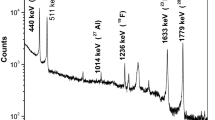
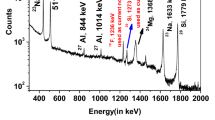
Abstract
Particle induced gamma-ray emission (PIGE) method using 4 MeV proton beam was utilized to analyze two types of barium borosilicate glass (BaBSG) samples for quantification of concentrations of low Z elements. The in situ current normalization method was applied in the analysis of eight samples containing varying concentration of F along with Si, B and Na. Charge normalized PIGE method was applied to determine concentrations of above low Z elements including Li and Al in samples having simulated nuclear waste from reprocessing of thoria spent fuel. Synthetic samples and NIST SRMs were used for method validation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kakodkar A (2001) Shaping the third stage of Indian Nuclear Power Programme. In: 12th Annual Conference of Indian Nuclear Society (INSAC-2001), Indore, India, 10–12 Oct 2001
Balakrishnan K, Kakodkar A (1994) Optimization of the initial fuel loading of the Indian PHWR with thorium bundles for achieving full power. Annal Nucl Ener 21:1–9
Gresky AT (1956) Solvent extraction separation of 233U and thorium from fission products by means of tributyl phosphate. Peac Uses At Energy 9:505–510
Srinivas C, Yalmali V, Pente AS, Wattal PK, Misra SD (2012) Thoria/thoria-urania dissolution studies for reprocessing application, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) Report, BARC/2012/E/007, June 2012. Mumbai, India
Parkinson BG, Holland D, Smith ME, Howes AP, Scales CR (2007) Effect of minor additions on structure and volatilization loss in simulated nuclear borosilicate glasses. J Non-Cryst Sol 353:4076–4083
Lee WE, Ojovan MI, Stennett MC, Hyatt NC (2006) Immobilisation of radioactive waste in glasses, glass composite materials and ceramics. Adv Appl Ceram 105:3–12
Kaushik CP, Mishra RK, Sengupta P, Kumar A, Das D, Kale GB, Raj K (2006) Barium borosilicate glass: a potential matrix for immobilization of sulfate bearing high-level radioactive liquid waste. J Nucl Mat 358:129–138
Ojovan MI, Lee WE (2007) New developments in glassy nuclear wasteforms. Nova Science Publishers Inc, New York. ISBN 1600217834
Eller PG, Tarvinen GO, Purson JD, Penneman RA, Ryan RR, Lytle FW, Greegor RB (1985) Actinide valences in borosilicate glass. Radiochim Acta 39:17–22
Mishra RK, Sudarsan V, Kaushik CP, Raj K, Vatsa RK, Body M, Tyagi AK (2009) Effect of fluoride ion incorporation on the structural aspects of barium–sodium borosilicate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 355:414–419
Farges F (1991) Structural environment around Th4+ in silicate glasses: implications for the geochemistry of incompatible Me4+ elements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:3303–3319
Mishra RK, Sengupta P, Kaushik CP, Tyagi AK, Kale GB, Raj K (2007) Studies on immobilization of thorium in barium borosilicate glass. J Nuc Mat 360:143–150
Nasir H, Kassandra P, Tristan L, Timothy A (2012) Thermal analysis and immobilisation of spent ion exchange resin in borosilicate glass. New J Glass Ceram 2:111–120
Mishra RK, Sudarsan V, Kaushik CP, Raj K, Kulshreshtha SK, Tyagi AK (2006) Structural aspects of barium borosilicate glasses containing thorium and uranium oxides. J Nucl Mat 359:132–138
Bickmore BR (2006) The effect of Al(OH) −4 on the dissolution rate of quartz. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:290–305
He F, Ping C, Zheng Y (2013) Viscosity and structure of lithium sodium borosilicate glasses. Phys Proced 48:73–80
Sengupta P, Kaushik CP, Dey GK (2013) Immobilization of high level nuclear wastes: the Indian scenario on a sustainable future of earth’s resources. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Raj K, Prasad KK, Bansal NK (2006) Radioactive waste management practices in India. Nucl Eng Des 226:914–930
Sengupta P, Kaushik CP, Mishra RK, Kale GB (2007) Microstructural characterization and role of glassy layer developed on inconel 690 during a nuclear high-level waste vitrification process. J Am Ceram Soc 90:3057–3062
Segebade C, Weise HP, Lutz GJ (1988) Photon Activation Analysis. W de Gruiter, Berlin, New York
Segebade C, Berger A (2008) Photon Activation Analysis. In: Meyers RA (ed) Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry. Wiley, New Jersey
De Soete D, Gijbels R, Hoste J (1972) Neutron activation analysis. Wiley-inter science. Wiley, London
Sudarshan K, Tripathi R, Nair AGC, Acharya R, Reddy AVR, Goswami A (2005) A simple method for correcting the neutron self-shielding effect of matrix and improving the analytical response in prompt gamma-ray neutron activation analysis. Anal Chim Acta 549:205–211
Acharya R (2009) Prompt gamma-ray neutron activation analysis methodology for determination of boron from trace to major contents. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 281:291–294
Chhillar S, Acharya R, Sodaye S, Sudarshan K, Santra S, Mishra RK, Kaushik CP, Choudhury RK, Pujari PK (2012) Application of particle induced gamma-ray emission for non-destructive determination of fluorine in barium borosilicate glass samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 294:115–119
Volfinger M, Robert JL (1994) Particle-induced-gamma-ray-emission spectrometry applied to the determination of light elements in individual grains of granite minerals. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 185:273–291
Macias ES, Radcliffe CD, Lewis CW, Sawicki CR (1978) Proton induced gamma-ray analysis of atmospheric aerosols for carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur composition. Anal Chem 50:1120–1124
Kiss AZ, Koltay E, Nyako B, Somorjal E, Anttila A, Raisanen J (1985) Measurement of thick-target gamma-ray production yields of the 7Li(p, p′)7Li and 7Li(p, γ)8Be reactions in the near-threshold energy region for the 7Li(p, n)7Be reaction. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 89:123–141
Savidou A, Aslanoglou X, Paradellis T, Pilakouta M (1999) Proton induced thick target γ-ray yields of light nuclei at the energy region Ep = 1.0–4.1 MeV. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 152:12–18
Molnar GL (ed) (2004) Handbook of prompt gamma activation analysis with neutron beams. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Raisanen J, Witting T, Keinonen J (1987) Absolute thick-target γ-ray yields for elemental analysis by 7 and 9 MeV protons. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 28:199–204
Chhillar S, Acharya R, Triptahi R, Sodaye S, Sudarshan K, Rout PC, Mukerjee SK, Pujari PK (2015) Compositional characterization of lithium titanate ceramic samples by determining Li, Ti and O concentrations simultaneously using PIGE at 8 MeV proton beam. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 305:463–467
Duerden P, Bird JR, Scott MD, Clayton E, Russel LH, Cohen DD (1980) Nucl Instrum Methods 168:447–453
Valković O, Jakšić M, Fazinić S, Valković V, Moschini G, Menapace E (1995) Quality control of PIXE and PIGE nuclear analytical techniques in geological and environmental applications. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 99:372–375
Willy M (1988) Applications of ion beam analysis in biology and medicine, a review. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 35:388–403
Dasari KB, Chhillar S, Acharya R, Ray DK, Behera A, Das NL, Pujari PK (2014) Simultaneous determination of Si, Al and Na concentrations by particle induced gamma-ray emission and applications to reference materials and ceramic archaeological artifacts. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 39:37–41
Chhillar S, Acharya R, Sodaye S, Pujari PK (2014) Development of particle induced gamma-ray emission methods for nondestructive determination of isotopic composition of boron and its total concentration in natural and enriched samples. Anal Chem 8:11167–11173
Chhillar S, Acharya R, Pai RV, Sodaye S, Mukerjee SK, Pujari PK (2012) A simple and sensitive particle induced gamma-ray emission method for non-destructive quantification of lithium in lithium doped Nd2Ti2O7 ceramic sample. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 293:437–441
Chhillar S, Acharya R, Vittal Rao TV, Bamankar YR, Mukerjee SK, Pujari PK, Aggarwal SK (2013) Non-destructive compositional analysis of sol–gel synthesized lithium titanate (Li2TiO3) by particle induced gamma-ray emission and instrumental neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298:1597–1603
Bugoi R, Cojocaru V, Constantinescu B, Calligaro T (2008) Compositional studies on Transylvanian gold nuggets: advantages and limitations of PIXE–PIGE analysis. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 266:2316–2319
Calligaro T, Dran JC, Poirot JP, Querre G, Salomon J, Zwaan JC (2000) PIXE/PIGE characterisation of emeralds using an external micro-beam. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B161–163:769–774
Muller K, Reiche R (2011) Differentiation of archaeological ivory and bone materials by micro-PIXE/PIGE with emphasis on two Upper Palaeolithic key sites: Abri Pataud and Isturitz, France. Archaeol Sci 38:3234–3243
Smita Z, Milavecc T, Fajfarb H, Rehrend Th, Lanktone JW, Gratuze B (2013) Analysis of glass from the post-Roman settlement Tonovcov grad (Slovenia) by PIXE–PIGE and LA-ICP-MS. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 311:53–59
Ziga S (2014) Analysis of historic glass by ion-beam methods. Archeometriai Műhely XI 3:159–167
Singh P (2002) Folded Tandem Ion Accelerator Facility at BARC, BARC Newsletter. Founder’s Day Special Issue, BARC, pp 22–32
Mukhopadhyay PK (2001) The operating software of the PHAST PC-MCA card. In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Intelligent Nuclear Instrumentation-2001 (INIT-2001), Mumbai, India, 6–9 Feb 2011. pp. 307–310
Tripathi R (2006) An insight into data analysis in neutron activation analysis. Proc. DAE-BRNS Discussion Meet on Current Trends and Future Perspectives on Neutron Activation Analysis (CFNAA 2006), BARC, Mumbai, 16–17 Nov 2006, pp. 52–57
Swain KK, Acharya R, Reddy AVR (2014) Analysis of SMELS by k0-based IM-NAA method using PFTS position of KAMINI reactor for quality control exercise. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300:33–37
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. A. Goswami, Ex-Head, Radiochemistry Division, Bhabha Atomic Research centre (BARC), Dr. P. Singh, Ex-Head, Ion Accelerator Development Division (IADD), BARC, Mr, P.V. Bhagwat, Head, IADD, BARC, Mr. S.K. Gupta, Ex-Head, FOlded Tandem Ion Accelerator (FOTIA) Section, IADD, Mr. A. Agarwal of IADD, BARC, Mumbai and Dr. P.V. Satyam, Mr. A.K. Behera and Dr. D.K. Ray of Institute of Physics (IOP), Bhubaneswar for their support and help during this work. Authors also thank operation crew members of FOTIA and Ion Beam laboratory (IBL), IOP for their help during the experiment. One of the authors (Sumit Chhillar) thanks Homi Bhabha National Institute (HBNI), Department of Atomic Energy, India for the financial support during this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chhillar, S., Acharya, R., Mishra, R.K. et al. Simultaneous determination of low Z elements in barium borosilicate glass samples by in situ current normalized particle induced gamma-ray emission methods. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 312, 567–576 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5251-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5251-9