Abstract
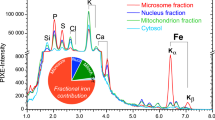
Post-mortem brain tissues substantia nigra pars compacta were investigated using PIXE and EDX methods for the presence of iron and other metal elements. Four different brain samples were irradiated with 3 MeV proton beam to collect X-ray spectra from which distribution of Fe, Mn, Cr and Zn in brain tissues were determined using GUPIXWIN software. The concentration of iron in the brain tissues varied from about 50 ng/cm2 to ~ 4 μg/cm2. The EDX method showed only a qualitative presence of Fe, Zn, Al and Si in investigated samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zucca FA, Bellei C, Giannelli S et al (2006) Neuromelanin and iron in human locus coeruleus and substantia nigra during aging: consequences for neuronal vulnerability. J Neural Transm 113:757–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-006-0453-2
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Lee AJ et al (1989) Increased nigral iron content and alterations in other metal ions occurring in brain in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 52:1830–1836. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07264.x
Zecca L, Youdim MBH, Riederer P et al (2004) Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:863–873. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1537
Thomas M, Jankovic J (2004) Neurodegenerative disease and iron storage in the brain. Curr Opin Neurol 17:437–442. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wco.0000137534.61244.d1
Tanner CM, Goldman SM (1996) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroepidemiology 14:317–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0733-8619(05)70259-0
Povinec PP, Masarik J, Ješkovský M et al (2016) Recent results from the AMS/IBA laboratory at the Comenius University in Bratislava: preparation of targets and optimization of ion sources. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4406-9
Povinec PP, Masarik J, Kúš P et al (2015) A new IBA-AMS laboratory at the Comenius University in Bratislava (Slovakia). Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 342:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2014.10.011
Zeman J, Ješkovský M, Kaiser R et al (2017) PIXE beam line at the CENTA facility of the Comenius University in Bratislava: first results. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 311:1409–1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-5004-1
Biesemeier A, Eibl O, Eswara S et al (2016) Elemental mapping of Neuromelanin organelles of human Substantia Nigra: correlative ultrastructural and chemical analysis by analytical transmission electron microscopy and nano-secondary ion mass spectrometry. J Neurochem. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13648
Zecca L, Shima T, Stroppolo A et al (1996) Interaction of neuromelanin and iron in substantia nigra and other areas of human brain. Neuroscience 73:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(96)00047-4
Zecca L, Bellei C, Costi P et al (2008) New melanic pigments in the human brain that accumulate in aging and block environmental toxic metals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:17567–17572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808768105
Kuisma-Kursula P (2000) Accuracy, precision and detection limits of SEM-WDS, SEM-EDS and PIXE in the multi-elemental analysis of medieval glass. X-Ray Spectrom 29:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4539(200001/02)29:1%3c111:AID-XRS408%3e3.0.CO;2-W
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the EU Research and Development Operational Program funded by the ERDF (Project No. 26,240,120,012, 26240120026 and 26240220004), and by the IAEA (TC Project RER7008 and SLR/1001). This study has also been supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency APVV 16-0039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pánik, J., Kopáni, M., Zeman, J. et al. Determination of metal elements concentrations in human brain tissues using PIXE and EDX methods. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 318, 2313–2319 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6208-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6208-3