Abstract
Prompt gamma-ray activation analysis facilities with high neutron currents (≥109 s−1) generate triton-induced fast neutrons from 6Li-loaded collimators and beam stops at rates that damage gamma-ray detectors. We develop an alternative beam stop design using 3He gas that produces negligible gamma-ray and fast-neutron background following neutron absorption. Replacing a 6Li glass beam stop with a test cell containing 2.5 MPa cm of 3He reduced fast neutron production by 73 %. An optimal 3He beam stop design with a 100-µm-thick entrance window, modeled using MCNP6, enables operation of detectors closer to the beam stop.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Certain commercial equipment, instruments, or materials are identified in this paper to foster understanding. Such identification does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, nor does it imply that the materials or equipment identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.
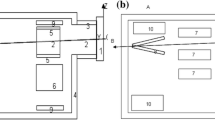
The neutron source is defined at the guide exit, with its divergences and spectrum obtained from guide simulations. MCNP6 tally results on a per-source-particle basis were multiplied by 1.55 × 1010 s−1, the neutron current at the guide exit (also determined by guide simulations).
References
Paul R, Lindstrom R (2000) Prompt gamma-ray activation analysis: fundamentals and applications. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 243(1):181–189
Molnár GL (2004) Handbook of prompt gamma activation. Analysis. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-23359-8
Canella L, Kudějová P, Schulze R et al (2011) Characterisation and optimisation of the new prompt gamma-ray activation analysis (PGAA) facility at FRM II. Nucl Instrum Methods A 636:108–113. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2011.01.126
Chadwick MB, Herman M, Obložinský P et al (2011) ENDF/B-VII.1 Nuclear data for science and technology: cross sections, covariances, fission product yields and decay data. Nucl Data Sheets 112:2887–2996. doi:10.1016/j.nds.2011.11.002
Lone M, Santry D, Inglis W (1980) MeV neutron production from thermal neutron capture in Li and B compounds. Nucl Instrum Methods 174:521–529. doi:10.1016/0029-554X(80)91105-2
Raudorf TW, Pehl R, Trammell RC, Wagner S (1984) Performance of reverse electrode HPGE coaxial detectors after light damage by fast neutrons. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci (United States) 31:1
Leleux P, Albernhe F, Borrel V et al (2003) Neutron-induced nuclear reactions and degradation in germanium detectors. Astron Astrophys 411:L85–L90. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20031366
Paul RL, Lindstrom RM, Heald AE (1997) Cold neutron prompt gamma-ray activation analysis at NIST—recent developments. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 215:63–68. doi:10.1007/BF02109879
Paul RL, Lindstrom RM, Brocker C, Mackey EA (2008) Design of a new instrument for cold neutron prompt gamma-ray activation analysis at NIST. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:697–701. doi:10.1007/s10967-008-1507-8
Paul RL, Şahin D, Cook JC et al (2015) NGD cold-neutron prompt gamma-ray activation analysis spectrometer at NIST. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 304:189–193. doi:10.1007/s10967-014-3635-7
Wolfs F, Freedman S, Nelson J et al (1989) Measurement of the 3He(n, γ)4He cross section at thermal neutron energies. Phys Rev Lett 63:2721–2724. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.63.2721
Sears VF (1992) Neutron scattering lengths and cross sections. Neutron News 3:26–37. doi:10.1080/10448639208218770
Stone CA, Blackburn DH, Kauffman DA et al (1994) 6Li-doped silicate glass for thermal neutron shielding. Nucl Instrum Methods A 349:515–520. doi:10.1016/0168-9002(94)91219-X
Chen WC, Gentile TR, O’Donovan KV et al (2004) Polarized neutron reflectometry of a patterned magnetic film with a 3He analyzer and a position-sensitive detector. Rev Sci Instrum 75:3256–3263. doi:10.1063/1.1791312
GE Lighting Component Sales, Bldg. 315D, 1975 Noble Rd., Cleveland, OH 44117. The largest standard GE180 tubing diameter is 16 mm; the 25 mm tubing was procured through a special glass run
Goorley T, James M, Booth T et al (2012) Initial MCNP6 release overview. Nucl Technol 180:298–315. doi:10.13182/NT11-135
Lindstrom RM (1994) Sum and Mean. Biol Trace Elem Res 43–45:597–603. doi:10.1007/BF02917362
Shetty M, Şahin D (2016) Data acquisition and analysis software for gamma coincidence spectrometry. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-016-4762-0
Kosyak YG, Chekushina LV, Ermatov AS (2002) Spins and lifetimes of 74 Ge levels from (n, n′γ) reaction. Izv Akad Nauk Ross Akad Nauk Seriya Fiz 67:140–144
Lässer R, Klatt K-H (1983) Solubility of hydrogen isotopes in palladium. Phys Rev B 28:748–758. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.28.748
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance of the Research Facilities Operations Group staff of the NIST Center for Neutron Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turkoglu, D., Downing, R.G., Chen, W. et al. A 3He beam stop for minimizing gamma-ray and fast-neutron background. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 311, 1243–1249 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-4954-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-4954-7