Abstract
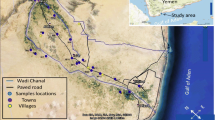
In this study, the levels of natural radioactivity in the groundwater samples collected from 26 different locations in Al-Zulfi, Al-Qassim and Al-Majmaah regions were determined. The estimated average values of 226Ra, 228Ra, 40K, gross α and gross β activities in the samples were 0.87 Bq L−1, 1.33 Bq L−1, 4.22 Bq L−1, 36.82 mBq L−1 and 831.91 mBq L−1, respectively. We found that age-dependent effective ingestion dose from radionuclides in all samples were higher than WHO recommended levels of 0.1 µSv y−1 for adults 0.2 µSv y−1 for children and 0.26 µSv y−1 for infants while 20 sampling locations have age-dependent effective dose equivalent from β contributors were higher than WHO recommended level of 0.1 mSv y−1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vesterbacka P (2007) Natural radioactivity in drinking water in Finland, Boreal. Environ Res 12:11–16
Alam MNC, Kamal MI, Ghose M, Islam S, Anwaruddin M (1999) Radiological assessment of drinking water of the Chittagong region of Bangladesh. Radiat Prot Dosim 82:207–214
Gruber V, Maringer FJ, Landstetter C (2009) Radon and other natural radionuclides in drinking water in Austria: measurement and assessment. Appl Radiat Isot 67:913–917
US-EPA (2003) List of drinking water contaminants and MCLs. United State of Environmental Protection Agency, EPA. http://www.epa.gov/safewater/mcl.html#mcls
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Chapter 9 Radiological Aspects, 4th Edition. World Health Organization Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data NLM classification: WA 675, Geneva
Bunotto DM, Bueno TO (2008) The natural radioactivity in Guarani aquifer groundwater, Brazil. Appl Radiat Isot 66:1507–1522
ICRP (1990) Recommendations of the international commission on radiological protection. International Commission on Radiological Protection, Publication 60, vol. 21 (Nos. 1–3), Pergamon Press Annals
Al-Refeai T, Al-Ghamdy D (1994) Geological and geotechnical aspects of Saudi Arabia. Geotech Geo Eng 12:253–276
RGME (1982) Al-Ghatt School soil investigations, Rashid Geotechnical and Material Engineers, unpublished report
Al-Moser AA (1988) Shear strength characteristics and effect of lime on strength parameters of soil from Al-Zulfi. BSc Project, Civil Engineering Department, King Saud University, Riyadh
Al-Santaly IM (1981) Al-Ghatt soil problems. BSc Project, Civil Engineering Department, King Saud University
RGME (1986) Geotechnical investigation. Rashid Geotechnical and Material Engineers, King Saud University, Gassim Campus, unpublished reports
Khalifa AM (2015) The Ediacaran–Cambrian and Ordovician rocks of Al Qasim Province, Saudi Arabia: facies, depositional history and regional correlation. J Afr Earth Sci 109:263–282
Jobbagy V, Watjen U, Meresova J (2010) Current status of gross alpha/beta activity analysis in water samples: a short overview of methods. J Radional Nucl Chem 286:393–399
Al-Dahaan MAS, Al-Ansari N, Knutsson S (2016) Influence of groundwater hypothetical salts on electrical conductivity total dissolved soilds. Eng (Sci Res Publ) 8:823–830
Abdurabu AW, Saleh AM, Ramli TA, Heryansyah A (2016) Occurrence of natural radioactivity and corresponding health risk in groundwater with an elevated radiation background in Juban District, Yemen. Environ Earth Sci 75:1360–1371
SM 7110 (1996) Gross alpha and gross beta radioactivity (total, suspended, and dissolved). Ed. 20th, EPA Approved
Krieger LH (1975) Interim radiochemical methodology for drinking water, EPA 600/4-75-008. US Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati
Herman L, Krieger EL, Whittaker (1980) Prescribed procedures for measurement of radioactivity in drinking, EPA-600/4-80-032, United States
ISO 9697 (2008) Water quality: measurement of gross beta activity in non-saline water. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
US-EPA (2007) Drinking water standards and health advisories table. United State of Environmental Protection Agency. http://www3.epa.gov/region9/water/drinking/files/dwsha_0607.pdf. Accessed 16 Dec 2015
Alkhomashi N, Ibhrahim Al-Hamarneh F, Almasoud IF (2016) Determination of natural radioactivity in irrigation water of drilled wells in northwestern Saudi Arabia. Chemosphere 144:1928–1936
Shabana EI, Kinsara AA (2014) Radioactivity in the groundwater of a high background radiation area. J Environ Radioact 137:181–189
Tomita J, Takada T, Tamamura S, Zhang J, Takahatake Y, Akita F, Nagao S, Yamamoto M (2014) Radium isotopes in saline groundwater from the western and central Hokkaido. Jpn. J Hot Spring Sci 64:146–164
ICRP (1996) Age-dependent doses to members of the public from intake of radionuclides: part 5, compilation of ingestion and inhalation dose coefficients, annals of the ICRP, 26 (1), ICRP publication 72. Pergamon Press, Oxford
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality, Recommendations, Vol. 1, 3rd Edition, World Health Organization, Geneva
UNSCEAR (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to General Assembly. Annex B: Exposure from Natural Radiation Sources and Report to General Assembly. With Scientific Annexes, United Nations Sales Publications No. E.00.IX.3 Volume I: Sources and No. E.00.IX.4 (Volume II: Effects). United Nations, New York, 1220 Pp
WHO (1996) Guidelines for drinking water quality, Vol. 2, 2nd Edition, World Health Organization, Geneva
US-EPA (2001) Health effect assessments summary tables (HEAST) for Radionuclides. United State of Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
WHO (2008) Guidelines for drinking water quality [electronic resource]: incorporating 1st and 2nd addenda recommendations, Vol. 1, World Health Organization, 197–209. Accessed 18 Jan 2015
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality: radiological aspects. World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/gdwq3/en/S
Calin MR, Ion AC, Radu I (2015) Evaluation of quality parameters and of natural radionuclides concentrations in natural mineral water in Romania. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303:305–313
Ramadan KA, Seddeek MK, Nijim A, Sharshar T, Badran HM (2011) Radioactivity of sand, groundwater and wild plants in northeast Sinai, Egypt. Isot Environ Health Stud 47:456–469
Desideri D, Roselli C, Feduzi L, Meli MA (2007) Radiological characterization of drinking waters in Central Italy. Microchem J 87:13–19
Altıkulac A, Turhan S, Gumus H (2015) The natural and artificial radionuclides in drinking water samples and consequent population doses. J Radiat Res Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.06.007
Beyermann M, Bunger T, Schmidt K, Obrikat D (2010) Occurrence of natural radioactivity in public water supples in Germany: 238U, 234U, 235U, 228Ra, 226Ra, 222Rn, 210Pb, 210Po and gross alpha activity concentration. Radiat Prot Dosim 141:72–81
Osman AA, Isam SMM, Ibrahim A, Saif S, Siddeeg MB, Eltayeb H, Idriss H, Hamza W, Yousif EH (2008) Investigation of natural radioactivity levels in water around Kadugli, Sudan. Appl Radiat Isot 66:1650–1653
Isam SMM, Pettersson HBL, Lund E (2002) Uranium and thorium series radionuclides in drinking water from drilled bedrock wells: correlation to geology and bedrock radioactivity, and dose estimation. Radiat Prot Dosim 102:249–258
Ajayi OS, Owolabi TP (2008) Determination of natural radioactivity in drinking water in private dug well in Akure, southwestern Nigeria. Radiat Prot Dosim 128(4):477–484
Dinh Chau N, Michalec B (2009) Natural radioactivity in bottled natural spring, mineral and therapeutic waters in Poland. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 279:121–129
Turhan S, Ozcitak E, Taskin H, Varinlioglu A (2013) Determination of natural radioactivity by gross alpha and beta measurements in ground water samples. Water Res 47:3103–3108
Al-Amir MS, Al-Hamarneh FI, Al-Abed T, Awadallah M (2012) Natural radioactivity in tap water and associated age-dependent dose and lifetime risk assessment in Amman, Jordan. Appl Radiat Isot 70:692–698
Jankovic MM, Todorovic JD, Todorovic AN, Nikolov J (2012) Natural radionuclides in drinking waters in Serbia. Appl Radiat Isot 70:2703–2710
Rangel DJI, Lopez DRH, Garcia MF, Torres QLL, Villalba ML, Sujo CL, Montero CME (2002) Radioactivity in bottled waters sold in Mexico. Appl Radiat Isot 56:931–936
Palomo M, Villa M, Casacuberta N, Penalver A, Borrull F, Aguilar C (2011) Evaluation of different parameters affecting the liquid scintillation spectrometry measurement of gross alpha and beta index in water samples. Appl Radiat Isot 69:1274–1281
Kovacs T, Bodrogi E, Dombovari P, Somlai J, Cs Nemeth, Capote A, Tarjan S (2004) 238U, 226Ra, 210Po concentrations of bottled mineral waters in Hungary and their committed effective dose. Radiat Prot Dosim 108:175–181
Karamanis D, Stamoulis K, Ioannides KG (2007) Natural radionuclides and heavy metals in bottled water in Greece. Desalination 213:90–97
Forte M, Rusconi R, Cazzaniga MT, Sgorbati G (2007) The measurement of radioactivity in Italian drinking waters. Microchem J 85:98–102
Darren A, Lytle Thomas S, Lili W, Abe C (2014) The accumulation of radioactive contaminants in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res 50:396–407
Gorur KF, Keser R, Akcay N, Dizman S, Okumusoglu TN (2011) Radionuclides and heavy metals concentrations in Turkish market tea. Food Control 22:2065–2070
US-EPA (1988) Limiting values of radionuclide intake and air concentration and dose conversion factors for inhalation. United State of Environmental Protection Agency, Submersion and Ingestion, Federal Guideline Report No. 11, EPA 520/1-88-020, Washington, DC
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledged the financial support provided by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (Project No. 35–37).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alharbi, T., Adel, A., Baloch, M.A. et al. Natural radioactivity measurements and age-dependent dose assessment in groundwater from Al-Zulfi, Al-Qassim and Al-Majmaah regions, Saudi Arabia. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 318, 935–945 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6053-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6053-4