Abstract
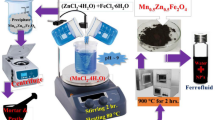
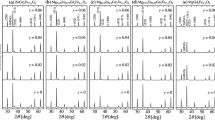
Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia applications were synthesized by a high temperature thermal decomposition method. The crystallographic, magnetic, and thermal properties of the prepared Mn–Zn nanoparticles were investigated using a vibrating-sample magnetometer, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Raman, Mössbauer spectroscopy, and magnetic hyperthermia system. Among Mn–Zn ferrites, the saturation magnetization of Mn0.2Zn0.8Fe2O4 reached maximum value (83.2 emu/g). The heating temperature of Mn0.2Zn0.8Fe2O4 was 118.5 and 48.1 °C for powder and agar solution at 50 kHz and 250 Oe. These results suggest that the synthesized nanoparticles can be potential candidates for their use in magnetic hyperthermia areas.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manohar A, Krishnamoorthi C, Chandra Babu Naidu K, Palajonnala Narasaiah B (2020) Dielectric, magnetic hyperthermia and photocatalytic properties of Mg0.7Zn0.3Fe2O4 nanocrystals. IEEE Trans Magn 56(12):5200207
Banobre-López M, Teijeiro A, Rivas J (2013) Magnetic nanoparticles-based hyperthermia for cancer treatment. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 18(6):397–400
Chandunika RK, Vijayaraghavan R, Kumar Sahu N (2020) Magnetic hyperthermia application of MnFe2O4 nanostructures processed through solvents with the varying boiling point. Mater Res Express 7(6):064002
Périgo EA, Hemery G, Sandre O, Ortega D, Garaio E, Plazaola F, Teran FJ (2015) Fundamentals and advances in magnetic hyperthermia. Appl Phys Rev 2(4):041302
Etemadi H, Plieger PG (2020) Magnetic fluid hyperthermia based on magnetic nanoparticles: physical characteristics, historical perspective, clinical trials, technological challenges, and recent advances. Adv Therap 3(11):2000061
Liu X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhu W, Li G, Ma X, Zhang Y, Chen S, Tiwari S, Shi K, Zhang S, Fan HM, Zhao YX, Liang X-J (2020) Comprehensive understanding of magnetic hyperthermia for improving antitumor therapeutic efficacy. Theranostics 10(8):3793–3815
Rajan A, Sharma M, Sahu NK (2020) Assessing magnetic and inductive thermal properties of various surfactants functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles hyperthermia. Sci Rep 10(1):15045
Sharifi I, Shokrollahi H, Amiri S (2012) Ferrite-based magnetic nanofluids used in hyperthermia applications. J Magn Magn Mater 324(6):903–915
Shibata M, Ogawa T, Kawashita M (2019) Synthesis of iron nitride nanoparticles from magnetite nanoparticles of different sizes for application to magnetic hyperthermia. Ceram Int 45(17):23707–23714
Babič M, Horák D, Molčan M, Timko M (2017) Heat generation of surface-modified magnetic γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles in applied alternating magnetic field. J Phys D Appl Phys 50(34):345002
Choi H, Kim SJ, Choi EH, Kim CS (2015) Study of hyperthermia through the bioplasma treatment and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. IEEE Trans Magn 51(11):2003603
Tran N, Webster TJ (2010) Magnetic nanoparticles: biomedical applications and challenges. J Mater Chem 20(40):8760–8767
Chang D, Lim M, Goos JACM, Qiao R, Ng YY, Mansfeld FM, Jackson M, Davis TP, Kavallaris M (2018) Biologically targeted magnetic hyperthermia: potential and limitations. Front Pharmacol 9:831
Boyer C, Whittaker MR, Bulmus V, Liu J, Davis TP (2010) The design and utility of polymer-stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles for nanomedicine applications. NPG Asia Mater 2(1):23–30
Garanina AS, Naumenko VA, Nikitin AA, Myrovali E, Petukhova AY, Klimyuk SV, Nalench YA, Ilyasov AR, Vodopyanov SS, Erofeev AS, Gorelkin PV, Angelakeris M, Savchenko AG, Wiedwald U, Majouga AG, Abakumov MA (2020) Temperature-controlled magnetic nanoparticles hyperthermia inhibits primary tumor growth and metastases dissemination. Nanomedicine: NBM 25:102171
Zverev VI, Pyatakov AP, Shtil AA, Tishin AM (2018) Novel applications of magnetic materials and technologies for medicine. J Magn Magn Mater 459:182–186
Tishin MA, Shtil AA, Pyatakov AP, Zverev VI (2016) Developing antitumor magnetic hyperthermia: principles, materials and devices. Recent Pat Anti-Cancer Drug Discov 11(4):360–375
Srinivasan SY, Paknikar KM, Bodas D, Gajbhiye V (2018) Applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in biomedical nanotechnology. Nanomedicine 13(10):1221–1238
Mameli V, Musinu A, Ennas G, Peddis D, Niznansky D, Sangregorio C, Innocenti C, Thanh NTK, Cannas C (2016) Studying the effect of Zn-substitution on the magnetic and hyperthermic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Nanoscale 8(19):10124–10137
He S, Zhang H, Liu Y, Sun F, Yu X, Li X, Zhang L, Wang L, Mao K, Wang G, Lin Y, Han Z, Sabirianov ZH (2018) Maximizing Specific Loss Power for Magnetic Hyperthermia by Hard-Soft Mixed Ferrites. Small 14(29):1800135
Iacovita C, Florea A, Scorus L, Pall E, Dudric R, Moldovan AI, Stiufiuc R, Tetean R, Lucaciu CM (2019) Hyperthermia, cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake properties of manganese and zinc ferrite magnetic nanoparticles synthesized by a polyol-mediated process. Nanomaterials 9(10):1489
Xie J, Yan C, Yan Y, Chen L, Song L, Zang F, An Y, Teng G, Gu N, Zhang Y (2016) Multi-modal Mn–Zn ferrite nanocrystals for magnetically-induced cancer targeted hyperthermia: a comparison of passive and active targeting effects. Nanoscale 8(38):16902–16915
Lin M, Huang J, Sha M (2014) Recent advances in nanosized Mn–Zn Ferrite Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia For Cancer Treatment. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14(1):792–802
Denton AR, Ashcroft NW (1991) Vegard’s law. Phys Rev A 43:3161–3164
Patterson A (1939) The Scherrer formula for X-Ray particle size determination. Phys Rev 56:978–982
Hou X, Feng J, Liu X, Ren Y, Fan Z, Zhang M (2011) Magnetic and high rate adsorption properties of porous Mn1-xZnxFe2O4 (0≤x≤0.8) adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 353(2):524–529
White W, DeAngelis B (1967) Interpretation of the vibrational spectra of spinels. Spectrochim Acta Part A 23(4):985–995
Varshney D, Verma K, Kumar A (2011) Structural and vibrational properties of ZnxMn1-xFe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.0) mixed ferrites. Mater Chem Phys 131(1–2):413–419
Yadav RS, Kuřitka I, Vilcakova J, Jamatia T, Machovsky M, Skoda D, Urbánek P, Masař M, Urbánek M, Kalina L, Havlica J (2020) Impact of sonochemical synthesis condition on the structural and physical properties of MnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. Ultrason Sonochem 61:104839
Fu Y, Xiong P, Chen H, Sun X, Wang X (2012) High photocatalytic activity of magnetically separable manganese ferrite-graphene heteroarchitectures. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(2):725–731
Ravichandran M, Velumani S (2020) Manganese ferrite nanocubes as an MRI contrast agent. Mater Res Express 7(1):016107
Shanmugavani A, Kalai Selvan R (2014) Synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles and their asymmetric configuration with Ni(OH)2 for a pseudocapacitor. RSC Adv 4(51):27022–27029
Phor L, Chahal S, Kumar V (2020) Zn2+ substituted superparamagnetic MgFe2O4 spinel-ferrites: Investigations on structural and spin-interactions. J Adv Ceram 9(5):576–587
Mørup S, Brok E, Frandsen C (2013) Spin structures in magnetic nanoparticles. J Nanomater 2013:1–8
Gupta M, Randhawa BS (2011) Mössbauer, magnetic and electric studies on mixed Rb-Zn ferrites prepared by solution combustion method. Chem Phys 130(1–2):513–518
Zhang Y, Lin J, Wen D (2010) Structure, infrared radiation properties and Mössbauer spectroscopic investigations of Co0.6Zn0.4NixFe2-xO4. Ceramics J Mater Sci Technol 26(8):687–692
Siddique M, Butt NM (2010) Effect of particle size on degree of inversion in ferrites investigated by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 405(19):4211–4215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors do not have any possible conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.J., Hyun, S.W., Kim, S.H. et al. Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles for application in magnetic hyperthermia. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 330, 445–454 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07830-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07830-9