Abstract
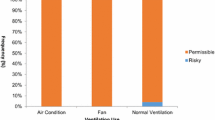
This study aims to: (1) Acquire the radon level in closed office rooms, providing radon exposure data for preliminary health risk assessment of office-working population. (2) Pre-analyze the relationship between radon concentration and indoor temperature, relative humidity. (3) Estimate seasonal, annual and total radon effective dose for ordinary office-working population. The results show that the 24-h or 8-h average radon concentrations in closed office rooms were about 32.0 Bq/m3 and 29.5 Bq/m3 during detection period, and the estimated effective doses in office rooms calculated by using 24-h and 8-h average radon concentrations were all far below that in residential environment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNSVCEAR (1993) Report to the general assembly with scientific annexes. http://www.unscear.org/unscear/en/publications/1993.html
ICRP (1993) ICRP Publication 50: Lung Cancer Risk from Exposures to Radon Daughters. http://www.icrp.org/publication.asp?id=ICRPPublication50
IARC (1988) Directory of on-going research in cancer epidemiology, 1988. http://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Scientific-Publications/Directory-Of-On-Going-Research-In-Cancer-Epidemiology-1988
Khan AJ (2000) A study of indoor radon levels in Indian dwellings, influencing factors and lung cancer risks. Radiat Meas 32(2):87–92
Al-Jarallah MI, Fazal-ur-Rehman A-JF, Al-Shukri A (2003) Indoor radon measurements in dwellings of four Saudi Arabian cities. Radiat Meas 36(1–6):445–448
Khayrat AH, Al-Jarallah MI, Fazal-Ur-Rehman X, Abu-Jarad F (2003) Indoor radon survey in dwellings of some regions in Yemen. Radiat Meas 36(1):449–451
Papaefthymiou H, Mavroudis A, Kritidis P (2003) Indoor radon levels and influencing factors in houses of Patras, Greece. J Environ Radioact 66(3):247–260
Rafique M, Rahman SU, Akram M (2012) Estimation of concentration and exposure doses due to radon by using CR-39 plastic track detectors in the residences of Sudhnuti, Azad Kashmir, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 66(4):1225–1232
Girault F, Perrier F (2012) Estimating the importance of factors influencing the radon-222 flux from building walls. Sci Total Environ 433:247–263
Demoury C, Ielsch G, Hemon D, Laurent O, Laurier D, Clavel J, Guillevic J (2013) A statistical evaluation of the influence of housing characteristics and geogenic radon potential on indoor radon concentrations in France. J Environ Radioact 126(4):216–225
Espinosa G, Chavarria A, Golzarri JI (2013) A study of indoor radon in greenhouses in Mexico City, Mexico. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 296(1):37–41
Li W, Li X, Wang F, Xu Y (2016) Occupational exposure assessment and radiation dose estimation of vegetable-plant farmers to 222 Rn in greenhouses of Shouguang county, China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 1:1–6
Li X, Xu X, Li W, Wang F, Hai C (2016) Preliminary study on the variation of radon-222 inside greenhouse of Shouguang county, China. J Environ Radioact 153:120–125
Wiegand J, Feige S, Quingling X, Schreiber U, Wieditz K, Wittmann C, Xiarong L (2000) Radon and thoron in cave dwellings (Yan’an, China). Health Phys 78(4):438–444
Yamada Y, Tokonami S, Zhuo W, Yonehara H, Ishikawa T, Furukawa M, Fukutsu K, Sun Q, Hou C, Zhang S, Akiba S (2005) Rn-Tn discriminative measurements and their dose estimates in Chinese loess plateau. Int Congr 1276:76–80
Shang B, Chen B, Gao Y, Wang Y, Cui H, Li Z (2005) Thoron levels in traditional Chinese residential dwellings. Radiat Environ Biophys 44(3):193–199
Tschiersch J, Haninger T (2006) Comments on “Adjusting Lung Cancer Risks for Temporal and Spatial Variations in Radon Concentrations in Dwellings in Gansu Province, China” by Lubin et al. (Radiat. Res. 163, 571-579, 2005). Radiat Res 166:38–69
Yamada Y, Sun Q, Tokonami S, Akiba S, Zhou W, Hou C, Zhang S, Ishikawa T, Furukawa M, Fukutsu K, Yonehara H (2006) Radon-thoron discriminative measurements in Gansu Province, China, and their implication for dose estimates. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 69(7):723–734
Shang B, Tschiersch J, Cui H, Xia YX (2008) Radon survey in dwellings of Gansu, China: the influence of thoron and an attempt for correction. Radiat Environ Biophys 47(3):367–373
Lu X, Li LY, Zhang X (2009) An environmental risk assessment of Radon in Lantian Karst Cave of Shaanxi, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 198(1):307–316
Radford EP (1985) Radon daughters and lung cancer. N Engl J Med 313(313):1610–1611
Archer VE (1987) Lung cancer risks of underground miners: cohort and case-control studies. Yale J Biol Med 61(3):183–193
Howe GR, Nair RC, Newcombe HB, Miller AB, Abbatt JD (1986) Lung cancer mortality (1950-80) in relation to radon daughter exposure in a cohort of workers at the Eldorado Beaverlodge uranium mine. J Natl Cancer Inst 77(2):357–362
Kristan J, Kobal I (1973) A modified scintillation cell for the determination of radon in uranium mine atmosphere. Health Phys 24(1):103–104
Cohen BL (1982) Radon daughter exposure to uranium miners. Health Phys 42(42):449–457
Inoue K, Hosoda M, Tokonami S, Ishikawa T, Fukushi M (2013) Investigation of radon and thoron concentrations in a landmark skyscraper in Tokyo. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298(3):2009–2015
Sugino M, Tokonami S, Zhuo W (2005) Radon and thoron concentrations in offices and dwellings of the Gunma prefecture, Japan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 266(2):205–209
Ćurguz Z, Stojanovska Z, Žunić ZS, Kolarž P, Ischikawa T, Omori Y, Mishra R, Sapra BK, Vaupotič J, Ujić P, Bossew P (2015) Long-term measurements of radon, thoron and their airborne progeny in 25 schools in Republic of Srpska. J Environ Radioact 148:163–169
Stojanovska Z, Zunic ZS, Bossew P, Bochicchio F, Carpentieri C, Venoso G, Mishra R, Rout RP, Sapra BK, Burghele BD, Cucos-Dinu A (2014) Results from time integrated measurements of indoor radon, thoron and their decay product concentrations in schools in the Republic of Macedonia. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 162(1–2):152–156
Afolabi OT, Esan DT, Banjoko B, Fajewonyomi BA, Tobih JE, Olubodun BB (2015) Radon level in a Nigerian University Campus. BMC Res Notes 8:677
Stojanovska Z, Boev B, Zunic ZS, Ivanova K, Ristova M, Tsenova M, Ajka S, Janevik E, Taleski V, Bossew P (2016) Variation of indoor radon concentration and ambient dose equivalent rate in different outdoor and indoor environments. Radiat Environ Biophys 55(2):171–183
Porstendörfer J, Butterweck G, Reineking A (1994) Daily variation of the radon concentration indoors and outdoors and the influence of meteorological parameters. Health Phys 67(3):283–287
Steck JD (2009) Annual average indoor radon variations over two decades. Health Phys 96(1):37–47
Wallner P, Munoz U, Tappler P, Wanka A, Kundi M, Shelton JF, Hutter HP (2015) Indoor environmental quality in mechanically ventilated, energy-efficient buildings vs. conventional buildings. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(11):14132–14147
Boice JDJR (1997) Radon, your home or mine? Radiat Res 147(2):135–137
Wang Z (1992) Radon level in China and elevated indoor exposure in carbon brick and cave dwellings. In: Proceedings of the international conference on radiattion effects and protection, pp 325–328
Barazza F, Gfeller W, Palacios M, Murith C (2015) An investigation of the potential causes for the seasonal and annual variations in indoor radon concentrations. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 167(1–3):75–81
Rogers VC, Nielson KK (1991) Multiphase radon generation and transport in porous materials. Health Phys 60(6):807–815
Gadd MS, Borak TB (1995) In-situ determination of the diffusion coefficient of 222Rn in concrete. Health Phys 68(6):817–822
Pal MVD, Graaf ERVD, Meijer RJD, Hendriks NA (2001) Experimental set-up for measuring diffusive and advective transport of radon through building materials. Sci Total Environ 272(1–3):315–321
ICRP (1993) ICRP Publication 65: Protection Against Radon-222 at Home and at Work. http://www.icrp.org/publication.asp?id=ICRP
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the natural science foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2015HL099 and ZR2014JL016) and supported by the youth innovation fundation of Weifang medical university (K1302016) and supported by Scientific and Technological Project of Weifang Science and Technology Bureau (20121234), the authors express gratitude for financially support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Li, W., Shan, H. et al. Radon survey in office room and effective dose estimation for staff. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 324, 561–568 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07082-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07082-z