Abstract
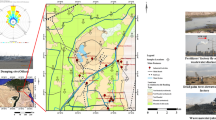
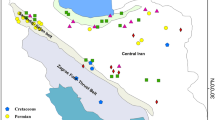
This study determines the provenance of the 106 sediments samples deposited by the Solimões and Negro rivers in the tectonic depressions in Manaus, Amazon state, Brazil. Twenty-four chemical elements in the sediment samples collected before the confluence of Negro and Solimões rivers have been determined using instrumental neutron activation analysis, INAA. It is inferred from the multivariate statistical methods that samples from the basin of the Solimões river and tectonic depression 1 (the most significant of the region) are not significantly different. These results indicate the contribution this river in the sedimentary fill during the evolution in the Quaternary.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guyot JL, Jouanneau JM, Soares L, Boaventura GR, Maillet N, Lagane C (2007) Clay mineral composition of river sediments in the Amazon Basin. Catena 71:340–356
Gaillardet JL, Dupré B, Allègre CJ, Négrel P (1997) Chemical and physical denudation in the Amazon River Basin. Chem Geol 142:141–173
Soares EAA, Tatumi SH, Riccomini C (2010) OSL age determinations of Pleistocene fluvial deposits in Central Amazonia. An Acad Bras Cienc 82(3):691–699
Soares EAA (2007) Depósitos pleistocenos da região de confluência dos rios Negro e Solimões, porção oeste da Bacia do Amazonas. Tese (Doutorado)—Instituto de Geociências, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/44/44136/tde-14082008-141522/pt-br.php. Accessed 11 May 2015
Bouchez J, Lupker M, Gaillardet J, Frace-Lanor C, Maurice L (2011) How important is it to integrate riverine suspended sediment chemical composition with depth? Clues from Amazon River depth-profiles. Geochim Cosmochim 75:6955–6970
Weltje GJ, Eynatten H (2004) Quantitative provenance analysis of sediments: review and outlook. Sedim Geol 171:1–11
Ravisankar R, Manikandan E, Dheenathayalu M, Rao B, Seshadreesan NP, Nair KGM (2006) Determination and distribution of rare earth elements in beach rock samples using instrumental neutron activation analysis. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 251:496–500
Phedorin MA, Bobrov VA, Goldberg EL, Navez J, Zolotaryov KV, Grachev MA (2000) SR-XRA as method of choice in the search of signals of changing paleoclimates in the sediments of Lake BaiKal, compared to INAA and ICP-MS. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A 448:394–399
Reimann C, Filzmoser P (1999) Normal and lognormal data distribution in geochemistry: death of myth. Consequences for the statistical treatment of geochemical and environmental data. Earth Environ Sci Trans 39(9):1001–1014
Filzmoser P, Garret RG, Reimann C (2005) Multivariate outlier detection in exploration geochemistry. Comput Geosci 31:579–587
Laraque A, Guyot JL, Filizola N (2009) Mixing processes in the Amazon River at confluences of the Negro and Solimões Rivers, Encontro das Águas, Manaus, Brazil. Hidrol Processes 23:3131–3140
Cogswell JA, Neff H, Glascock MD (1996) The effect of firing temperature on the elemental characterization of pottery. J Archaeolog Sci 23:283–287
Schwedt A, Mommsen H (2007) On the influence of drying and firing of clay on the formation of trace element concentration profiles within pottery. Archaeometry 49:495–509
Santos JO, Munita CS, Toyota RG, Vergne C, Silva RS, Oliveira PMS (2009) The archaeometry study of the chemical and mineral composition of pottery from Brazil Northeast. J Radional Nucl Chem 281:189–192
Hadi A (1992) Identifying multiple outliers in multivariate data. J R Stat Soc 54:761–771
Rousseeuw PJ, Van Zomeren BC (1990) Unmasking multivariate outliers and leverage points. J Am Stat Assoc 85(411):633–651
Rousseeuw PJ, Van Driessen K (1999) A fast algorithm for the minimum covariance determinant estimator. Technometrics 41(3):212–223
Filzmoser P (2005) Identification of multivariate outliers: A performance study. Aust J Stat 34(2):127–138
Varmuza K, Filzmoser P (2009) Introduction to multivariate statistical analysis in chemometrics. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hardin J, Rocke DM (2004) Outlier detection in multiple cluster setting using the minimum covariance determinant estimator. Comput Stat Data Anal 44:625–638
R development core team (2013) R: A language and environment for statistical computing: Vienna. http://www.r-project.org. Accessed 02 out 2014
Filzmoser P, Hron K, Reimann C (2012) Interpretation of multivariate outliers for compositional data. Comput Geosci 39:77–85
Schultz RB (2004) Geochemical relationships of Late Paleozoic carbon-rich shales of the Midcontinent, USA: a compendium of results advocating changeable geochemical conditions. Chem Geol 206:347–372
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (1992) Applied multivariate statistical analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Munita CS, Barroso LP, Oliveira PMS (2006) Stopping rule for variable selection using stepwise discriminant analysis. J Radional Nucl Chem 269:335–338
Bode P (1996) Instrumental and organizational aspects of a neutron activation analysis laboratory. PhD Thesis, Interfaculty Reactor Institute, Delft, p 148
Munita CS, Paiva RP, Alves MA, Oliveira PMS, Momose EF (2000) Contribution of neutron activation analysis to archaeological studies. J Trace Microprobe Tech 18:381–387
Acknowledgments
We thank the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for partial sponsoring of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, J.O., Munita, C.S. & Soares, E.A.A. Provenance studies in Amazon basin by means of chemical composition obtained by INAA. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 306, 713–719 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4243-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4243-x