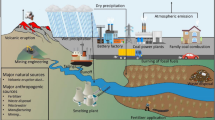
Abstract
Currently, the existing microbial radionuclides transformations processes are not completely understood. Bacteria, however, solubilize radionuclides by direct enzymatic reduction, or indirectly by its metabolites and by facilitating electrochemical redox systems. Microbes exchange electrons from proteins, organelles, metabolites to metals and electrodes have strengthened the novel bioremediation methods. In contrast, MRCs based on this redox behavior has offered considerable value over traditional treatment because of growing renewable and conception of energy incentives methods. Moreover, MRCs provides a flexible platform that enables us to access integrated treatment process of generating power and for recovering valuable resources from the contaminated sites.

Obtained and modified with the permission, Copyright Elsevier


Obtained with the permission, Copyright, Biochemical Society Transactions, Portland Press


Obtained with the permission, Copyright Elsevier, and American Chemical Society
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lloyd JR, Renshaw JC (2005) Microbial transformations of radionuclides: fundamental mechanisms and biogeochemical implications. Met Ions Biol Syst 44:205–240
Prakash D, Gabani P, Chandel AK, Ronen Z, Singh OV (2013) Bioremediation: a genuine technology to remediate radionuclides from the environment. Microb Biotechnol 6(4):349–360. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12059
Francis AJ, Nancharaiah YV (2015) 9—in situ and ex situ bioremediation of radionuclide-contaminated soils at nuclear and norm sites A2—Velzen, Leo van. In: Environmental Remediation and Restoration of Contaminated Nuclear and Norm Sites. Woodhead Publishing, pp 185–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-78242-231-0.00009-0
None (1970) Toxicity and metabolism of radionuclides. Argonne National Lab, Argonne
Gorby YA, Lovley DR (1992) Enzymatic uranium precipitation. Environ Sci Technol 26(1):205–207
Lloyd JR, Gadd GM (2011) The geomicrobiology of radionuclides. Geomicrobiol J 28(5–6):383–386. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2010.547551
Lloyd JR, Macaskie LE (2000) Bioremediation of radionuclide-containing wastewaters. In: Lovley D (ed) Environmental microbe-metal interactions. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.1128/9781555818098.ch13
Newsome L, Morris K, Lloyd JR (2014) The biogeochemistry and bioremediation of uranium and other priority radionuclides. Chem Geol 363:164–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.10.034
Beveridge TJ, Murray RG (1980) Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 141(2):876–887
Lovley DR, Phillips EJP, Gorby YA, Landa ER (1991) Microbial reduction of uranium. Nature 350(6317):413–416
Lovley DR, Phillips EJ (1992) Reduction of uranium by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(3):850–856
Francis AJ, Dodge CJ, Lu F, Halada GP, Clayton CR (1994) XPS and XANES studies of uranium reduction by Clostridium sp. Environ Sci Technol 28(4):636–639
Shelobolina ES, Sullivan SA, O’Neill KR, Nevin KP, Lovley DR (2004) Isolation, characterization, and U(VI)-reducing potential of a facultatively anaerobic, acid-resistant Bacterium from Low-pH, nitrate- and U(VI)-contaminated subsurface sediment and description of Salmonella subterranea sp. nov. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(5):2959–2965
Suzuki Y, Kelly SD, Kemner KM, Banfield JF (2002) Nanometre-size products of uranium bioreduction. Nature 419(6903):134
Kelly SD, Kemner KM, Carley J, Criddle C, Jardine PM, Marsh TL, Phillips D, Watson D, Wu WM (2008) Speciation of uranium in sediments before and after in situ biostimulation. Environ Sci Technol 42(5):1558–1564
Bernier-Latmani R, Veeramani H, Vecchia ED, Junier P, Lezama-Pacheco JS, Suvorova EI, Sharp JO, Wigginton NS, Bargar JR (2010) Non-uraninite products of microbial U(VI) reduction. Environ Sci Technol 44(24):9456–9462
Williams KH, Bargar JR, Lloyd JR, Lovley DR (2013) Bioremediation of uranium-contaminated groundwater: a systems approach to subsurface biogeochemistry. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(3):489–497
Lovley DR, Phillips EJP (1992) Bioremediation of uranium contamination with enzymatic uranium reduction. Environ Sci Technol 26(11):2228–2234
Lovley DR, Giovannoni SJ, White DC, Champine JE, Phillips EJ, Gorby YA, Goodwin S (1993) Geobacter metallireducens gen. nov. sp. nov., a microorganism capable of coupling the complete oxidation of organic compounds to the reduction of iron and other metals. Arch Microbiol 159(4):336–344
Richter K, Schicklberger M, Gescher J (2012) Dissimilatory reduction of extracellular electron acceptors in anaerobic respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(4):913–921
Wall JD, Krumholz LR (2006) Uranium reduction. Annu Rev Microbiol 60:149–166
Marshall MJ, Beliaev AS, Dohnalkova AC, Kennedy DW, Shi L, Wang Z, Boyanov MI, Lai B, Kemner KM, McLean JS, Reed SB, Culley DE, Bailey VL, Simonson CJ, Saffarini DA, Romine MF, Zachara JM, Fredrickson JK (2006) c-Type cytochrome-dependent formation of U(IV) nanoparticles by Shewanella oneidensis. PLoS Biol 4(8):e268. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040268
Lovley DR, Widman PK, Woodward JC, Phillips EJ (1993) Reduction of uranium by cytochrome c3 of Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(11):3572–3576
Lloyd JR, Leang C, Hodges Myerson AL, Coppi MV, Cuifo S, Methe B, Sandler SJ, Lovley DR (2003) Biochemical and genetic characterization of PpcA, a periplasmic c-type cytochrome in Geobacter sulfurreducens. Biochem J 369(Pt 1):153–161
Orellana R, Hixson KK, Murphy S, Mester T, Sharma ML, Lipton MS, Lovley DR (2014) Proteome of Geobacter sulfurreducens in the presence of U(VI). Microbiology 160(12):2607–2617. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.081398-0
Holmes DE, O’Neil RA, Chavan MA, N’Guessan LA, Vrionis HA, Perpetua LA, Larrahondo MJ, DiDonato R, Liu A, Lovley DR (2009) Transcriptome of Geobacter uraniireducens growing in uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments. ISME J 3(2):216–230
Shi L, Belchik SM, Wang Z, Kennedy DW, Dohnalkova AC, Marshall MJ, Zachara JM, Fredrickson JK (2011) Identification and characterization of UndAHRCR-6, an outer membrane endecaheme c-type cytochrome of Shewanella sp. strain HRCR-6. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(15):5521–5523
Khijniak TV, Slobodkin AI, Coker V, Renshaw JC, Livens FR, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Birkeland NK, Medvedeva-Lyalikova NN, Lloyd JR (2005) Reduction of uranium(VI) phosphate during growth of the thermophilic bacterium Thermoterrabacterium ferrireducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(10):6423–6426
Reguera G (2012) Electron transfer at the cell-uranium interface in Geobacter spp. Biochem Soc Trans 40(6):1227–1232
Cologgi DL, Lampa-Pastirk S, Speers AM, Kelly SD, Reguera G (2011) Extracellular reduction of uranium via Geobacter conductive pili as a protective cellular mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(37):15248–15252
Reguera G, McCarthy KD, Mehta T, Nicoll JS, Tuominen MT, Lovley DR (2005) Extracellular electron transfer via microbial nanowires. Nature 435(7045):1098–1101
Leang C, Qian X, Mester T, Lovley DR (2010) Alignment of the c-type cytochrome OmcS along pili of Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(12):4080–4084
Mehta T, Coppi MV, Childers SE, Lovley DR (2005) Outer membrane c-type cytochromes required for Fe(III) and Mn(IV) oxide reduction in Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8634–8641
Orellana R, Leavitt JJ, Comolli LR, Csencsits R, Janot N, Flanagan KA, Gray AS, Leang C, Izallalen M, Mester T, Lovley DR (2013) U(VI) reduction by diverse outer surface c-type cytochromes of Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(20):6369–6374
Fletcher KE, Boyanov MI, Thomas SH, Wu Q, Kemner KM, Löffler FE (2010) U(VI) reduction to mononuclear U(IV) by desulfitobacterium species. Environ Sci Technol 44(12):4705–4709. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903636c
Childers SE, Ciufo S, Lovley DR (2002) Geobacter metallireducens accesses insoluble Fe(III) oxide by chemotaxis. Nature 416(6882):767–769
Suzuki Y, Kitatsuji Y, Ohnuki T, Tsujimura S (2010) Flavin mononucleotide mediated electron pathway for microbial U(VI) reduction. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12(34):10081–10087
von Canstein H, Ogawa J, Shimizu S, Lloyd JR (2008) Secretion of flavins by Shewanella species and their role in extracellular electron transfer. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(3):615–623
Wang H, Ren ZJ (2013) A comprehensive review of microbial electrochemical systems as a platform technology. Biotechnol Adv 31(8):1796–1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.10.001
Morris JM, Jin S, Crimi B, Pruden A (2009) Microbial fuel cell in enhancing anaerobic biodegradation of diesel. Chem Eng J 146(2):161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.05.028
Wang X, Cai Z, Zhou Q, Zhang Z, Chen C (2012) Bioelectrochemical stimulation of petroleum hydrocarbon degradation in saline soil using U-tube microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(2):426–433
Pham H, Boon N, Marzorati M, Verstraete W (2009) Enhanced removal of 1,2-dichloroethane by anodophilic microbial consortia. Water Res 43(11):2936–2946
Luo H, Liu G, Zhang R, Jin S (2009) Phenol degradation in microbial fuel cells. Chem Eng J 147(2–3):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.07.011
Wang G, Huang L, Zhang Y (2008) Cathodic reduction of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] coupled with electricity generation in microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol Lett 30(11):1959–1966
Gregory KB, Lovley DR (2005) Remediation and recovery of uranium from contaminated subsurface environments with electrodes. Environ Sci Technol 39(22):8943–8947
Williams KH, Nevin KP, Franks A, Englert A, Long PE, Lovley DR (2010) Electrode-based approach for monitoring in situ microbial activity during subsurface bioremediation. Environ Sci Technol 44(1):47–54
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21777155, 21322703 and 41471260), the National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project (2013YQ17058508).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest exists.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dummi Mahadevan, G., Zhao, F. A concise review on microbial remediation cells (MRCs) in soil and groundwater radionuclides remediation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314, 1477–1485 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5612-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5612-4