Abstract
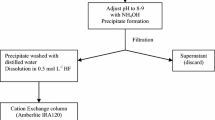
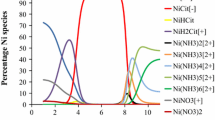
A radiochemical method was developed for the accurate 55Fe determination in various radioactive waste, in particular samples contaminated with 241Pu. It consisted of three purification steps based on first ammonium hydroxide precipitation, and then anion exchange separation followed by TRU®-based extraction chromatography. It was characterized by an iron recovery yield of about 80% for all the studied samples and a 60Co decontamination factor of 106. In comparison to a standard protocol based on iron cupferrate extraction in chloroform, an improvement of a 30-fold factor was achieved towards plutonium. The developed TRU®-based procedure was validated by participating in interlaboratory exercises.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laboratoire National Henri Becquerel (2005) In: Tables de radionucléides – 55Fe, 239Pu, 240Pu, 241Pu, 239Pu, 237Np, 241Am
Remenec B, Dulanska S, Matel L (2014) Determination of alpha, beta, X-ray and gamma emitting radionuclides in reactor components and fuel assemblies from NPP V1 Jaslovske Bohunice. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299:1799–1804
Hou X, Østergaard LF, Nielsen SP (2005) Determination of 63Ni and 55Fe in nuclear waste samples using radiochemical separation and liquid scintillation counting. Anal Chim Acta 535:297–307
Lee CH, Lee MH, Ha YK, Song KS (2011) Systematic radiochemical separation for the determination of 99Tc, 90Sr, 94Nb, 55Fe and 59,63Ni in low and intermediate radioactive waste samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288:319–325
Choi KS, Lee CH, Im HJ et al (2017) Separation of Tc-99, Sr-90, Ni-59, Ni-63, Fe-55 and Nb-94 from activated carbon and stainless steel waste samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 3:2145–2154
Curionia A, Dinara N, La Torrea FP, Leidnera J, Murtasa F, Puddua S, Silari M (2017) Measurements of 55Fe activity in activated steel samples with GEMPix. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res 849:60–71
Leskinen A, Salminen–Paatero S, Räty A, Tanhua–Tyrkkö M, Iso–Markku T, Puukko E (2020) Determination of 14C, 55Fe, 63Ni and gamma emitters in activated RPV steel samples: a comparison between calculations and experimental analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 323:399–413
Taddei MHT, Macacini JF, Vicente R, Marumo JT, Sakata SK, Terremoto LAA (2013) A comparative study using liquid scintillation counting and X-ray spectrometry to determine 55Fe in radioactive wastes. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 295:2267–2272
Warwick PE, Croudace IW (2006) Isolation and quantification of 55Fe and 63Ni in reactor effluents using extraction chromatography and liquid scintillation analysis. Anal Chim Acta 567:277–285
Mikelic L, Orescanin V, Lulic S (2007) Determination of 55Fe in waste waters of the Krsko nuclear power plant measured simultaneously by liquid scintillation spectrometer (LSC) and X-ray spectrometer (XRS). Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 263:95–98
Song L, Ma L, Ma Y, Yang Y, Dai X (2019)Method for sequential determination of 55Fe and 63Ni in leaching solution from cement solidification. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 319:1227–1234
Nielsen JM (1960) In the Radiochemistry of Iron. NAS-NS 3017. National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council, Washington
Reddy BR, Sarma PVRB (1996) Extraction of iron(III) at macro-level concentrations using TBP, MIBK and their mixtures. Hydrometallurgy 43:299–306
AFNOR Standard NF M60-322 (2005) Nuclear energy - Nuclear fuel cycle technology - Waste - Determination of iron 55 activity in effluents and waste by liquid scintillation after prior chemical separation
Furman NH, Mason WB, Pekola JS (1949) Extraction of cupferrates. Anal Chem 21:1325–1330
Sandell EB, Cummings PF (1949) Chloroform extraction of ferric cupferrate. Anal Chem 21:1356–1358
Stary J, Smizanska J (1963) A systematic study of the solvent extraction of metal cupferrates. Anal Chim Acta 29:545–551
Rassou S, Vercouter T, Mariet C (2020) Sustainable solvent extraction process for Fe analysis in radioactive samples based on microfluidic tools. Solvent Extr Ion Exc 38:236–249
Horwitz EP, Chiarizia R, Dietz ML, Diamond H, Nelson DM (1993) Separation and preconcentration of actinides from acidic media by extraction chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 281:361–372
Quidelleur S, Granet M, Laszak I, Isnard H, Pons-Branchu E, Brennetot R, Caussignac C (2009) One step U-Pu-Cs-Ln-steel separation using TRU preconditioned extraction resins from Eichrom for application on transmutation targets. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 280:507–517
Grahek Z, Macefat R (2004) Isolation of iron and strontium from liquid samples and determination of 55Fe and 89,90Sr in liquid radioactive waste. Anal Chem Acta 511:339–348
Grahek Z, Macefat R (2006) Extraction chromatographic separation of iron from complex liquid samples and the determination of 55Fe. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 267:131–137
Augeray C, Mouton M, Broustet N, Perdereau MF, Laconici C, Loyen J, Fayolle C, Picolo JL (2015) Development of a protocol to measure iron-55 in solid matrices in the environment. J Environ Radioact 141:164–173
Eichrom Technologies, Inc. (2014) Analytical procedures FEW01, iron-55 in water, May 1
Gautier C, Colin C, Garcia C (2016) A comparative study using liquid scintillation counting to determine 63Ni in low and intermediate level radioactive waste. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 308:261–270
ANDRA, National Radioactive Waste Management Agency (2014) ACO.SP.ASRE.99.0002D ANDRA specifications. Accessed 14 May 2020
Hou X (2007) Radiochemical analysis of radionuclides difficult to measure for waste characterization in decommissioning of nuclear facilities. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273:43–48
Coleman GH (1965) In the Radiochemistry of Plutonium. NAS-NS 3058. National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council, Washington
Burney GA, Harbour RM (1974) In the Radiochemistry of Neptunium. NAS-NS 3060, National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council, Washington
Wish L (1959) Quantitative radiochemical analysis by ion exchange. Anion exchange behavior in mixed acid solutions and development of a sequential separation scheme. Anal Chem 31:326–330
Faris JP, Buchanan RF (1964) Anion exchange characteristics of the elements in nitric acid medium. Anal Chem 36:1157–1158
Stary J (1964) The solvent extraction of metal chelates. Pergamon Press, New York
Akatsu E, Hoshi M, Ono R, Ueno K (1968) Some complexes of Americium and Curium with oxine, cupferron and N-Benzoylphenylhydroxylamine. J Nucl Sci Technol 5:252–255
Leskinen A, Salminen-Paatero S, Gautier C, Räty A et al (2020) Intercomparison exercise on difficult to measure radionuclides in activated steel - statistical analysis of radioanalytical results and activation calculations. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07181-x
Analysis method establishment Committee, CETAMA, Bagnols-sur-Ceze, France. https://cetama.partenaires.cea.fr/Local/cetama/files/496/Plaquette.CETAMA.Anglais.pdf. Accessed 14 May 2020
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Céline Cruchet for ICP-AES analysis and Pascal Fichet for his wise corrections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gautier, C., Laporte, E., Lambrot, G. et al. Accurate measurement of 55Fe in radioactive waste. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 326, 591–601 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07332-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07332-0