Abstract
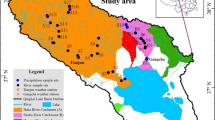
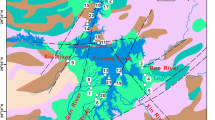
Stable isotope composition in precipitation, river water, and groundwater was used to investigate the hydrological conditions in the Pihe River catchment of Southwest China. Significant seasonal isotopic variations exist in precipitation and river water, and there is 1-month delay in the river water response to precipitation. The river water is gradually enriched under the influence of evaporation. However, due to the influence of recharge from external water source, the evaporation ratios do not strictly increase with the flow distance. The seasonal isotopic values in groundwater fluctuate the least. River water supplies groundwater more than precipitation in dry season.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kendall C, McDonnell JJ (1998) Isotope traces in catchment hydrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gat RJ (1996) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 24(1):225–262. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.24.1.225
Tetzlaff D, Waldron S, Brewer MJ, Soulsby C (2007) Assessing nested hydrological and hydrochemical behaviour of a mesoscale catchment using continuous tracer data. J Hydrol 336(3–4):430–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.01.020
Koeniger P, Leibundgut C, Stichler W (2009) Spatial and temporal characterisation of stable isotopes in river water as indicators of groundwater contribution and confirmation of modelling results; a study of the Weser river, Germany. Isot Environ Health Stud 45(4):289–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256010903356953
Reckerth A, Stichler W, Schmidt A, Stumpp C (2017) Long-term data set analysis of stable isotopic composition in German rivers. J Hydrol 552:718–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.07.022
Šanda M, Sedlmaierová P, Vitvar T, Seidler C, Kändler M, Jankovec J, Kulasová A, Paška F (2017) Pre-event water contributions and streamwater residence times in different land use settings of the transboundary mesoscale Lužická Nisa catchment. J Hydrol Hydromech 65(2):154–164. https://doi.org/10.1515/johh-2017-0003
Rozanski K, Araguas-Araguas L, Gonfiantini R (1992) Relation between long-term trends of oxygen-18 isotope composition of precipitation and climate. Science 258(5084):981–985. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.258.5084.981
Thompson LG, Yao T, Mosley-Thompson E, Davis ME, Henderson KA, Lin P (2000) A high-resolution millennial record of the South Asian monsoon from Himalayan ice cores. Science 289(5486):1916–1920. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5486.1916
Zhisheng A, Kutzbach JE, Prell WL, Porter SC (2001) Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature 411(6833):62–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/35075035
Paces JB, Wurster FC (2014) Natural uranium and strontium isotope tracers of water sources and surface water-groundwater interactions in arid wetlands—Pahranagat Valley, Nevada, USA. J Hydrol 517:213–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.05.011
Brooks JR, Gibson JJ, Birks SJ, Weber MH, Rodecap KD, Stoddard JL (2014) Stable isotope estimates of evaporation: inflow and water residence time for lakes across the United States as a tool for national lake water quality assessments. Limnol Oceanogr 59(6):2150–2165. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2014.59.6.2150
Gibson JJ, Edwards TWD (2002) Regional water balance trends and evaporation-transpiration partitioning from a stable isotope survey of lakes in northern Canada. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 16(2):10–11–10–14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001gb001839
Gibson JJ, Edwards TWD, Bursey GG, Prowse TD (1993) Estimating evaporation using stable isotopes: quantitative results and sensitivity analysis for 2 catchments in Northern Canada. Nord Hydrol 24(2–3):79–94
Qian H, Wu JH, Zhou YH, Li PY (2014) Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes as indicators of lake water recharge and evaporation in the lakes of the Yinchuan Plain. Hydrol Process 28(10):3554–3562. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9915
Wang SQ, Tang CY, Song XF, Wang QX, Zhang YH, Yuan RQ (2014) The impacts of a linear wastewater reservoir on groundwater recharge and geochemical evolution in a semi-arid area of the Lake Baiyangdian watershed, North China Plain. Sci Total Environ 482:325–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.130
Xu CY, Singh VP (1998) Dependence of evaporation on meteorological variables at different time-scales and intercomparison of estimation methods. Hydrol Process 12(3):429–442. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(19980315)12:33.0.CO;2-A
Jasechko S, Sharp ZD, Gibson JJ, Birks SJ, Yi Y, Fawcett PJ (2013) Terrestrial water fluxes dominated by transpiration. Nature 496(7445):347–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11983
Zhang XP, Yao TD, Tian LD (2003) Study on the fractionation mechanism of stable isotope in evaporating water body. J Glaciol Geocryol 01:65–71
Hu HY, Bao WM, Wang T, Qu SM (2007) Derivation of rayleigh fractionation formula and its experiment study in water evaporation. J Hydraul Eng S1:314–317
Bao WM, Hu HY, Wang T, Qu SM (2008) Experimental study on the fractionation mechanism of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in evaporation from water surface of evaporation pans. Adv Water Sci 19(06):780–785
Ma B, Liang X, Jin MG, Li J, Niu H (2015) Characteristics of fractionation of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in evaporating water in the typical region of the North China Plain. Adv Water Sci 26(05):639–648 (in Chinese)
Wang YS, Ma ZM, Xu ZH (2011) Slope of evaporation lines in a model based on Rayleigh fractionation formula. Adv Water Sci 22(06):795–800
Ma Q, Zhang MJ, Wang SJ, Wang BL, Ma XN (2012) Contributions of local moisture to precipitations in Western China. Progr Geogr 31(11):1452–1459
Ma Q, Zhang MJ, Wang SJ, Wang BL (2013) Contributions of moisture from local evaporation to precipitations in Southeast China based on hydrogen and oxygen isotopes. Progr Geogr 32(11):1712–1720
Chen JF, Fang HD, Wu JJ, Lin JM, Lan WB, Chen JS (2019) Distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soils using PMF and lead isotopic composition. J Agro Enviro Sci 38(05):1026–1035
Chen DS, Gao L, Peng XH, Chen XM (2018) Hydrogen and oxygen isotope mixing model of soil water in arid and semiarid region. Soils 50(01):190–194
Pearce AJ, Stewart MK, Sklash MG (1986) Storm runoff generation in humid headwater catchments.1. Where does the water come from. Water Resour Res 22(8):1263–1272. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr022i008p01263
Sklash MG, Stewart MK, Pearce AJ (1986) Storm runoff generation in humid headwater catchments. 2. A case-study of hillslope and low-order stream response. Water Resour Res 22(8):1273–1282. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr022i008p01273
Hooper RP, Christophersen N, Peters NE (1990) Modeling streamwater chemistry as a mixture of soilwater end-members: an application to the Panola Mountain catchment, Georgia, USA. J Hydrol 116(1–4):321–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(90)90131-G
Hinton MJ, Schiff SL, English MC (1994) Examining the contributions of glacial till water to storm runoff using 2-component and 3-component hydrograph separations. Water Resour Res 30(4):983–993. https://doi.org/10.1029/93wr03246
Zeng SQ, Chen JY, Fu CS (2010) Application of environment isotope in base flow calculation for small costal basin in Zhuhai. Hydrology 30(02):20–24
Tao P, Yuan QH, Guo FZ, Ning NZ, Jian KD, Chun FW (2013) Characteristics of water stable isotopes and hydrograph separation in Baishui catchment during the wet season in Mt.Yulong region, south western China. Hydrol Process 27(25):3641–3648
Wang MLGL, Gao PY, Hua Fu (2006) Discussion on water security problem and countermeasure in Minjiang River. J Chongqing Jiaotong Univ (Nat Sci) 25:140–142 (in Chinese)
Chen W, Qing D, Zhang XB (2011) Comparison of microclimate characteristics between forest in the Tuojiang River valley. J Fujian For Sci Tech 38(1):19–22. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-7351.2011.01.05(in Chinese)
Shi X, Liu HB, Zhang J, Li JJ, Jin GS, Han J, Jf Z (2016) Laser spectrometry for stable isotope analysis and its application status. World Nucl Geosci 33(4):237–243. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2016.04.008(in Chinese)
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16(4):436–468
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133(3465):1702–1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Zheng SC, Sh Z (1986) Kinetic fractionation of stable isotopes. Geol Geochem 12:53–59 (in Chinese)
Majoube M (1971) Oxygen-18 and deuterium fractionation between water and steam. J Chim Phys Phys Chim Biol 68(10):1423–1436. https://doi.org/10.1051/jcp/1971681423
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology Lewis. Springer, Berlin
Chen ZX, Cheng J, Guo PW, Lin ZY, Zhang FY (2010) Distribution characters and its control factors of stable isotope in precipitation over China. Trans Atmos Sci 33(06):667–679. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1037.2010.00186
Xia CC, Chen K, Zhou J, Mei J, Liu YP, Liu GD (2019) Comparison of precipitation stable isotopes during wet and dry seasons in a subtropical monsoon climate region of China. Appl Ecol Environ Res 17(5):11979–11993. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1705_1197911993
Tian LD, Yao TD, Shen YP, Yang MX (2002) Study on stable isotope in river water and precipitation in Naqu River basin, Tibetan Plateau. Adv Water Sci 13(02):206–210
Li G, Zhang XP, Zhang LF, Wang YF, Deng XJ, Yang L, Lei CG (2015) Stable isotope characteristics in different water bodies in Changsha and implications for the water cycle environmental. Science 36(06):2094–2101
Chen FL, Zhang MJ, Wang SJ, Qiu X, Du MX (2017) Environmental controls on stable isotopes of precipitation in Lanzhou, China: an enhanced network at city scale. Sci Total Environ 609:1013–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.216
Zheng SH, Hou FG, Ni BL (1983) Study on hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in atmospheric precipitation in China. Chin Sci Bull 13:801–806
Zemp DC, Schleussner CF, Barbosa HMJ, van der Ent RJ, Donges JF, Heinke J, Sampaio G, Rammig A (2014) On the importance of cascading moisture recycling in South America. Atmos Chem Phys 14(23):13337–13359. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-13337-2014
Wang SJ, Zhang MJ, Che YJ, Chen FL, Qiang F (2016) Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in oases of arid central Asia: a stable isotope approach. Water Resour Res 52(4):3246–3257. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015wr018135
Xia CC, Liu GD, Mei J, Meng YC, Liu W, Hu Y (2019) Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in precipitation and the environmental controls in tropical monsoon climatic zone. Int J Hydrog Energy 44(11):5417–5427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.10.171
Pang ZH, Kong YL, Froehlich K, Huang TM, Yuan LJ, Li ZQ, Wang FT (2011) Processes affecting isotopes in precipitation of an arid region. Tellus Ser B Chem Phys Meteorol 63(3):352–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0889.2011.00532.x
Zong-Jie L, Zong-Xing L, Ling-Ling S, Jin-Zhu M (2020) Characteristic and factors of stable isotope in precipitation in the source region of the Yangtze River. Agric For Meteorol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.107825
Lemma B, Kebede S, Nemomissa S, Otte I, Glaser B, Zech M (2020) Spatial and temporal 2H and 18O isotope variation of contemporary precipitation in the Bale Mountains, Ethiopia. Isot Environ Health Stud. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256016.2020.1717487
Xu Q, Hoke GD, Jing LZ, Ding L, Yang Y (2014) Stable isotopes of surface water across the Longmenshan margin of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 15(8):3416–3429
Qian H, Dou Y, Xi-Jian LI, Yang BC, Zhao ZH (2007) Changes of δ18O and δD along Dousitu River and its indication of river water evaporation. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 1:107–117
Yi Y, Gibson JJ, Helie JF, Dick TA (2010) Synoptic and time-series stable isotope surveys of the Mackenzie River from Great Slave Lake to the Arctic Ocean, 2003 to 2006. J Hydrol 383(3–4):223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.12.038
Katsuyama M, Yoshioka T, Konohira E (2015) Spatial distribution of oxygen-18 and deuterium in stream waters across the Japanese archipelago. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19(3):1577–1588. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-1577-2015
Kendall C, Coplen TB (2001) Distribution of oxygen-18 and deuterium in river waters across the United States. Hydrol Process 15(7):1363–1393. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.217
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51979177). The authors are very grateful for the help of Xiaohua Huang, Jie Mei et al. in the laboratory of eco-hydrology and water-soil conservation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, K., Meng, Y., Liu, G. et al. Identifying hydrological conditions of the Pihe River catchment in the Chengdu Plain based on spatio-temporal distribution of 2H and 18O. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 324, 1125–1140 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07163-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07163-z