Abstract
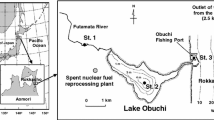
The 129I inventory in sediment of brackish lake, beside a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Rokkasho, Japan, was clarified from 1997 to 2016. The 129I was discharged to the atmosphere and ocean during cutting and chemical processing the spent fuel in the test operation from April 2006 to October 2008, although the plant is under final safety assessment as of May 2018. The 129I concentration and 129I/127I ratio in the surface sediment were 5–6 and 4–5 times higher than those in 1997, respectively. The 129I to a depth of 25 cm in the sediment increased until 2010–2012, then stabilized with accumulated state.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao U, Fehn U (1999) Source and reservoirs of anthropogenic iodine-129 in western New York. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:1927–1938
Reithmeier H, Lazarev V, Rühm W, Nolte E (2010) Anthropogenic 129I in the atmosphere: overview over major sources, transport processes and deposition pattern. Sci Tot Environ 408:5052–5064
Hou X, Povinec PP, Zhang L, Shi K, Biddulph D, Chang CC, Fan Y, Golser R, Hou Y, Jeskovsky M, Jull AJT, Liu Q, Luo M, Steier P, Zhou W (2013) Iodine-129 in seawater offshore Fukushima: distribution, inorganic speciation, sources, and budget. Environ Sci Technol 47:3091–3098
Aldahan A, Alfimov V, Possnert G (2007) 129I anthropogenic budget: major sources and sinks. Appl Geochem 22:606–618
Michel R, Daraoui A, Gorny M, Jakob D, Sachse R, Tosch L, Nies H, Goroncy I, Herrmann J (2012) Iodine-129 and iodine-127 in European seawaters and in precipitation from Northern Germany. Sci Total Environ 419:151–169
JFNL (Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited) (2016) Our business. http://www.jnfl.co.jp/ja/business/report/public_archive/safety-agreement-report/. Accessed 21 Nov 2017 (in Japanese)
Hasegawa H, Kakiuchi H, Akata N, Ohtsuka Y, Hisamatsu S (2017) Regional and global contributions of anthropogenic iodine-129 in monthly deposition samples collected in North East Japan between 2006 and 2015. J Environ Radioact 171:65–73
Ueda S, Hasegawa H, Kakiuchi H, Akata N, Ohtsuka Y, Hisamatsu S (2015) Iodine-129 in water samples collected adjacent to a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Rokkasho, Japan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303:1211–1215
Ueda S, Kakiuchi H, Hasegawa H, Kawamura H, Hisamatsu S (2015) Concentration of 129I in aquatic biota collected from a lake adjacent to the spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Rokkasho, Japan. Radiat Prot Dosim 167:176–180
Ueda S, Kawabata H, Hasegawa H, Kondo K (2000) Characteristics of fluctuations in salinity and water quality in brackish Lake Obuchi. Limnology 1:57–62
Ueda S, Hasegawa H, Hisamatsu S (2017) Long-term variations in water quality of lakes in Rokkasho, Aomori, Japan, from 2004 to 2015. Jpn J Limnol 78:75–85
Schmidt A, Schnabel Ch, Handl J, Jakob D, Michel R, Synal H-A, Lopez JM, Suter M (1998) On the analysis of iodine-129 and iodine-127 in environmental materials by accelerator mass spectrometry and ion chromatography. Sci Total Environ 223:131–156
Ueda S, Ohtsuka Y, Kondo K, Inaba J (2005) Sedimentation rate in brackish Lake Obuchi, Rokkasho Village, Japan, bordered by nuclear fuel cycle facilities. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 264:343–349
Aldahan A, Englund E, Possnert G, Cato I, Hou XL (2007) Iodine-129 enrichment in sediment of the Baltic Sea. Appl Geochem 22:637–647
Englund E, Aldahan A, Possnert G (2008) Tracing anthropogenic nuclear activity with 129I in lake sediment. J Environ Radioact 99:219–229
Englund E, Aldahan A, Hou XL, Petersen R, Possnert G (2010) Speciation of iodine (127I and 129I) in lake sediments. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res B 268:1102–1110
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. M. Murakami and Mrs. S. Nakamura of Zax Co., Ltd. for their help with the sampling, and Drs. H. Kawamura and Y. Tennichi of the Kyushu Environmental Evaluation Association for their technical help with pretreatment of the samples. This study was performed under a contract with the government of Aomori Prefecture, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, S., Kakiuchi, H. & Hisamatsu, S. Inventory of 129I in brackish lake sediments adjacent to a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Japan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 318, 89–96 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6073-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6073-0