Abstract
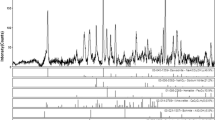
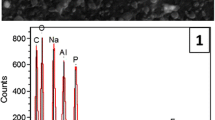
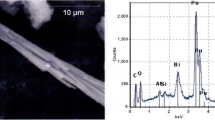
The Hanford site, near Richland, WA, in the U.S.A., has legacy radioactive waste left over from plutonium production. Strontium-90 and its short-lived daughter Y-90 account for about half of the radioactivity of the waste, yet there has been limited understanding of the speciation of strontium in the waste. The speciation of strontium will drive its behavior during any waste separation or treatment options, and may determine the Sr-90 source term to the environment after tank closure. A strontium-bearing phase containing sodium, phosphorus, and oxygen, was found in Hanford waste using energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). Polarized light microscopy determined that this phase was isotropic so had to have a cubic structure. NaSrPO4·9H2O is the only known cubic phase containing these EDS observable elements. These results confirm that NaSrPO4·9H2O is present, so the solubility of this species may drive the behavior of strontium in the waste.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
US DOE (2012) Final tank closure and waste management environmental impact statement for the Hanford site, Richland. United States Department of Energy, Washington, Washington, DC
Cantrell KJ, Krupka KM, Deutsch WJ, Lindberg MJ (2006) Residual waste from Hanford tanks 241-C-203 and 241-C-204. 2. Contaminant release model. Environ Sci Technol 40:3755–3761
Cantrell KJ, Krupka KM, Deutsch WJ, Lindberg MJ (2009) Contaminant release from residual waste in single shell tank at the Hanford site, Washington, USA. In: Proceedings of waste management symposium 2009. Waste Management Symposia Inc., Tuscon, AZ
Cantrell KJ, Deutsch WJ, Lindberg MJ (2011) Thermodynamic model for uranium release from Hanford site tank residual waste. Environ Sci Technol 45:1473–1480
Cantrell KJ, Carroll KC, Buck EC, Neinter D, Geiszler KN (2013) Single-pass flow-through test Elucidation of weathering behavior and evaluation of contaminant release models for Hanford tank residual radioactive waste. Appl Geochem 28:119–127
Deutsch WJ, Cantrell KJ, Krupka KM, Lindberg ML, Serne RJ (2011) Hanford tank residual waste: contaminant source terms and release models. Appl Geochem 26:1681–1693
Wang G, Um W, Cantrell KJ, Snyder MV, Bowden ME, Triplett MB, Buck E (2017) Effects of hydrated lime on radionuclides stabilization of Hanford tank residual waste. Chemosphere 185:171–177
Felmy AR, Mason M, Qafoku O, Dixon DA (2005) Development of accurate chemical equilibrium models for the Hanford waste tanks: the system Na–Ca–Sr–OH–CO3-NO3-EDTA-HEDTA-H2O from 25 to 75 °C. In: Subsurface contamination remediation, ACS symposium series, vol 904, pp 251–281
Warrant RW, Cooke GA (2003) Characterization of the solids waste in the Hanford waste tanks using a combination of XRD, SEM and PLM. Adv X-Ray Anal 46:251–256
Buck EC, McNamara BK (2004) Precipitation of nitrate–cancrinite in Hanford Tank Sludge. Environ Sci Technol 38:4432–4438
Krupka KM, Schaef HT, Arey BW, Heald SM, Deutsch WJ, Lindberg MJ, Cantrell KJ (2006) Residual waste from Hanford tanks 241-C-203 and 241-C-204. 1. Solids characterization. Environ Sci Technol 40:3749–3754
Reynolds JG, Page JS, Cooke GA, Pestovich JA (2015) A scanning electron microscopy study of bismuth and phosphate phases in bismuth phosphate process waste at Hanford. J Radioanalytical Nucl Chem 304:1253–1259
Reynolds JG, Huber HJ, Cooke GA, Pestovich JA (2014) Solid-phase speciation of zirconium and fluoride in alkaline zircaloy cladding waste at Hanford. J Hazard Mater 278:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.097
Reynolds JG, Cooke GA, Herting DL, Warrant RW (2013) Salt mineralogy of Hanford high-level waste staged for treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:9741–9751. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie400822r
Reynolds JG, Cooke GA, Herting DL, Warrant RW (2012) Evidence for dawsonite in Hanford high-level waste tanks. J Hazard Mat 209–210:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.018
Lumetta GJ, McNamara BK, Buck EC, Fiskum SK, Snow LA (2009) Characterization of high phosphate radioactive tank waste and simulant development. Environ Sci Technol 43:7843–7848
ASTM (2011) Standard guide for sampling radioactive tank waste. Standard C1751-11. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Winchell AN (1937) Elements of optical mineralogy, part 1. Principles and methods, Fifth. Wiley, Long
Gribble CD, Hall AJ (1992) Optical mineralogy: principles and practice. CRC Press, New York
Sokolova E, Hawthorne F, Khomyakov AP (2005) Refinement of the crystal structure and revision of the chemical formula of olgite (Ba,Sr)(Na,Sr,REE)2Na[PO4]. Can Min 43:1521–1526
Takagi S, Mathew M, Brown WE (1982) The structure of sodium strontium phosphate nonahydrate. Acta Cryst B38:1408–1413
Huminicki DMC, Hawthorne FC (2002) The crystal chemistry of phosphate minerals. Rev Min Geochem 48:123–253
Page J, Reynolds JG, Ely TM, Cooke GA (2018) Development of a carbonate crust on alkaline nuclear waste sludge at Hanford. J Hazard Mater 342:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.08.033
Page JS, Reynolds JG, Cooke GA, Wells BE (2020) Large cemented gibbsite agglomerates in alkaline nuclear waste at the Hanford site and the impacts to remediation. J Hazard Mater 384:121318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121318
Zhang S, Nakai Y, Tsuboi T, Huang Y, Jin Seo H (2011) The thermal stabilities of luminescence and microstructures of Eu2+-doped KBaPO4 and NaSrPO4 with β-K2SO4 type structures. Inorg Chem 50:2897–2904
Jawaher KR, Jagannathan R, Das SJ, Krishnan S (2015) Optical and spectral studies on pure and europium doped olgite type Na(Sr,Ba)PO4 ceramics. Spectrochim Acta A 140:364–371
Chen KH, Weng MH, Pan CT, Yang RY (2016) Effect of different sintering method on the microstructure and photoluminescent properties of NaSrPO4:Tb3+ phosphors. Powder Technol 288:117–122
Hill OF, Cooper VR (1958) Scale-up problems in the plutonium separation program. Ind Eng Chem 50:599–602
Gee GW, Oostrom M, Freshley MD, Rockhold ML, Zachara JM (2007) Hanford site vadose zone studies, an overview. Vadose Zone J 6:899–905
Choi S, O’Day PA, Rivera NA, Mueller KT, Vairavamurthy MA, Seraphin S, Chorover J (2006) Strontium speciation during reaction of kaolinite with simulated tank-waste leachate: bulk and microfocused EXAFS analysis. Environ Sci Technol 40:2608–2614
Chorover J, Choi S, Rotenberg P, Serne RJ, Rivera N, Strepka C, Thompson A, Mueller KT, O’Day PA (2008) Silicon control of strontium and cesium partitioning in hydroxide-weathered sediments. Geoch Cosmochim Acta 72:2024–2047
Deng Y, Flury M, Harsh JB, Felmy AR, Qafoku Q (2006) Cancrinite and sodalite formation in the presence of cesium, potassium, magnesium, calcium and strontium in Hanford tank waste simulants. Appl Geochem 21:2049–2063
Perdrial N, Thompson A, O’Day PA, Steefle CI, Chorover J (2014) Mineral transformation controls speciation and pore-fluid transmission of contaminates in waste-weathered Hanford sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 141:487–507
Rivera N, Choi S, Strepka C, Mueller K, Perdrial N, Chorover J, O’Day PA (2011) Cesium and strontium incorporation into zeolite-type phases during homogeneous nucleation from caustic solutions. Am Min 96:1809–1820
Wang G, Um W (2013) Facilitated strontium transport by remobilization of strontium-containing secondary precipitates in Hanford site subsurface. J Hazard Mater 248–249:364–370
Reynolds JG, Cooke GA, Huber HJ (2013) Degradation of dome cutting minerals in Hanford waste. In: Waste management 13 proceedings, waste management symposia Inc., Tucson, AZ
Fletcher M, Chao GY, Mandaring JA (1982) New mineral names. Am Min 67:854–860
Britvin SN, Ferraris G, Ivaldi G, Bogdanoca AN, Chukanov NV (2002) Cattiite, Mg3(PO4)2*22H2O, a new mineral from Zhelezny mine (Kovdor Massiv, Kola peninsula, Russia). Neues Jb F Miner Monat. https://doi.org/10.1127/0028-3649/2002/2002-0160
Khomyakov AP (2001) The distribution of minerals in hyper-agpaitic rocks in terms of symmetry: evolution of views on the number and symmetry of minerals. Geol Greenland Surv Bull 190:73–82
Liferovich RP, Sokolova EV. Hawthorne FC, Laajoki KVO, Gehor S, Pakhomovsky YA, Sorokhtina NV (2000) Gladiusite, Fe3 + 2(Fe2+,Mg)4(PO4)(OH)11(H2O), a new hydrothermal mineral species from the phoscorite–carbonatite unit, Kovdor Complex, Kola Peninsula, Russia. Can Min 38:1477–1485
Khomyakov AP (1987) Salt minerals in ultra-agpaitic rocks and the ore potential of alkaline massifs. Int Geol Rev 29:1446–1456
Lapustin YL, Bykova AV, Bukin BI (1972) Natrophosphate, a new mineral. Int Geol Rev 14:984–989
Bolling SD, Reynolds JG, Ely TM, Lachut JS, Lamothe MW, Cooke GA (2020) Natrophosphate and kogarkoite precipitated from alkaline nuclear waste at Hanford. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 323:329–339
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Washington River Protection Solutions, LLC as part of the Tank Operations Contract with the United States Department of Energy, Office of River Protection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynolds, J.G., Cooke, G.A. & Herting, D.L. Sodium strontium phosphate nonahydrate (NaSrPO4·9H2O) found in Hanford nuclear waste. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 326, 435–443 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07296-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07296-1