Abstract
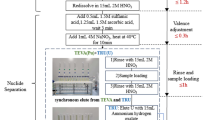
Responding to a radiological or nuclear incident may require assessing tens to hundreds of thousands of people for possible radionuclide contamination. The measurement of radioactive Sr is important because of its impact on people’s health. The existing analytical method for urine Sr-90 analysis using crown ethers is laborious and involves possible exposure to concentrated acids; therefore, this work is devoted to the development of the automated Sr-90 separation process, which became possible with the prepFast pre-analytical system (Elemental Scientific, Inc).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
U.S.E.P.A. (2002) http://www.epa.gov/radiation/radioniclides/strontium.htm. Accessed 28 July 2020
CDC Radiation Emergencies/Strontium-90 (Sr-90). https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/radiation/emergencies/isotopes/strontium/index.htm. Accessed 12 Aug 12 2020
Dietz ML, Horwitz EP, Nelson DM, Wahlgren M (1991) An improved method for determining Sr-89 and Sr-90 in urine. Health Phys 61(6):871–877
Maxwell SL (2008) Rapid analysis of emergency urine and water samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 275(3):497–502
Piraner O, Jones RL (2010) Urine Sr-90 analysis through chemical extraction followed by liquid scintillation counting with ICP-MS method for Sr recovery. In: 56th Radiobioassay and Radiochemical Measurements Conference, Sandestin, FL, October 2010
Piraner O, Jones RL (2021) The effect of Sr-Spec resin cartridges age on gravimetric and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) strontium recovery used for strontium-90 analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07628-9
Piraner O, Preston R, Shanks S, Jones RL (2010) Sr-90 liquid scintillation urine analysis utilizing different approaches for tracer recovery. Sandia Report SAND2010-5878. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque
Romaniello SJ, Field MP, Smith HB, Gordon GW, Kim MH, Anbar AD (2015) Fully automated chromatographic purification of Sr and Ca for isotopic analysis. JAAS 30(9):1906–1912
Piraner O, Jones RL (2009) Urine gross alpha/beta analysis by liquid scintillation counting for emergency and terrorism preparedness and response. In: Eikenberg J, Jäggi M, Beer H, Baehrle H (eds) LSC 2008, advances in liquid scintillation spectrometry. University of Arizona, Tucson
NE581—Radiation protection—OSU extended Campus—Bateman equation. https://courses.ecampus.oregonstate.edu/ne581/four/decay_chains.htm. Accessed 28 July 2020
D’Haese PC, Van Landeghem GF, Lamberts LV, Bekaert VA, Schrooten I, De Broe ME (1996) Measurement of strontium in serum, urine, bone, and soft tissues by Zeeman atomic absorption spectrometry. Clin Chem 43:121–128
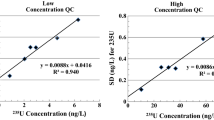
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2012) EP17-A2, Protocols for determination of limit of detection and limit of quantification, 2nd edn, V24, N34
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to J. Sakowski, D. Quarles, and P. Field (all from ESI) for their help in the production of both automated systems and to S. Maxwell (Las Alamos National Lab) for practical advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The findings and conclusions in this study are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not constitute endorsement by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piraner, O., Jones, R.L. Urine strontium-90 (Sr-90) manual and automated pre-analytical separation followed by liquid scintillation counting. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 329, 383–390 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07759-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07759-z