Abstract
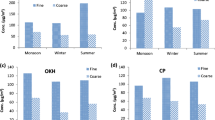
Monitoring the air quality in ambient air is an important step for assessing the air pollution level in one region and its impact to the human health. In this study, the determination of chemical elements concentrations in airborne particulate matter collected in suburban area of Lembang, Indonesia was carried out. Samples were collected using a Gent stacked filter unit sampler in two size fractions of <2.5 μm (fine) and 2.5–10 μm (coarse). Sampling was conducted twice a week for 24 h from January 2008 to June 2009 and 123 pairs of samples were collected. Black carbon was determined by reflectance and chemical elements analysis were performed using particle induced X-ray emission (PIXE). PIXE as one of ion beam analysis techniques is suitable for analyzing particulate matter for its multielemental analysis with good limits of detection. Results showed that none of daily concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 exceeded the 24 h Indonesian NAAQS for PM2.5 and PM10. Chemical elements such as Mg, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Hg and Pb were determined and the correlation between these elements was reported in order to understand the anthropogenic sources of particulate matter.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dockery DW, Pope CA, Xu X, Spengler JD, Ware JH, Fay ME et al (1993) An association between air pollution and mortality in six US cities. N Engl J Med 329:1753–1759
Pope CA, Burnett RT, Thun MJ et al (2002) Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 287:1132–1141
WHO (2000). Air quality guidelines for Europe, 2nd edn. World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen. WHO Regional Publications, European series no. 91. ISBN 92-890-1358-3
Tolocka MP, Lake DA, Johnston MV, Wexler AS (2004) Number concentrations of fine and ultrafine particles containing metals. Atmos Environ 38(20):3263–3273
Kim Oanh NT, Upadhayay N, Zhuang YH et al (2006) Particulate air pollution in six cities: spatial and temporal distributions, and associated sources. Atmos Environ 40:3367–3380
Santoso M, Hopke PK, Hidayat A, Lestiani DD (2008) Source identification of atmospheric aerosol at urban and suburban sites in Indonesia by positive matrix factorization. Sci Total Environ 397:229–237
Hopke PK, Xie Y, Raunemaa T, Biegalski S, Landsberger S, Maenhaut W, Artaxo P, Cohen D (1997) Characterization of the gent stacked filter unit PM10 sampler. Aerosol Sci Technol 27:726–735
Cohen DD, Gorton D, Stelcer E, Hawas O (2004) Accelerator based studies of atmospheric pollution processes. Radiat Phys Chem 71:759–767
Biswas SK, Tarafdar SA, Islam A, Khaliquzzaman M, Tervahattu H, Kupiainen K (2003) Impact of unleaded gasoline introduction on the concentration of lead in the air of Dhaka, Bangladesh. J Air Waste Manag 53:1355–1362
Chueinta W, Hopke PK, Paatero P (2000) Investigation of sources of atmospheric aerosol at urban and suburban residential areas in Thailand by positive matrix factorization. Atmos Environ 34:3319–3329
Begum BA, Kim E, Biswas SK, Hopke PK (2004) Investigation of sources of atmospheric aerosol at urban and semi-urban areas in Bangladesh. Atmos Environ 38:3025–3038
Chung YS, Kim SH, Moon JH, Kim YJ, Lim JM, Lee JH (2005) Source identification and long term monitoring of airborne particulate matter PM2.5/PM10 in an urban region of Korea. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 267:35–48
Hien PD, Bac VT, Thinh NTH (2005) Investigation of sulfate and nitrate formation on mineral dust particles by receptor modeling. Atmos Environ 39:7231–7239
Maxwell JA, Teesdale WJ, Campbell JL (1995) The Guelph PIXE software package II. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 95:407–421
Cohen DD, Grahama MB, Kondepudi R (1996) Elemental analysis by PIXE and other IBA techniques and their application to source fingerprinting of atmospheric fine particles pollution. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 109:218–226
Government Regulation (1999) PP no. 41/1999 National ambient air quality standard
Hopke PK, Cohen DD, Begum BA, Biswas SK, Ni Bangfa, Pandit GG, Santoso M et al (2008) Urban air quality in the Asian region. Sci Total Environ 404:103–112
Santoso M, Lestiani DD, Rita M, Esrom H, Halimah S, Markwitz A, Hopke PK (2011) Preliminary study of the sources of ambient air pollution in Serpong, Indonesia. Atmos Pollut Res 2:190–196
Begum BA, Tazmin A, Rabbani KA, Biswas SK, Nasiruddin M (2009) Investigation of sources of particulate matter from the Tejgaon industrial area, Dhaka. J Bangladesh Acad Sci 33:71–85
Avino P, Capannesi G, Rosada A (2008) Heavy metal determination in atmospheric particulate matter by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Microchem J 88:97–106
European Council Directive 1999/30/EC (1999) Limit values for sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxides of nitrogen, particulate matter and lead in ambient air, 22 April 1999
Santoso M, Lestiani DD, Markwitz A (2010) Determination of PM2.5’s heavy metals in Bandung by particle induced X-ray emission (PIXE). In: Proceeding of the 2nd international conference on chemical sciences, Yogyakarta, pp 439–442
Landsberger S, Creatchman M (eds) (1998) Elemental analysis of airborne particles. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Directorate General of Oil and Gas, Minister of Energy and Mineral Resources (2006) Regulation no. 3674K/24/DJM/2006 standard and specification of gasoline Ron 88
Acknowledgment
This study was partly financial supported by International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under RAS/7/015 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lestiani, D.D., Santoso, M., Trompetter, W.J. et al. Determination of chemical elements in airborne particulate matter collected at Lembang, Indonesia by particle induced X-ray emission. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 297, 177–182 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2348-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2348-z