Abstract
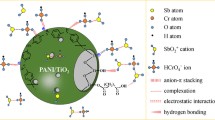
To effectively protect the marine ecological environment, herein, the silver-loaded organometallic framework material ((MIL-101(Cr)@Ag) was synthesized to study the rapid enrichment of iodide ions. Under the best experimental conditions, the reaction was in adsorption equilibrium within 10 min, and the maximum adsorption capacity could attain 57 mg/g. The XPS and XRD analysis indicated that the iodide ions mainly interacted with silver atoms in MIL-101(Cr)@Ag to form AgI. The adsorption behavior was well fitted by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm model, showed that adsorption process was mainly monolayer chemisorption. Therefore, MIL-101(Cr)@Ag could be used as a potential material for removing iodide ions from aqueous solutions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mcnally RJQ, Wakeford R, James PW, Basta NO, Alston RD, Pearce MS, Elliott AT (2016) A geographical study of thyroid cancer incidence in north-west England following the Windscale nuclear reactor fire of 1957. J Radiol Prot 36(4):934–952
Han YY, Youk AO, Sasser H, Talbott E (2011) Cancer incidence among residents of the Three Mile Island accident area: 1982–1995. Environ Res 111(8):1230–1235
Boehm BO, Steinert M, Dietrich JW, Peter RU, Belyi D, Wagemaker G, Rosinger S, Fliedner TM, Weiss MJ (2009) Thyroid examination in highly radiation-exposed workers after the Chernobyl accident. Eur J Endocrinol 160(4):625–630
Xu C, Zhang S, Sugiyama Y, Ohte N, Ho YF, Fujitake N, Kaplan DI, Yeager CM, Schwehr K, Santschi PH (2016) Role of natural organic matter on iodine and 239,240 Pu distribution and mobility in environmental samples from the northwestern Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. J Environ Raidoact 153(3):156–166
Fabryka-Martin J, Bentley H, Elmore D, Airey PL (1985) Natural iodine-129 as an environmental tracer. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 49(2):337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(85)90027-4
Shimamoto YS, Takahashi Y, Terada Y (2011) Formation of organic iodine supplied as iodide in a soil-water system in Chiba. Jpn Environ Sci Technol 45(6):2086–2092. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1032162
Sungwook C, Wooyong U, Minkyung K, Min-Gyu K (2013) Uptake mechanism for iodine species to black carbon. J Environ Sci Technol 47(18):10349–10355
Wong G (1991) The marine geochemistry of iodine. Rev Aquat Sci 4:45–73
Lee S-H, Takahashi Y (2020) Selective immobilization of iodide onto a novel bismuth-impregnated layered mixed metal oxide: Batch and EXAFS studies. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121223
Fuge R, Johnson CC (1986) The geochemistry of iodine—a review. Environ Geochem Health 8(2):31–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02311063
Hou X, Povinec PP, Zhang L, Shi K, Biddulph D, Chang C-C, Fan Y, Golser R, Hou Y, Ješkovský M, Jull AJT, Liu Q, Luo M, Steier P, Zhou W (2013) Iodine-129 in seawater offshore Fukushima: distribution, inorganic speciation, sources, and budget. Environ Sci Technol 47(7):3091–3098. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304460k
Tietze S, Foreman MRS, Ekberg C (2013) Synthesis of I-131 labelled iodine species relevant during severe nuclear accidents in light water reactors. Radiochim Acta 101(10):675–680. https://doi.org/10.1524/ract.2013.2070
Nakayama M, Sato A, Nakagawa K (2015) Selective sorption of iodide onto organo-MnO2 film and its electrochemical desorption and detection. Anal Chim Acta 877:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.03.041
Kodama H (1999) Removal of iodide ion from simulated radioactive liquid waste. Czech J Phys 49(1):971–977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10582-999-1026-z
Warchol J, Misaelides P, Petrus R, Zamboulis D (2006) Preparation and application of organo-modified zeolitic material in the removal of chromates and iodides. J Hazard Mater 137(3):1410–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.04.028
Theiss FL, Couperthwaite SJ, Ayoko GA, Frost RL (2014) A review of the removal of anions and oxyanions of the halogen elements from aqueous solution by layered double hydroxides. J Colloid Interface Sci 417:356–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.11.040
Liang L, Li L (2007) Adsorption behavior of calcined layered double hydroxides towards removal of iodide contaminants. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273(1):221–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-007-0740-x
Theiss FL, Ayoko GA, Frost RL (2017) Sorption of iodide (I-) from aqueous solution using Mg/Al layered double hydroxides. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl 77:1228–1234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.284
Liu L, Liu W, Zhao X, Chen D, Cai R, Yang W, Komarneni S, Yang D (2014) Selective capture of iodide from solutions by microrosette-like delta-Bi2O3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(18):16082–16090. https://doi.org/10.1021/am504000n
Zhang L, Jaroniec M (2017) SBA-15 templating synthesis of mesoporous bismuth oxide for selective removal of iodide. J Colloid Interface Sci 501:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.04.063
Liu S, Kang S, Wang H, Wang G, Zhao H, Cai W (2016) Nanosheets-built flowerlike micro/nanostructured Bi2O2.33 and its highly efficient iodine removal performances. Chem Eng J 289:219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.12.101
Kim T, Lee S-K, Lee S, Lee JS, Kim SW (2017) Development of silver nanoparticle-doped adsorbents for the separation and recovery of radioactive iodine from alkaline solutions. Appl Radiat Isot 129:215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.07.033
Mao P, Qi L, Liu X, Liu Y, Jiao Y, Chen S, Yang Y (2017) Synthesis of Cu/Cu2O hydrides for enhanced removal of iodide from water. J Hazard Mater 328:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.12.065
Zhang X, Gu P, Li X, Zhang G (2017) Efficient adsorption of radioactive iodide ion from simulated wastewater by nano Cu2O/Cu modified activated carbon. Chem Eng J 322:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.102
Mao P, Liu Y, Liu X, Wang Y, Liang J, Zhou Q, Dai Y, Jiao Y, Chen S, Yang Y (2017) Bimetallic AgCu/Cu2O hybrid for the synergetic adsorption of iodide from solution. Chemosphere 180:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.038
Zhang H, Gao X, Guo T, Li Q, Liu H, Ye X, Guo M, Wu Z (2011) Adsorption of iodide ions on a calcium alginate-silver chloride composite adsorbent. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 386(1–3):166–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.07.014
Mu W, Yu Q, Li X, Wei H, Jian Y (2017) Niobate nanofibers for simultaneous adsorptive removal of radioactive strontium and iodine from aqueous solution. J Alloy Compd 693:550–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.09.200
Liu S, Wang N, Zhang Y, Li Y, Han Z, Na P (2015) Efficient removal of radioactive iodide ions from water by three-dimensional Ag2O-Ag/TiO2 composites under visible light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 284:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.10.054
Mao P, Qi B, Liu Y, Zhao L, Jiao Y, Zhang Y, Jiang Z, Li Q, Wang J, Chen S, Yang Y (2016) Ag-II doped MIL-101 and its adsorption of iodine with high speed in solution. J Solid State Chem 237:274–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2016.02.030
Zhao X, Han X, Li Z, Huang H, Liu D, Zhong C (2015) Enhanced removal of iodide from water induced by a metal-incorporated porous metal-organic framework. Appl Surf Sci 351:760–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.05.186
Ferey G, Mellot-Draznieks C, Serre C, Millange F, Dutour J, Surble S, Margiolaki I (2005) A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science 309(5743):2040–2042. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1116275
Bai Z-Q, Yuan L-Y, Zhu L, Liu Z-R, Chu S-Q, Zheng L-R, Zhang J, Chai Z-F, Shi W-Q (2015) Introduction of amino groups into acid-resistant MOFs for enhanced U(VI) sorption. J Mater Chem A 3(2):525–534. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta04878d
Zhang J-Y, Zhang N, Zhang L, Fang Y, Deng W, Yu M, Wang Z, Li L, Liu X, Li J (2015) Adsorption of uranyl ions on amine-functionalization of MIL-101(Cr) nanoparticles by a facile coordination-based post-synthetic strategy and x-ray absorption spectroscopy studies. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13514
Zhou X-P, Xu Z, Zeller M, Hunter AD (2009) Reversible uptake of HgCl2 in a porous coordination polymer based on the dual functions of carboxylate and thioether. Chem Commun 36:5439–5441. https://doi.org/10.1039/b910265e
Ke F, Qiu L-G, Yuan Y-P, Peng F-M, Jiang X, Xie A-J, Shen Y-H, Zhu J-F (2011) Thiol-functionalization of metal-organic framework by a facile coordination-based postsynthetic strategy and enhanced removal of Hg2+ from water. J Hazard Mater 196:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.069
Bagheri A, Taghizadeh M, Behbahani M, Asgharinezhad AA, Salarian M, Dehghani A, Ebrahimzadeh H, Amini MM (2012) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic metal-organic framework (MOF) as a novel sorbent, and its optimization by experimental design methodology for determination of palladium in environmental samples. Talanta 99:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.030
Aijaz A, Karkamkar A, Choi YJ, Tsumori N, Roennebro E, Autrey T, Shioyama H, Xu Q (2012) Immobilizing highly catalytically active pt nanoparticles inside the pores of metal-organic framework: a double solvents approach. J Am Chem Soc 134(34):13926–13929. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3043905
Zhu Q-L, Li J, Xu Q (2013) Immobilizing metal nanoparticles to metal-organic frameworks with size and location control for optimizing catalytic performance. J Am Chem Soc 135(28):10210–10213. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja403330m
Li D, Dai X, Zhang X, Zhuo H, Jiang Y, Yu Y-B, Zhang P, Huang X, Wang H (2017) Silver nanoparticles encapsulated by metal-organic-framework give the highest turnover frequencies of 105 h−1 for three component reaction by microwave-assisted heating. J J Catal 348:276–281
Riebe B, Dultz S, Bunnenberg C (2005) Temperature effects on iodine adsorption on organo-clay minerals: I. Influence of pretreatment and adsorption temperature. Appl Clay Sci 28(1):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2004.01.004
Bors J, Gorny A, Dultz S (1997) Iodide, caesium and strontium adsorption by organophilic vermiculite. J Clay Miner 32(1):21–28. https://doi.org/10.1180/claymin.1997.032.1.04
Lu Y, Yan B (2014) Luminescent lanthanide barcodes based on postsynthetic modified nanoscale metal–organic frameworks. J Mater Chem C. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC01077A
Hu Z, Khurana M, Seah YH, Zhang M, Guo Z, Zhao D (2015) Ionized Zr-MOFs for highly efficient post-combustion CO2 capture. Chem Eng Sci 124:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2014.09.032
Zhao X, Han X, Li Z, Huang H, Liu D, Zhong C (2015) Enhanced removal of iodide from water induced by a metal-incorporated porous metal–organic framework. Appl Surf Sci 351:760–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.05.186
Jayaram K, Murthy IYLN, Lalhruaitluanga H, Prasad MNV (2009) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solution by seed powder of Strychnos potatorum L. Colloids Surf, B 71(2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.02.016
Sari A, Citak D, Tuzen M (2010) Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies on adsorption of Sb(III) from aqueous solution using low-cost natural diatomite. Chem Eng J 162(2):521–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.05.054
Al Lafi AG, Assfour B, Assaad T (2020) Metal organic framework MIL-101(Cr): spectroscopic investigations to reveal iodine capture mechanism. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30(4):1218–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01236-7
Chen L, Zhao D, Chen S, Wang X, Chen C (2016) One-step fabrication of amino functionalized magnetic graphene oxide composite for uranium(VI) removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 472:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.03.044
Ye Z, Chen L, Liu C, Ning S, Wang X, Wei Y (2019) The rapid removal of iodide from aqueous solutions using a silica-based ion-exchange resin. React Funct Polym 135:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.12.002
Mao P, Liu Y, Jiao Y, Chen S, Yang Y (2016) Enhanced uptake of iodide on Ag@Cu2O nanoparticles. Chemosphere 164:396–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.116
Rong J, Zhao Z, Jing Z, Zhang T, Qiu F, Xu J (2017) High-specific surface area hierarchical Al2O3 carbon fiber based on a waste paper fiber template: preparation and adsorption for iodide ions. J Wood Chem Technol 37(6):485–492. https://doi.org/10.1080/02773813.2017.1347684
Li J, Yang X, Bai C, Tian Y, Li B, Zhang S, Yang X, Ding S, Xia C, Tan X, Ma L, Li S (2015) A novel benzimidazole-functionalized 2-D COF material: Synthesis and application as a selective solid-phase extractant for separation of uranium. J Colloid Interface Sci 437:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.09.046
Lu Y, Liu H, Gao R, Xiao S, Zhang M, Yin Y, Wang S, Li J, Yang D (2016) Coherent-interface-assembled Ag2O-anchored nanofibrillated cellulose porous aerogels for radioactive iodine capture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(42):29179–29185. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b10749
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part of the project titled “The National Key Project of Research and Development Plan” (Grant No. 2016YFC1402504). The authors thank the funding source of this research and the research platform provided by Wuhan University of technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no any conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, J., Li, Y., Jiang, Y. et al. Silver-doped MIL-101(Cr) for rapid and effective capture of iodide in water environment: exploration on adsorption mechanism. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 328, 1041–1054 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07705-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07705-z