ, Xiao FZ, Yang Z (2018) Adsorption of Cu~ (2+) and Cr~ (6+) on Deinococcus radiodurans. Chem Res Appl 30(03):327–332
Brim H, Mcfarlan SC, Fredrickson JK (2000) Engineering Deinococcus radiodurans for metal remediation in radioactive mixed waste environments. Nat Biotechnol 18(1):85–90
Chaturvedi R, Archana G (2014) Cytosolic expression of synthetic phytochelatin and bacterial metallothionein genes in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 for enhanced tolerance and bioaccumulation of cadmium. Biometals 27(3):471–482
He Y, Jiang DW, Wang QR (2018) Preparation of immobilized microorganism and its ability to treat radioactive wastewater. Shanghai Environ Sci 37(06):231–234
Kim HK, Jeong SW, Yang JE (2019) Highly efficient and stable removal of arsenic by live cell fabricated magnetic nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 20(14):3566
Yang J, Faqin D, Qunwei D (2015) Study on the adsorption behavior of radionuclide uranium by Dixococcus radiodurans. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 35(04):1010–1014
Yang J (2015) Study on the adsorption of water soluble nuclide uranium by typical microorganisms under irradiation conditionsSouthwest. University of Science and Technology
Guo K, Cheng C, Chen L (2021) Uranium enrichment performence and uranium stress mechanism of Deinococcus radiodurans. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08018-x
Liu XL (2015) Study on the Breeding of microorganisms removing U (VI) and their interaction with U (VI). University of Science and Technology.
Liang Songjun (2010) Construction of recombinant strain D. radiodurans containing phoN and its Enrichment performance of U (VI). University of South China
Appukuttan D, Rao AS, Apte SK (2006) Engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans R1 for bioprecipitation of uranium from dilute nuclear waste. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(12):7873–7878
Appukuttan D, Seetharam C, Padma N (2011) PhoN-expressing, lyophilized, recombinant Deinococcus radiodurans cells for uranium bioprecipitation. J Biotechnol 154(4):285–290
Kulkarni S, Ballal A, Apte SK (2013) Bioprecipitation of uranium from alkaline waste solutions using recombinant Deinococcus radiodurans. J Hazard Mater 262:853–861
Xu R, Wu K, Han H (2018) Co-expression of YieF and PhoN in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 improves uranium bioprecipitation by reducing chromium interference. Chemosphere 211:1156–1165
Qin YL, Dong QF, Nie XQ (2016) Study on the adsorption and reduction of uranium by immobilized Deinococcus radiodurans. Funct Mater 47(06):6125–6129
Xiao FZ, He SY, Peng GW (2016) Fixation of Diplococcus radiodurans by functional magnetic carrier and its adsorption behavior and mechanism for uranium. Chin J Nonferrous Metals 26(07):1568–1575
Choi MH, Jeong SW, Shim HE (2017) Efficient bioremediation of radioactive iodine using biogenic gold nanomaterial-containing radiation-resistant bacterium, Deinococcus radiodurans R1. Chem Commun (Camb) 53(28):3937–3940
Shim HE, Yang JE, Jeong SW (2018) Silver nanomaterial-immobilized desalination systems for efficient removal of radioactive iodine species in water. Nanomater (Basel, Switzerland) 8(9):660
Raghu G, Satyanarayana SS, Kumari LS (2015) Engineered Deinococcus radiodurans R1 with NiCoT genes for bioremoval of trace cobalt from spent decontamination solutions of nuclear power reactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(21):9203–9213
Huang T, Liu MX, Dong QF (2015) Comparative study on calstrontium biomineralization induced by different microorganisms. Geolo J China Univ 21(04):584–593
Liu MX, Dong QF (2014) Li S (2014) Study on adsorption and reduction of strontium column by immobilized Deinococcus radiodurans. Environ Sci Technol 37(06):32–37
Ding L (2019) Experimental study on the fixation of uranium in soil by Leifsonia SP. University of South China.
Xu YB, Qian CX, Lu ZW (2013) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by bacteria biomineralization. Chin J Environ Eng 7(7):2763–2768
Wang T (2013) Study on remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by high-efficiency mutagens and biochar. Nankai University.
Tan H, Wang C, Li H (2020) Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by nano-FeS coated humic acid complex in combination with Cr- resistant microflora. Chemosphere 242(Mar.):125251.1-125251.10
Peng D, Wu B, Tan H (2019) Effect of multiple ironbased nanoparticles on availability of lead and iron, and micro-ecology in lead contaminated soil. Chemosphere 228:44–53
Sorokin ND, Afanasova EN (2011) Microbial indication of soils contaminated with industrial emissions. Contemp Probl Ecol 4(5):508–512
Cheng C, Xie J, Zhu Q (2021) The reduction effect and mechanism of Deinococcus radiodurans transformed dsrA gene to uranyl ions. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08038-7
Luo J, Zhu Q, Li S (2021) Construction of Deino-flr-2 radiation-tolerant genetically engineered strain containing flr-2 fluoride-tolerant gene and its enrichment behavior for U (VI). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 328(3):1265–1278
Yang H (2019) Study on stability and environmental effect of microbial induced carbonate deposition in remediation of soil contaminated by violet and chromium. Yangzhou University.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Nature Science Foundation of Hunan. Province in 2020 (2020JJ6050, 2020JJ4077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, K., Cheng, C., Chen, L. et al. Application of Deinococcus radiodurans in the treatment of environmental pollution by heavy metals and radionuclides. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331, 655–664 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08141-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08141-9