Abstract
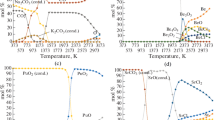
The behaviour of radionuclides was studied by the method of thermodynamic modelling in the wide temperature range 400–3200 K during interaction of radioactive graphite with water vapour, taken in the ratio C (s):H2O (g) = 1:10 and 1:20 (by mass). It was determined that the main components of the gaseous phase over the whole temperature range are H2O vapour, H2, gaseous CO and CO2 containing radioactive 14C. Their partial pressures exceed 103 Pa. Cs, Sr, Ca, Be, Ni radionuclides, which radioactive graphite contains, form volatile hydroxides, U, Pu radionuclides—volatile oxides. The partial pressure of these radionuclides does not exceed 10−1 Pa.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Power Generation. http://www.rosatom.ru/aboutcorporation/activity/energy_complex/electricitygeneration. Accessed 05 May 2014
Vorob’yev AV, Antonova AM (2013) Improvement of efficiency of installation with water-cooled graphite-moderated reactor at fractional loads. Bull Tomsk Polytech Univ 322(2):182–186
22 Years of Chernobyl Disaster. http://pripyat.com/articles/22-goda-chernobylskoi-katastrofe-memuary-uchastnika-i-mnenie-eksperta-chast-1.html. Accessed 05 May 2014
International Atomic Energy Agency (2006) Characterization, treatment and conditioning of radioactive graphite from decommissioning of nuclear reactors. IAEA-TECDOC-1521, IAEA, Vienna
Barbin NM, Terentiev DI, Alexeev SG, Peshkov AV (2012) Special features of reprocessing of radioactive graphite by incineration method. In: Proceedings of International Congress ‘‘Fundamental principles of technogenic waste treatment and management technology’’. Yekaterinburg
Yang H-C, Eun H-C, Lee D-G (2005) Behavior of radioactive elements during thermal treatment of nuclear graphite waste. Thermodynamic model analysis. J Nucl Sci Technol 42(10):869–876
Barbin NM, Terentiev DI, Alexeev SG, Barbina TM (2014) Thermodynamic analysis of radioactive graphite reprocessing by incineration in air and oxidation in molten salt. J Raioanal Nucl Chem. 299:1747–1757
Guéneau C, Chatillon C, Sundman B (2008) Thermodynamic modelling of the plutonium–oxygen system. J Nucl Mater 378:257–272
Guéneau C, Dupin N, Sundman B, Martial C, Dumas J-C, Gossé S, Chatain S, De Bruycker F, Manara D, Konings RJM (2011) Thermodynamic modelling of advanced oxide and carbide nuclear fuels: description of the U–Pu–O–C systems. J Nucl Mater 419:145–167
Ho TC, Kuo TH, Hopper JR (2000) Thermodynamic study of the behavior of uranium and plutonium during thermal treatment under reducing and oxidizing modes. Waste Manag 20:355–361
Engel’sht VS, Balan RK (2011) Chemical thermodynamics of the vapor-oxygen gasification of graphite. High Temp 49(5):736–743
Barbin NM, Terentiev DI, Alekseyev SG, Tuktarov MA, Romenkov AA (2009) Modeling of radioactive graphite oxidation in molten salts. In: The 33rd international symposium ‘‘Scientific basis for nuclear waste management’’. Book of abstracts, St. Petersburg
Barbin NM, Terentiev DI, Alekseyev SG, Tuktarov MA, Romenkov AA (2009) Modeling of radioactive graphite oxidation in molten salts: computer experiment. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 1193:359–366
Vatolin NA, Moiseev GK, Trusov BG (1994) Thermodynamic modelling in high-temperature systems. Metallurgiya, Moscow
Moiseev GK, Vyatkin GP, Barbin NM (2002) Use of thermodynamic modelling for the studies of interactions involving ionic melts. South Ural State University, Chelyabinsk
Moiseev G, Kazantzev G, Barbin N, Marshuk L, Vatolin N (1998) Thermodynamic and experimental study of complex waste products treatment in the alkaline carbonates melt. J Min Metall 34(3B):177–194
Barbin NM, Terentiev DI, Alekseyev SG, Barbina TM (2013) Thermodynamic modeling of the Pb + Bi melt evaporation under various pressure and temperatures. Comput Mater Sci 66:28–33
Barbin N, Terentiev D, Alekseyev S (2011) Computer calculation for thermal behavior of Na2CO3–Li2CO3 melt. J Eng Thermophys 20(3):308–314
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barbin, N.M., Terentiev, D.I., Alexeev, S.G. et al. Thermodynamic analysis of radionuclides behaviour in products of vapour phase hydrothermal oxidation of radioactive graphite. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 307, 1459–1470 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4587-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4587-2