Abstract
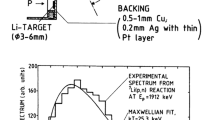
A high-power liquid-lithium target (LiLiT) was built and commissioned with a 1.2 mA, 1.91 MeV (2.3 kW) proton beam from the SARAF (Soreq Applied Research Accelerator Facility, Israel). The lithium film acts both as a neutron-producing target via the 7Li(p,n)7Be reaction with a yield of ~ 2 × 1010 n/s/mA and as a power beam dump. The neutron source is suited for the study of neutron capture reactions on nuclides (stable or radioactive) of low abundance for nuclear astrophysics and to the needs of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halfon S et al (2013) High-power liquid-lithium jet target for neutron production. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84:123507–123511
Halfon S et al (2014) Note: Proton irradiation at kilowatt-power and neutron production from a free-surface liquid-lithium target. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85:3–056105
Berkovits D et al (2012) Operational experience and future goals of the SARAF proton/deuteron linac. In: Proceedings of LINAC2012, Tel-Aviv, Israel MO1A01:100–104. http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/accelconf/LINAC2012/papers/mo1a01.pdf. Accessed 21 Feb 2015
Ratynski W, Kaeppeler F (1988) Neutron capture cross section of 197Au: a standard for stellar nucleosynthesis. Phys Rev C 37:59–605
Sauerwein WAG, Wittig A, Moss R, Nakagawa Y (2012) Neutron capture therapy: principles and applications. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York
Chopra OK, Smith DL (1986) Influence of temperature and lithium purity on corrosion of ferrous alloys in a flowing lithium environment. J Nucl Mater 141–143:584–591
Halfon S et al (2014) High-power electron beam tests of a liquid-lithium target and characterization study of 7Li(p,n) near-threshold neutrons for accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy. Appl. Radiat. Isotopes 88:238–242
Acknowledgments
The support of the Pazi Foundation and the German Israeli Foundation (GIF Grant no. 1051/09 in collaboration with R. Reifarth) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, M., Arenshtam, A., Halfon, S. et al. A high-power liquid-lithium target (LiLiT) for neutron production. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 305, 783–786 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4027-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4027-3