Abstract
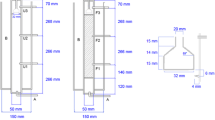
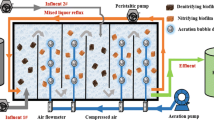
In this work, a down-flow fixed bed anaerobic biofilm reactor filled by biological ceramsites were prepared to remove the high concentration of NO3− (> 20 g/L) from nuclear industry wastewaters. The effects of hydraulic retention time, the concentration of NO3−, the molar ratio of C/N and temperature on the removal efficiencies of NO3− were investigated. The results showed that the removal rate of NO3− with the initial concentration of 6 g/L can reach 99% or more by controlling the hydraulic retention time at 0.75 h, the molar ratio of C/N at 1.5 and the temperature over 18 °C. In the process, the NO2− was not accumulated, and the autotrophic denitrifying bacteria grow well in anaerobic biofilm reactors, proving a usable method for removing the high concentration NO3− from nuclear industrial wastewaters.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernet N, Habouzit F, Moletta R (1996) Use of an industrial effluent as a carbon source for denitrification of a high-strength wastewater. J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46(1):92–97
Glass C, Silverstein JA (1999) Denitrification of high-nitrate, high-salinity wastewater. J Water Res 33(1):223–229
Dhamole PB, Nair RR, D'Souza SF, Lele SS (2007) Denitrification of high strength nitrate waste. J Bioresour Technol 98(2):247–252
Krishna MTV, Nancharaiah YV, Venugopalan VP, Satyam SPM (2016) Effect of C/N ratio on denitrification of high-strength nitrate wastewater in anoxic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. J Ecol Eng 91:441–448
Organization WH (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn.
Sadeq M, Moe CL, Attarassi B, Cherkaoui I, Elaouad R, Idrissi L (2008) Drinking water nitrate and prevalence of methemoglobinemia among infants and children aged 1–7 years in Moroccan areas. J Int J Hyg Environ Health 211(5–6):546–554
Maanen JMSV, Dijk AV, Mulder K, Baets MHD, Menheere PCA, Heide DVD, Mertens PLJM, Kleinjans JCS (1994) Consumption of drinking water with high nitrate levels causes hypertrophy of the thyroid. J Toxicol Lett 72(1–3):365
Eskiocak S, Dundar C, Basoglu T, Altaner S (2005) The effects of taking chronic nitrate by drinking water on thyroid functions and morphology. J Clin Exp Med 5(2):66–71
Richard YR (2010) Operating experiences of full-scale biological and ion‐exchange denitrification plants in France. J Water Environ J 3(2):154–167
Schoeman JJ, Steyn A (2003) Nitrate removal with reverse osmosis in a rural area in South Africa. J Desalination 155(1):15–26
Elmidaoui E, Sahli MMA, Chay L, Elabbassi H (2001) Pollution of nitrate in Moroccan ground water: removal by electrodialysis. J Desalination 136(1):325–332
Lecloux AJ (1999) Chemical, biological and physical constrains in catalytic reduction processes for purification of drinking water. J Catal Today 53(1):23–34
Fanning JC (2000) The chemical reduction of nitrate in aqueous solution. J Coord Chem Rev 199(1):159–179
Kapoor A, Viraraghavan T (1998) Nitrate removal from drinking water: review. J J Environ Eng 124(9):903–903
Sahinkaya E, Dursun N (2012) Sulfur-oxidizing autotrophic and mixotrophic denitrification processes for drinking water treatment: elimination of excess sulfate production and alkalinity requirement. J Chemosphere 89(2):144–149
Foglar L, Briški F (2003) Wastewater denitrification process: the influence of methanol and kinetic analysis. J Process Biochem 39(1):95–103
Ding A, Zheng P, Zhang M, Zhang Q (2017) Impacts of electron donor and acceptor on the performance of electrotrophic denitrification. J Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(24):19693–19702
Broman E, Jawad A, Wu X, Christel S, Ni G, Lopez-Fernandez M, Sundkvist JE, Dopson M (2017) Low temperature, autotrophic microbial denitrification using thiosulfate or thiocyanate as electron donor. J Biodegrad 28(4):287–301
Zhu C, Wang H, Yan Q, He R, Zhang G (2017) Enhanced denitrification at biocathode facilitated with biohydrogen production in a three-chambered bioelectrochemical system (BES) reactor. J Chem Eng J 312:360–366
Singh P, Singh MK, Beg YR, Nishad GR (2019) A review on spectroscopic methods for determination of nitrite and nitrate in environmental samples. J Talanta 191:364–381
Wang QH, Yu LJ, Liu Y, Lin L, Lu RG, Zhu JP, He L, Lu ZL (2017) Methods for the detection and determination of nitrite and nitrate: a review. J Talanta 165:709–720
Li X, Yuan Y, Yuan Y, Bi Z, Liu X, Huang Y, Liu H, Chen C, Xu S (2018) Effects of salinity on the denitrification efficiency and community structure of a combined partial nitritation-anaerobic ammonium oxidation process. J Bioresour Technol 249:550–556
Zhai S, Ji M, Zhao Y, Pavlostathis SG, Zhao Q (2018) Effects of salinity and COD/N on denitrification and bacterial community in dicyclic-type electrode based biofilm reactor. J Chemosphere 192:328–336
Nordstrom A, Herbert RB (2017) Denitrification in a low-temperature bioreactor system at two different hydraulic residence times: laboratory column studies. J Environ Technol 38(11):1362–1375
Nguyen TNP, Chao SJ, Chen PC, Huang C (2018) Effects of C/N ratio on nitrate removal and floc morphology of autohydrogenotrophic bacteria in a nitrate-containing wastewater treatment process. J J Environ Sci (China) 69:52–60
Chen H, Jogler M, Rohde M, Klenk HP, Busse HJ, Tindall BJ, Sproer C, Overmann J (2012) Reclassification and emended description of Caulobacter leidyi as Sphingomonas leidyi comb. nov., and emendation of the genus Sphingomonas. J Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(Pt 12):2835–2843
Hsu YH, Lai WA, Lin SY, Hameed A, Shahina M, Shen FT, Zhu ZL, Young LS, Young CC (2013) Chiayiivirga flava gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium of the family Xanthomonadaceae isolated from an agricultural soil, and emended description of the genus Dokdonella. J Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(Pt 9):3293–3300
Hwang CY, Cho BC (2008) Ponticoccus litoralis gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine bacterium in the family Rhodobacteraceae. J Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58(Pt 6):1332–1338
Chen WM, Xie PB, Hsu MY, Sheu SY (2018) Parvibium lacunae gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Alcaligenaceae isolated from a freshwater pond. J Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68(4):1291–1299
Song J, Choo YJ, Cho JC (2008) Perlucidibaca piscinae gen. nov., sp. nov., a freshwater bacterium belonging to the family Moraxellaceae. J Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58(Pt 1):97–102
Zhang WY, Fang MX, Zhang WW, Xiao C, Zhang XQ, Yu ZP, Zhu XF, Wu M (2013) Extensimonas vulgaris gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Comamonadaceae. J Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(Pt 6):2062–2068
Drobish AM, Emery BD, Whitney AM, Lauer AC, Metcalfe MG, McQuiston JR (2016) Oblitimonas alkaliphila gen. nov., sp. nov., in the family Pseudomonadaceae, recovered from a historical collection of previously unidentified clinical strains. J Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(8):3063–3070
Mu Y, Zhou L, Zeng XC, Liu L, Pan Y, Chen X, Wang J, Li S, Li WJ, Wang Y (2016) Arsenicitalea aurantiaca gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Hyphomicrobiaceae, isolated from high-arsenic sediment. J Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(12):5478–5484
Straub KL, Schönhuber WA, Buchholz-Cleven BEE, Schink B (2004) Diversity of ferrous iron-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing bacteria and their involvement in oxygen-independent iron cycling. J Geom J 21(6):371–378
Kiskira K, Papirio S, van Hullebusch ED, Esposito G (2017) Fe(II)-mediated autotrophic denitrification: a new bioprocess for iron bioprecipitation/biorecovery and simultaneous treatment of nitrate-containing wastewaters. J Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 119:631–648
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the nuclear energy development project of the State Administration of Science. Technology and Industry for National Defense. PRC and CNNC Jianzhong Nuclear fuel Co., Ltd. (190GHN001), the Opening Project of Cooperative Innovation Center for Nuclear Fuel Cycle Technology and Equipment, University of South China (2019KFQ06) and Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Hunan (18C0448).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Lei, Z., Hu, E. et al. Removal of high concentrations of NO3− from nuclear industrial wastewater by using a fixed-bed bioreactor. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 324, 803–811 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07104-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07104-w