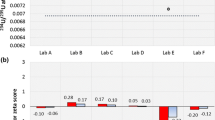
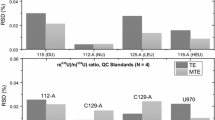
Abstract
Modern mass spectrometry and separation techniques have made measurement of major uranium isotope ratios a routine task; however accurate and precise measurement of the minor uranium isotopes remains a challenge as sample size decreases. One particular challenge is the presence of isobaric interferences and their impact on the accuracy of minor isotope 234U and 236U measurements. We present techniques used for routine U isotopic analysis of environmental nuclear safeguards samples and evaluate polyatomic interferences that negatively impact accuracy as well as methods to mitigate their impacts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donohue DL (1998) Strengthening IAEA safeguards through environmental sampling and analysis. J Alloy Compd 271:11–18
Donohue DL (2002) Key tools for nuclear inspections: advances in environmental sampling strengthen safeguards. IAEA Bull. 44(2):17–23
Mayer K, Wallenius M, Fanghanel T (2007) Nuclear forensic science—from cradle to maturity. J Alloy Compd 444:50–56
Bouman, C, Lloyd, NS, Schwieters JB (2011) Advances in multicollector ICPMS for precise and accurate isotope ratio measurements of Uranium isotopes. Abstract V33G-01 presented at 2011 Fall Meeting, AGU. San Francisco, Calif., 5–9 Dec
Zhao XL, Nadeau MJ, Kilius LR, Litherland AE (1994) The 1st detection of naturally-occurring 236U with accelerator mass-spectrometry. Nucl Instrum Methods B 92(1–4):249–253
Zhao XL, Kilius LR, Litherland AE, Beasley T (1997) AMS measurement of environmental 236U preliminary results and perspectives. Nucl Instrum Methods B 126(1–4):297–300
Richter S, Alonso A, De Bolle W, Wellum R, Taylor PDP (1999) Isotopic “fingerprints” for natural uranium ore samples. Int J Mass Spectrom 193(1):9–14
Berkovits D, Feldstein H, Ghelberg S, Hershkowitz A, Navon E, Paul M (2000) 236U in uranium minerals and standards. Nucl Instrum Methods B 172:372–376
Boulyga SF, Heumann KG (2006) Determination of extremely low 236U/238U isotope ratios in environmental samples by sector-field inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry using high-efficiency sample introduction. J Environ Radioact 88(1):1–10
Ferguson JW, Houk RS (2006) High resolution studies of the origins of polyatomic ions in inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, Part I. Identification methods and effects of neutral gas density assumptions, extraction voltage, and cone material. Spectrochim Acta B 61(8):905–915
Newman K, Freedman PA, Williams J, Belshaw NS, Halliday AN (2009) High sensitivity skimmers and non-linear mass dependent fractionation in ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 24(6):742–751
Newman K (2012) Effects of the sampling interface in MC-ICP-MS: relative elemental sensitivities and non-linear mass dependent fractionation of Nd isotopes. J Anal At Spectrom 27(1):63–70
Oh SY, Lee SA, Park JH, Lee M, Song K (2012) Isotope measurement of uranium at ultratrace levels using multicollector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Lett 3(2):54–57
Mitroshkov AV, Olsen KB, Thomas ML (2015) Estimation of the formation rates of polyatomic species of heavy metals in plutonium analyses using a multicollector ICP-MS with a desolvating nebulizer. J Anal At Spectrom 30(2):487–493
Acknowledgments
The work presented in this manuscript was supported by the US National Nuclear Security Administration. Los Alamos National Laboratory, an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, for the National Nuclear Security Administration of the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC52-06NA25396. We would like to thank the handling editor and two anonymous reviewers for constructive comments that improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollington, A.D., Kinman, W.S., Hanson, S.K. et al. Polyatomic interferences on high precision uranium isotope ratio measurements by MC-ICP-MS: applications to environmental sampling for nuclear safeguards. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 307, 2109–2115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4419-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4419-4